In today’s world, technology has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. We rely on it for everything from communication and entertainment to work and productivity. However, with the increasing demand for faster and more efficient processing of data, traditional cloud computing systems are no longer able to keep up. This is where edge computing comes in, offering a solution to the limitations of cloud computing by bringing computing power closer to the end-users.
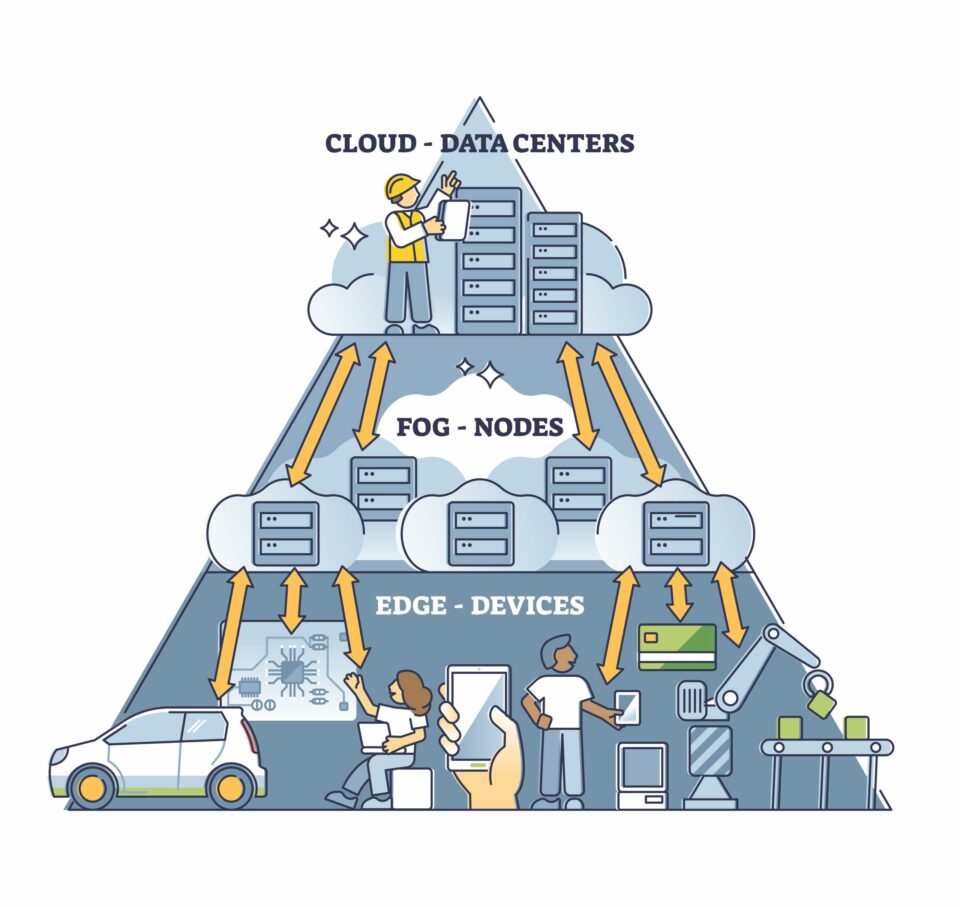
But what exactly is edge computing and how does it work? Edge computing, also known as fog computing, is a distributed computing model that brings data processing and storage closer to the devices and sensors that generate the data, rather than relying on a centralized cloud infrastructure. By doing so, it reduces the latency and bandwidth requirements, improves data security and privacy, and enables real-time processing and analysis of data. In this article, we will explore the concept of edge computing in more detail, its benefits and use cases, and how it is changing the way we interact with technology.
Edge Computing is a form of distributed computing which brings computing and data storage closer to the edge of the network. It helps to reduce latency and bandwidth costs by processing data closer to the source of the data. Edge Computing also helps to improve the quality of service and latency for applications, as well as providing a secure environment for the data.
Edge Computing is different from traditional cloud computing, as it is performed at the edge of the network, rather than in the cloud. This enables applications to be run on devices such as smartphones and IoT devices, instead of relying on cloud infrastructure. Edge Computing also reduces latency, as data is processed closer to the source.
Edge Computing can be used in a variety of scenarios, such as providing low-latency access to data for applications, providing secure data processing for IoT devices, and providing a secure environment for data. Edge Computing also helps to reduce bandwidth costs, as data is processed closer to the source, and not in the cloud.

What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a type of computing that is done at the edge of a network, or near the source of the data, rather than in a centralized data center. Edge computing moves processing and storage closer to the source of the data, allowing for faster processing and more efficient use of resources. Edge computing also allows for more efficient use of network bandwidth, since data does not need to be sent over long distances.
Edge computing is becoming increasingly popular as more devices are connected to the Internet of Things (IoT). By bringing processing and storage closer to the source of the data, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to a centralized data center. This can reduce the latency of data processing, as well as the costs associated with long-distance data transmission.
Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing can bring many benefits to businesses and consumers. By bringing processing and storage closer to the source of the data, edge computing can reduce latency and improve the speed of data processing. This can be especially beneficial in applications such as streaming video, where latency can be a major factor in user experience.
Edge computing can also reduce the costs associated with long-distance data transmission. Since data does not need to be sent over long distances, the costs associated with bandwidth and data storage can be reduced. Additionally, edge computing can be used to reduce the load on centralized data centers, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks.
Challenges of Edge Computing
Edge computing can bring many benefits, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. One of the main challenges is security. Since edge computing moves data processing and storage closer to the source of the data, it can increase the risk of data breaches. Additionally, edge computing can be more difficult to manage than centralized data centers, since there is no single point of control.
Another challenge of edge computing is scalability. As more devices are connected to the edge, it can become difficult to manage the data processing and storage needs. Additionally, edge computing can require specialized hardware and software, which can add to the cost and complexity of the system.
The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing is becoming increasingly popular as more devices are connected to the Internet of Things. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that edge computing will become even more important. Edge computing can be used to reduce latency, improve the speed of data processing, and reduce the load on centralized data centers.
Edge computing is also likely to become more secure as the technology continues to evolve. Security measures such as encryption, authentication, and authorization can be used to protect data at the edge. Additionally, edge computing can be used to collect and analyze data in real time, allowing for more efficient use of resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
Edge computing is a distributed computing system that enables data storage and processing closer to the source of the data. It is a form of distributed computing that helps to reduce latency and improve scalability by bringing computing power closer to the user or data source.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a type of distributed computing system that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of the data. Edge computing is designed to reduce latency and improve scalability by bringing computing power closer to the user or data source. It is often used in IoT (Internet of Things) applications where data needs to be collected and analyzed quickly and in real-time.
Edge computing helps to reduce latency by reducing the distance data must travel before it can be processed. By bringing computing resources closer to the source, edge computing can reduce latency and improve scalability. Edge computing also enables data to be processed more quickly and efficiently, making it ideal for applications that require real-time analysis.
What are the benefits of edge computing?
The main benefits of edge computing include improved latency and scalability, reduced data costs, enhanced security, and improved performance. By bringing computing resources closer to the user or data source, edge computing can reduce latency and improve scalability. Edge computing also reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, reducing data costs and improving performance. Additionally, edge computing enables data to be processed securely, as data is stored and processed closer to the source.
Edge computing also provides the ability to process data in real-time, making it ideal for applications that require near-instant analysis. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing enables applications to respond quickly to changes in the environment. Edge computing also enables applications to be more reliable, as the data does not need to travel as far before it can be processed.
How does edge computing work?
Edge computing works by bringing computation and data storage closer to the source of the data. This is done by placing computing resources, such as servers and storage, in close proximity to the source of the data. By reducing the distance data must travel before it can be processed, edge computing can reduce latency and improve scalability.
Edge computing also enables data to be processed more securely, as data is stored and processed closer to the source. Additionally, edge computing enables data to be processed more quickly and efficiently, making it ideal for applications that require real-time analysis. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, reducing data costs and improving performance.
What are some applications of edge computing?
Edge computing is most commonly used in IoT (Internet of Things) applications where data needs to be collected and analyzed quickly and in real-time. Edge computing is also used in applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and smart homes, where data needs to be collected and analyzed quickly and in real-time. Additionally, edge computing is used in applications such as augmented reality and virtual reality, where data needs to be collected and analyzed quickly and in real-time.
Edge computing is also used in applications such as industrial automation and robotics, where data needs to be collected and analyzed quickly and in real-time. Additionally, edge computing can be used to improve the performance of distributed systems such as cloud computing, by bringing computation and storage closer to the user or data source.
What are the challenges of edge computing?
One of the challenges of edge computing is the complexity of managing distributed systems. Edge computing requires the deployment of computing resources in close proximity to the source of the data, which can be difficult to manage. Additionally, edge computing requires the ability to process data in real-time, which can be challenging to achieve.
Another challenge of edge computing is the security of data. Edge computing requires data to be stored and processed closer to the source, which can create additional security risks. Additionally, edge computing requires the ability to securely transmit data between multiple distributed resources, which can also create additional security risks.
In conclusion, edge computing is an innovative technology that is changing the landscape of computing. It provides a new way of processing data by bringing the computational power closer to the source of data. This approach eliminates the need for long-distance data transfers and reduces latency, making real-time data processing and analysis possible.
As more devices become connected to the internet, the demand for edge computing is expected to grow rapidly. With its ability to process data quickly and efficiently, it has the potential to transform industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. As a professional writer, it is exciting to see the advancements in technology and the impact it has on our daily lives. Edge computing is just one example of how technology is shaping the future, and it will be interesting to see how it continues to evolve and shape the way we live and work.