The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a landmark piece of legislation that provides unprecedented privacy rights to California consumers. In short, the CCPA applies to any business that collects or processes the personal data of California residents. This legislation has far-reaching implications for businesses that operate in the state, as well as for those who conduct business with them.
Understanding who the CCPA applies to is essential for any business operating in the state. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at who is affected by the CCPA, what types of data are covered, and what businesses need to do to comply with the law. With this information, businesses can ensure that they’re taking the necessary steps to protect the privacy of their customers and comply with the law.
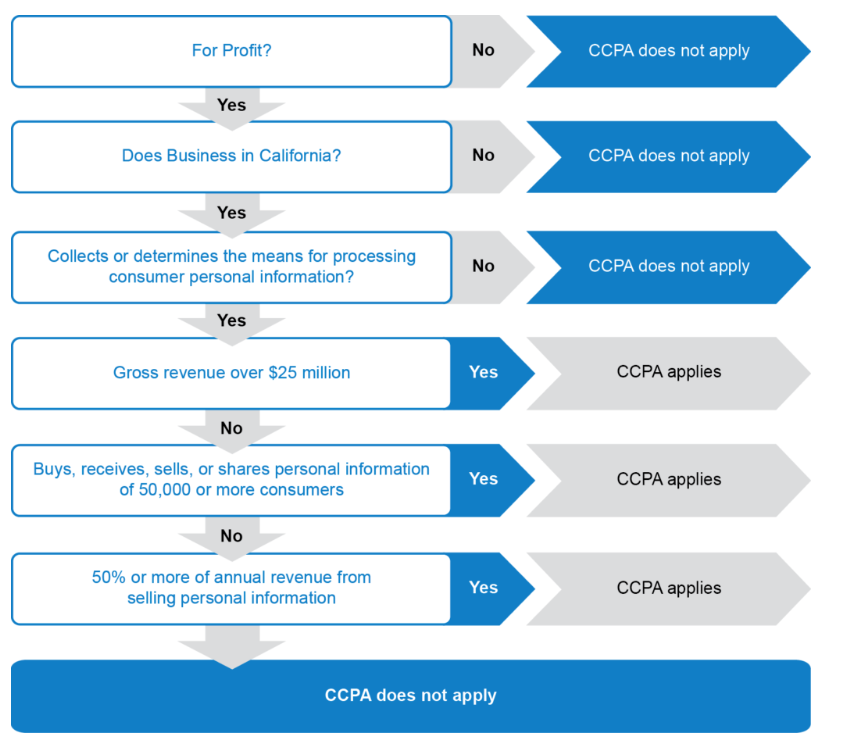
- Has annual gross revenues over $25 million;
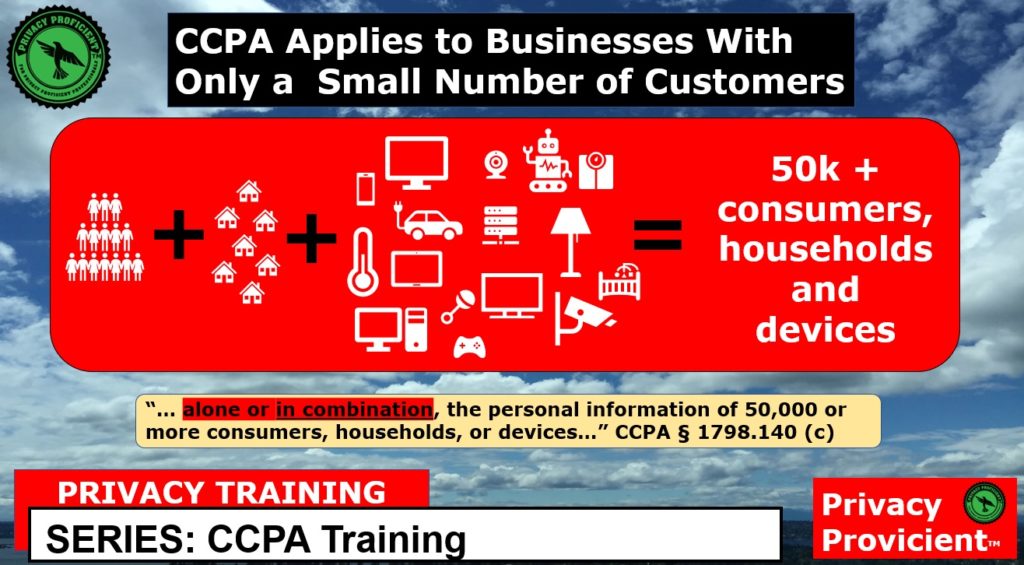
- Buys, receives, or sells the personal information of 50,000 or more consumers, households, or devices; or
- Earns 50 percent or more of its annual revenue from selling consumers’ personal information.

Who is Subject to the CCPA?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a wide-reaching data privacy law that grants consumers certain rights with regards to their data. It applies to companies that fit certain criteria, and it is important to understand who falls under the scope of this law in order to comply with it.
What is the CCPA?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a data privacy law that was passed in 2018 and went into effect in 2020. It grants consumers certain rights with regards to their data, such as the right to know what personal information a company holds about them, the right to delete that information, and the right to opt-out of the sale of that information. It applies to all companies that meet certain criteria.
The CCPA applies to for-profit companies that do business in California, that have gross annual revenues over $25 million, that buy, sell, or share the personal information of 50,000 or more consumers, households, or devices, or that generate a majority of their revenues from selling consumers’ personal information.
What Companies are Exempt from CCPA?
The CCPA does not apply to certain types of companies. These include companies that collect or process personal information in the course of providing services as a “service provider”, companies that process personal information for “non-profit” or “government” purposes, and companies that process personal information for “journalistic” purposes. Additionally, the CCPA does not apply to certain types of data, such as publicly available information or de-identified or aggregate information.
It is important to note that even if a company falls outside the scope of the CCPA, it may still be subject to other data privacy laws. It is therefore important to understand the laws that apply to a company in order to ensure compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a data privacy law that provides California-based consumers with greater control over their personal information. It also imposes additional obligations on businesses.
Who does the CCPA apply to?
The CCPA applies to for-profit businesses that operate in California, have annual gross revenues of more than $25 million, or buy, receive, sell, and/or share the personal information of 50,000 or more consumers, households, or devices. This includes any business that is owned or operated by a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or other legal entity.
The law also applies to businesses that do not meet the criteria above but derive at least 50% of their annual revenue from the sale of consumers’ personal information. This includes companies that sell personal data to third parties or use it to target ads. Businesses must also comply with the CCPA if they control or are controlled by a business that meets the criteria.
What are a business’s obligations under the CCPA?
Under the CCPA, businesses must provide a clear and conspicuous link on their website’s home page titled “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” which allows consumers to opt-out of the sale of their personal data. Businesses must also provide consumers with the ability to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information. Businesses must also provide the same information when consumers ask for it, and provide it in a format that is easy to understand.
Additionally, businesses must take reasonable steps to protect consumers’ personal information from unauthorized access, destruction, use, modification, or disclosure. Businesses must also train their employees on how to handle consumers’ personal information. Finally, businesses must comply with any additional requirements imposed by the Attorney General of California.
What are the penalties for non-compliance?
Businesses that fail to comply with the CCPA are subject to civil penalties of up to $7,500 per violation. Additionally, the Attorney General of California may pursue criminal penalties for violations, including fines of up to $2,500 per violation and/or imprisonment of up to one year.
How do businesses comply with the CCPA?
Businesses must take a number of steps to comply with the CCPA, including updating their privacy policies, providing consumers with the ability to opt-out of the sale of their personal information, and providing consumers with the ability to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information. Additionally, businesses must take reasonable steps to protect consumers’ personal information from unauthorized access, destruction, use, modification, or disclosure.
Businesses must also train their employees on how to handle consumers’ personal information, and comply with any additional requirements imposed by the Attorney General of California. Finally, businesses should consider hiring a privacy professional or consulting firm to help them ensure that they are compliant with the CCPA.
What is the deadline for compliance?
Businesses must comply with the CCPA by January 1, 2020. The Attorney General of California may extend the deadline for certain businesses, but this is not guaranteed. Businesses should take steps to ensure that they are compliant as soon as possible in order to avoid potential penalties.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is an important piece of legislation that has the potential to transform how businesses interact with consumers. It is designed to give consumers more control over their personal data, ensuring that companies respect their privacy. The CCPA applies to a wide range of businesses and organizations, including those that collect or process personal information from California residents. This includes companies that have annual gross revenues in excess of $25 million, those that buy or sell personal information of 50,000 or more consumers, and those that derive 50% or more of their annual revenues from selling consumers’ personal information.
The CCPA is an important step towards greater consumer privacy protection, and businesses should take the time to ensure that they are compliant with the law. By taking the time to understand the CCPA and how it applies to their operations, businesses can ensure that they are providing the highest levels of privacy protection to their customers. This will not only help to protect the rights of consumers, but also help businesses maintain their competitive edge in the marketplace.