Malware attacks have become increasingly common in the modern world, with hackers finding new and innovative ways to infiltrate systems and networks. Malware is malicious software that can be used to gain access to a system, steal data, or cause disruption. One of the most common methods of malware delivery is through the use of scripts. Scripts are small programs that can be used to automate tasks and can be used to deliver malware to unsuspecting victims. In this article, we’ll look at how an attacker can execute malware through a script and the steps they must take to do so successfully. We’ll also discuss some of the ways that organizations can protect themselves against malicious scripts. By understanding the methods of malware delivery, organizations can take the necessary steps to protect their data and networks.
An attacker can execute malware through a script by sending malicious code through an email, by exploiting a vulnerability in a website, or by uploading malicious files to an online storage service. Attackers can also use social engineering techniques to lure victims into downloading malware. They can also take advantage of programs that automatically run scripts, such as JavaScript. Once the malicious script is executed, the malware can be installed and the attacker can gain access to the system.
Introduction
Malware is malicious software that is designed to damage or disable computers, networks, or other electronic devices. Malware can be spread through various methods, including malicious scripts. Scripts are programs that are written in a scripting language and can be used to automate tasks or perform malicious activities. In this article, we will discuss how an attacker can execute malware through a script.
How Can an Attacker Execute Malware Through a Script?
Creating the Script
An attacker can create a malicious script to execute malware on a target system. The script can be written in any scripting language such as Python, JavaScript, or Powershell. The script must contain instructions that will download and execute the malware on the target system. The script can also be used to delete files, modify registry settings, and install backdoors on the system.
Distributing the Script
Once the malicious script has been created, the attacker must distribute it to the target systems. This can be done in various ways, such as sending it in an email attachment, hosting it on a website, or sending it via a messaging app. Once the script has been distributed, the attacker must ensure that the script is executed on the target system. This can be done by exploiting vulnerabilities in the system or by using social engineering techniques.
Executing the Script
Once the malicious script has been distributed, the attacker must ensure that the script is executed on the target system. This can be done by exploiting vulnerabilities in the system or by using social engineering techniques. Once the script is executed, the malicious code contained within the script will be executed on the target system, allowing the attacker to gain access to the system or perform malicious activities.
Monitoring the System
Once the malicious script has been executed, the attacker must monitor the system to ensure that the malicious code is running properly. The attacker can use a variety of tools to monitor the system, such as network sniffers, keyloggers, and remote access tools. The attacker can also use these tools to gain access to the system and perform other malicious activities.
Covering Their Tracks
Once the attacker has gained access to the system and performed their malicious activities, they must cover their tracks to avoid detection. This can be done by deleting the malicious script, disabling any logging functions, and removing any traces of their activities from the system. The attacker can also use encryption and other techniques to hide their presence on the system.
Conclusion
Malware can be executed on a target system through a malicious script. The attacker must create the script, distribute it to the target system, execute it, and monitor the system to ensure that the malicious code is running properly. The attacker must also cover their tracks to avoid detection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Malware is malicious software designed to cause damage, steal data, or gain access to a system. Attackers can use scripts to execute malware, potentially allowing them to gain access to systems or networks with minimal effort.
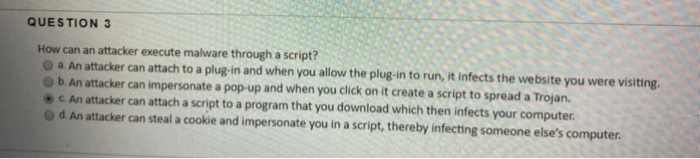
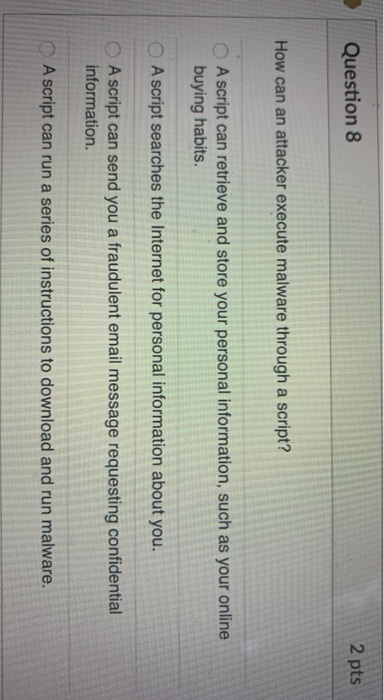
How can an attacker execute malware through a script?
Attackers can execute malware through scripts by injecting malicious code into legitimate scripts. This malicious code is usually hidden within the script, allowing it to run without being noticed. It can also be disguised as an innocuous file, such as an image or document. Once the attacker has injected the code, they can use the script to run the malicious code and gain access to the system or network.
Another way attackers can execute malware through scripts is by using malicious programs, such as trojans and worms. These malicious programs can be disguised as legitimate programs, and can be used to spread malware across a network. They can also be used to gain access to a system, allowing the attacker to execute the malicious code.
Malware can be a serious problem for any network or system, and knowing how an attacker can execute malware through a script is an important step in understanding and preventing attacks. Scripts are often used to automate tasks and can be used to move malicious code onto a system without the user’s knowledge. Attackers can use a variety of techniques to execute malware, such as inserting malicious code into a legitimate script or using malicious code to modify an existing script. Attackers can also use scripts to bypass security measures and gain access to a system. By understanding how attackers can use scripts to execute malware, IT professionals can take steps to prevent and mitigate these types of attacks. Security measures such as regularly updating software, using strong passwords, and restricting user permissions can help protect networks and systems from malicious scripts. Taking these steps can help ensure that networks and systems remain secure and safe from malicious attacks.