As technology continues to advance, networking has become an essential part of our lives. From our homes to our workplaces, we rely heavily on networks to communicate and share information. However, as with any technology, there are bound to be issues that arise. One such issue is redundancy in networking.
Redundancy in networking refers to the duplication of components or systems within a network. This duplication is done in order to ensure that the network remains operational even if a component or system fails. This is critical for networks that are used in mission-critical applications such as hospitals, financial institutions, and government agencies. In this article, we will explore the different types of redundancy in networking and how they work to ensure that networks remain operational even in the face of failure.
Redundancy in networking is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system, usually with the intention of decreasing downtime. This is done by creating multiple components of a single system, such that if one part fails, the entire system is still operational. Redundancy can be implemented in many forms, such as extra power supplies, servers, switches, routers, or even entire sites. In addition to reliability, redundancy can also increase speed and availability of a system.
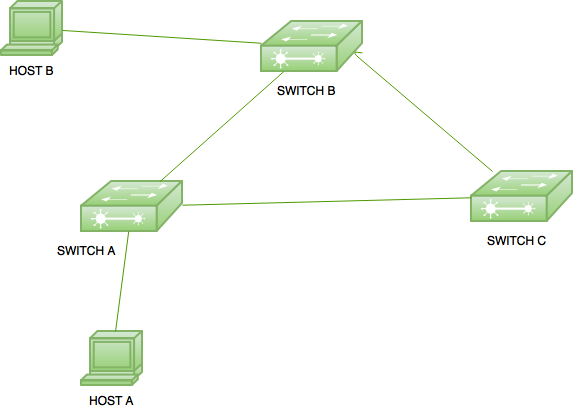
What is Redundancy in Networking?
Redundancy in networking is the practice of providing alternative paths for data to travel across a network. It serves as a safeguard against downtime due to network outages, server failure, or other disruptions. Redundancy is an important factor when designing a network, as it ensures that data can always reach its destination, even in the event of an unexpected event.
Types of Redundancy
There are two main types of redundancy in networking: hardware redundancy and software redundancy. Hardware redundancy involves having multiple components of a network in place to ensure that if one fails, the other can take its place. This could include having multiple routers, switches, or servers. Software redundancy involves having multiple programs or applications running at the same time to ensure that if one fails, the other can take its place. Examples of software redundancy include clustering applications and using virtualization.
Benefits of Redundancy
Redundancy in networking is beneficial for a variety of reasons. First, it ensures that the network is available even if one component fails. This helps to reduce downtime and keep the network running smoothly. Additionally, redundancy can provide a more reliable and secure network, as it helps to protect against malicious attacks or natural disasters. Finally, redundancy can also improve performance by ensuring that data can always reach its destination, even if one route is blocked.
Network Redundancy Strategies
When designing a network, it is important to consider the various redundancy strategies that can be implemented. One strategy is to use redundant links, which provide alternative pathways for data to travel in the event of a link failure. Additionally, using redundant servers or clusters can help to ensure that applications or services remain available, even if one server fails. Finally, it is important to also consider power redundancy, which involves having multiple sources of power for the network in case of an outage.
Redundancy Protocols
When implementing redundancy in networking, it is important to use the appropriate protocols and technologies. Common protocols used for redundancy include Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP). Additionally, technologies such as virtualization and clustering can be used to ensure that applications and services remain available in the event of a failure.
Conclusion
Redundancy in networking is an important factor when designing a network, as it helps to ensure that data can always reach its destination, even in the event of an unexpected event. Redundancy can come in the form of hardware redundancy, software redundancy, or a combination of both. Additionally, there are various strategies and protocols that can be used when implementing redundancy in networking. By properly implementing redundancy, networks can be more reliable, secure, and available.
Frequently Asked Questions: What is Redundancy in Networking?
Two of the most important aspects of networking are redundancy and reliability. Redundancy means having multiple systems in place that can take over in the event of a failure, while reliability guarantees that the systems will remain operational even in the face of outages.
What is Redundancy in Networking?
Redundancy in networking refers to the use of multiple systems to ensure continuity of service. This includes having multiple physical connections (such as using two different ISPs), using redundant network hardware (such as multiple routers or switches), and using redundant software (such as redundant web servers). By having multiple systems that can take over in the event of a failure, businesses can stay operational with minimal disruption.
What are the Benefits of Redundancy in Networking?
One of the major benefits of having redundancy in networking is that it increases reliability. By having multiple systems that can take over in the event of a failure, businesses can stay operational with minimal disruption. Additionally, redundancy allows for the quick and efficient resolution of outages, as the redundant systems can take over while the issue is being addressed.
What are the Types of Redundancy in Networking?
There are several types of redundancy in networking, including physical redundancy, hardware redundancy, and software redundancy. Physical redundancy involves having multiple physical connections (such as using two different ISPs) to ensure continuity of service. Hardware redundancy involves having multiple routers or switches that can take over in the event of a failure. Software redundancy involves having redundant web servers that can take over in the event of a failure.
What are the Challenges of Redundancy in Networking?
One of the challenges of having redundancy in networking is the cost. Redundancy requires multiple systems, which can be expensive to purchase and maintain. Additionally, it can be difficult to ensure that the redundant systems are up-to-date and functioning properly. Finally, redundant systems require ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure they remain operational.
What is a Redundancy Protocol?
A redundancy protocol is a set of rules and guidelines that determine how redundant systems are configured and managed. These protocols are designed to maximize reliability and uptime by ensuring that redundant systems are functioning properly and that outages are quickly resolved. Examples of redundancy protocols include the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol and the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP).
In conclusion, redundancy in networking is an essential aspect of ensuring that network systems operate optimally. It involves having backup systems or devices that can take over the primary systems in case of a failure. This redundancy helps to prevent network downtime, which can be costly and inconvenient for businesses. Additionally, redundancy can enhance network performance by distributing traffic across multiple channels, reducing the risk of overloading any particular system.
While redundancy may seem like an unnecessary expense for some businesses, it is crucial for maintaining a reliable and scalable network. Investing in redundancy can help businesses avoid costly downtime and maintain productivity, which can ultimately lead to increased profitability. As technology continues to evolve, redundancy in networking will become even more critical, and businesses that fail to implement it will be left behind. Therefore, it is essential to understand the importance of redundancy in networking and incorporate it into any network design.