Ransomware is a type of malicious software used by cybercriminals to extort money from victims. It is a growing threat to businesses, as attackers can lock down computers and networks, preventing users from accessing their data until a ransom is paid. But is it legal to pay for ransomware?
This is an important question to consider, given the increasing prevalence of ransomware attacks. In some cases, it may be the only way to regain access to important data, but there are also risks associated with paying a ransom. This article will explore the legal implications of paying for ransomware and discuss the potential risks and benefits.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that is designed to restrict access to a user’s data or files until a ransom is paid. This type of malware is usually spread through malicious links or attachments in emails and can be used to encrypt or lock a user’s data or files, making them inaccessible until the ransom is paid.
Ransomware can be used to target individuals, businesses, organizations, and government institutions. It can be used to steal sensitive data, disrupt business operations, and even cause financial loss. In recent years, ransomware attacks have become increasingly common as cybercriminals have become more sophisticated in their use of this malicious software.
Is it Legal to Pay for Ransomware?
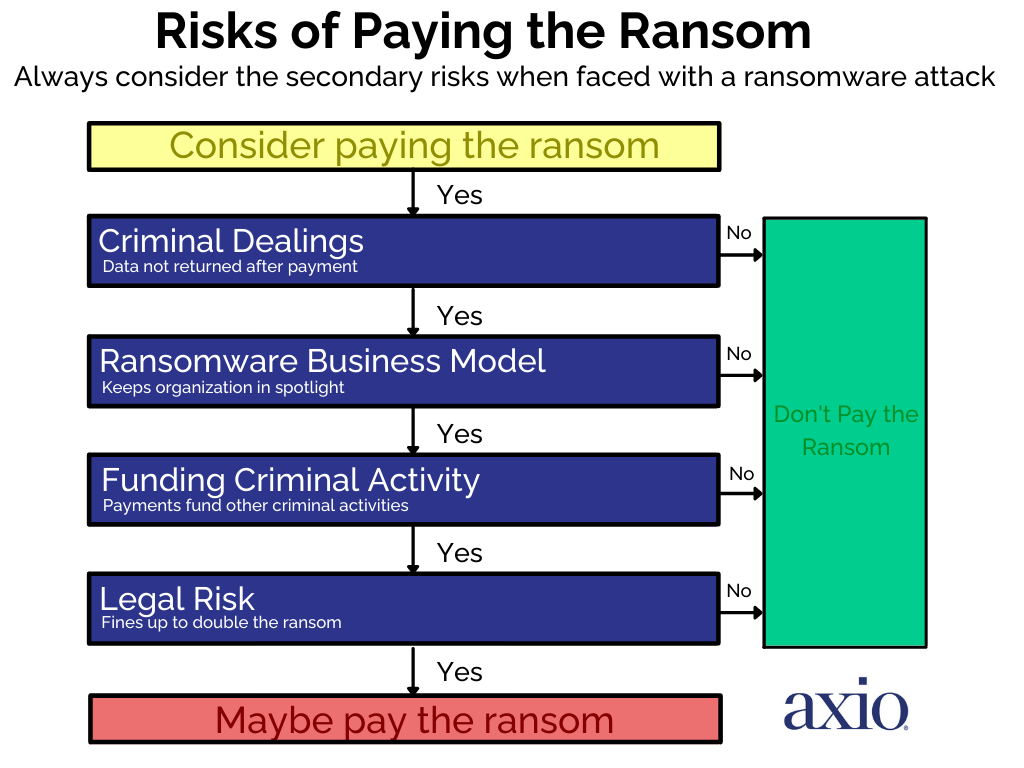
Paying a ransom to cybercriminals is not a recommended course of action, as it can encourage further attacks and may not even result in the restoration of the affected data or files. Additionally, the payment of a ransom can be seen as a form of criminal activity, as it is essentially providing payment for stolen goods.
In the United States, the FBI discourages businesses and individuals from paying a ransom to cybercriminals, as this can potentially embolden criminal behavior. The FBI also states that paying a ransom does not guarantee that the data or files will be restored and can even put the victim at further risk of additional attacks.
Payment of a Ransom
Payment of a ransom to cybercriminals is an illegal activity in the United States, punishable by law. Additionally, the payment of a ransom may be seen as an admission of guilt, which can result in civil or criminal penalties. Furthermore, the payment of a ransom may be seen as an act of aiding and abetting a criminal act, which can result in criminal prosecution.
The payment of a ransom is also generally discouraged by law enforcement agencies, as it can encourage further attacks and does not guarantee the restoration of the affected data or files. Additionally, the payment of a ransom can be seen as a form of criminal activity, as it is essentially providing payment for stolen goods.
Ransomware Prevention
The best way to protect against ransomware is to take proactive measures to reduce the risk of an attack. This includes regularly updating software and applications, using strong passwords, and avoiding suspicious websites and email attachments. Additionally, it is important to have an updated and reliable backup of all important data and files.
Businesses and organizations should also consider investing in cybersecurity solutions such as endpoint protection, firewalls, and anti-virus software. These measures can help to protect against ransomware attacks and reduce the risk of data loss or theft. Additionally, businesses and organizations should also consider implementing policies and procedures to ensure that staff are aware of the risks associated with ransomware and how to protect against it.
Frequently Asked Questions
This article provides information about the legality and implications of paying for ransomware. We provide answers to five of the most frequently asked questions.
Is it Legal to Pay for Ransomware?
The short answer is no, it is not legal to pay for ransomware. Paying for ransomware is illegal in many countries, as it violates anti-money laundering laws. It is also considered a form of extortion and is illegal in most jurisdictions. Additionally, the US Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) has issued a warning against the payment of ransomware.
However, while it is illegal to pay for ransomware, it is not illegal to pay a ransom to the criminals who have encrypted your data. In some jurisdictions, paying a ransom may be the only way to recover your data. In these cases, it is important to weigh the potential risks and benefits of making a payment. It is also important to note that paying a ransom does not guarantee that your data will be recovered.

The legal implications of paying for ransomware can be a tricky subject to navigate. It is important to understand the laws in your jurisdiction and the legal risks associated with ransomware payments. While some jurisdictions may be more lenient than others, it is important to recognize that paying a ransom may not be the best option. Consulting a lawyer or legal expert may help you make an informed decision on whether paying a ransom is a viable option.
In general, it is not recommended to pay a ransom in the case of a ransomware attack. In some cases, it can be the only option, but there are many ways to protect yourself and your data from ransomware attacks in the first place. Investing in a reliable cybersecurity solution and educating yourself on best practices is the best way to keep your data safe and reduce the risk of a ransomware attack.