The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a new law that affects the way businesses handle personal information. As a consumer, it’s important to understand what your rights are under the CCPA and what personal information businesses are allowed to collect and use. But what is “personal information” under the CCPA?
This article will explore what types of data businesses are allowed to collect and use under the CCPA and how it affects consumers. We’ll look at the definition of “personal information” according to the CCPA, what businesses need to do to protect your data, and how you can protect your own personal information. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of what “personal information” means and how to protect it.
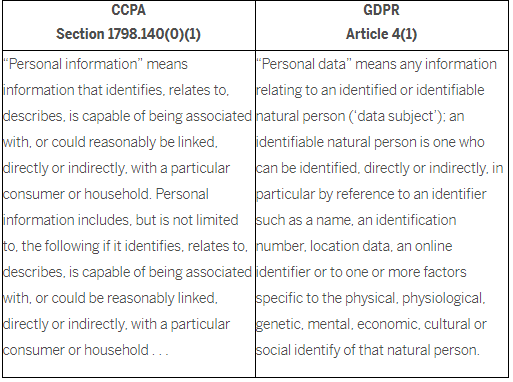
Personal information under CCPA is defined as any information that identifies, relates to, describes, is capable of being associated with, or could reasonably be linked, directly or indirectly, with a particular consumer or household. This includes identifiers such as a real name, alias, postal address, unique personal identifier, IP address, email address, account name, Social Security number, driver’s license number, passport number, or other similar identifiers. It also includes commercial information, internet or other electronic network activity information, geolocation data, audio, electronic, visual, or similar information, professional or employment-related information, education information, and inferences drawn from any of the above.
What is Personal Information Under CCPA?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a law that protects the personal information of consumers in California. It requires businesses to be transparent about the information they collect, how it is used, and how it is shared. Personal information is any information that can be used to identify, contact, or locate an individual.
Types of Personal Information
Under the CCPA, personal information includes a wide range of data about an individual, such as name, address, email address, phone number, Social Security number, and other identifiers. It also includes demographic information, commercial information, biometric information, internet or other electronic network activity information, audio, visual, and thermal information, and other data that can be used to identify an individual.
The CCPA also covers data that can be used to create a profile of an individual, such as purchasing history, browsing history, and other information collected over time. This data can be used to create a picture of an individual’s interests, preferences, and behavior, and can be used to target advertising and other marketing activities.
How Businesses Collect Personal Information
Businesses collect personal information from a variety of sources, including online forms, social media, customer surveys, third-party vendors, and cookies. They may also purchase personal information from data brokers or other sources. Businesses must be transparent about how they collect and use personal information, and must provide consumers with an easy way to opt out of the collection of their data.
Under the CCPA, businesses must also provide a way for consumers to request access to their personal information and request that their data be deleted. Consumers also have the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information. Businesses must be transparent about the sale of personal information and provide consumers with an easy way to opt out.
Protecting Personal Information
Businesses must implement reasonable security measures to protect the personal information they collect and must use it only for the purpose it was collected. They must also provide consumers with clear and conspicuous notice about the types of information they collect and how it is used. They must also provide a way for consumers to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal information.
Businesses must also delete personal information when it is no longer needed for the purpose it was collected or when the consumer requests that it be deleted. They must also ensure that any third-party vendors they work with adhere to the same privacy standards as the business itself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Personal information (PI) is any information that relates to an individual, household, or device that can be used to distinguish, identify, or contact a particular person. Under the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), PI includes any information that is collected, used, shared, or stored for any purpose.
What is personal information under CCPA?
Personal information under the CCPA includes any information that is collected, used, shared, or stored that identifies, relates to, describes, is capable of being associated with, or could reasonably be linked, directly or indirectly, with a particular consumer or household. This includes information such as name, address, email address, telephone number, and other identifying information. Additionally, the CCPA also applies to personal information that is derived from or associated with other personal information, such as inferences drawn from the personal information.
What types of information are excluded from the CCPA?
Certain types of information are excluded from the CCPA and are not considered personal information. These include public records, de-identified or aggregated consumer information, and information collected, used, shared, or stored for certain purposes, such as for certain medical research or for internal business processes. Additionally, the CCPA does not apply to certain businesses, such as those that are subject to certain federal laws or certain government entities.
What rights do consumers have under the CCPA?
Consumers have certain rights under the CCPA, including the right to know what personal information is being collected and used, the right to opt-out of data sales, the right to access their personal information, the right to delete their personal information, and the right to equal service and price, regardless of the exercise of the consumer’s privacy rights. Additionally, consumers have the right to not be discriminated against for exercising their rights.
What is the penalty for violating the CCPA?
Violations of the CCPA can result in civil penalties of up to $7,500 per violation, as well as other penalties and remedies. Additionally, consumers can seek damages from a business that violates the CCPA. The business may also be subject to penalties from the California Attorney General.
Does the CCPA apply to all businesses?
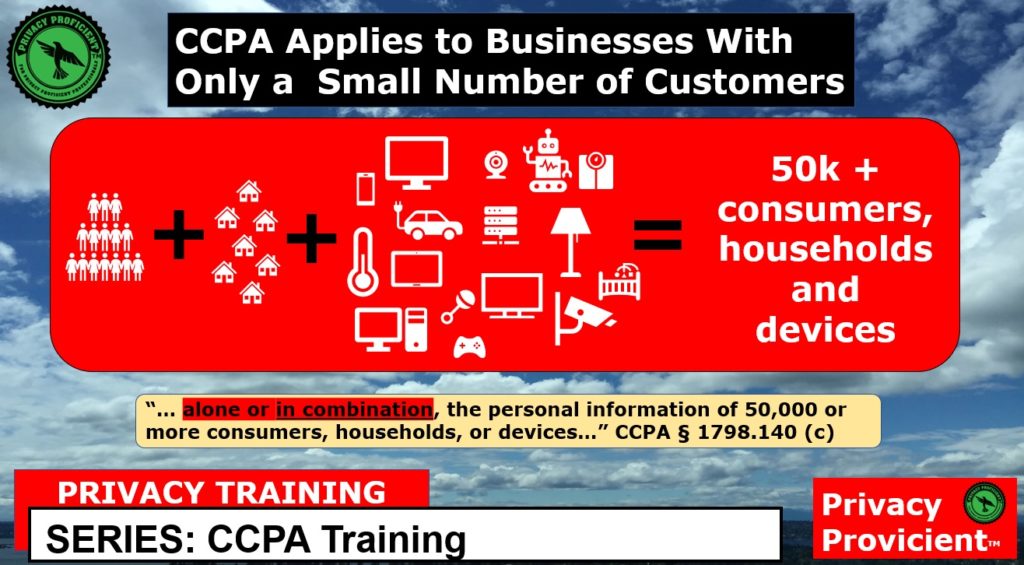
No, the CCPA does not apply to all businesses. Certain businesses are exempt from the CCPA, such as those that are subject to certain federal laws or certain government entities. Additionally, businesses that meet certain criteria, such as those that have less than $25 million in annual revenues, are not subject to the CCPA.
In conclusion, CCPA is an important piece of privacy legislation that helps protect the personal information of Californians. It sets out clear guidelines on when and how personal information can be collected, used, and shared. It also requires companies to provide consumers with the right to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information. In addition, it requires companies to take reasonable steps to protect the security of consumers’ personal information. While CCPA offers a great level of protection, it is important to remain vigilant when it comes to personal information. Consumers should always be aware of what type of data is being collected and how it is being used, and should take steps to protect their data in order to ensure their privacy.