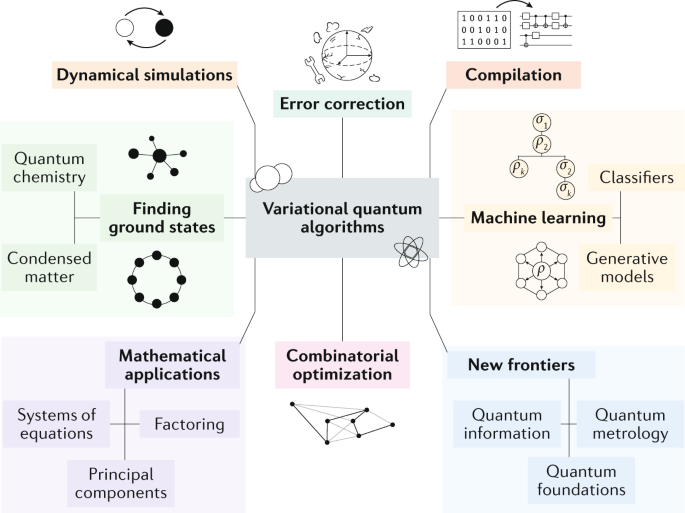
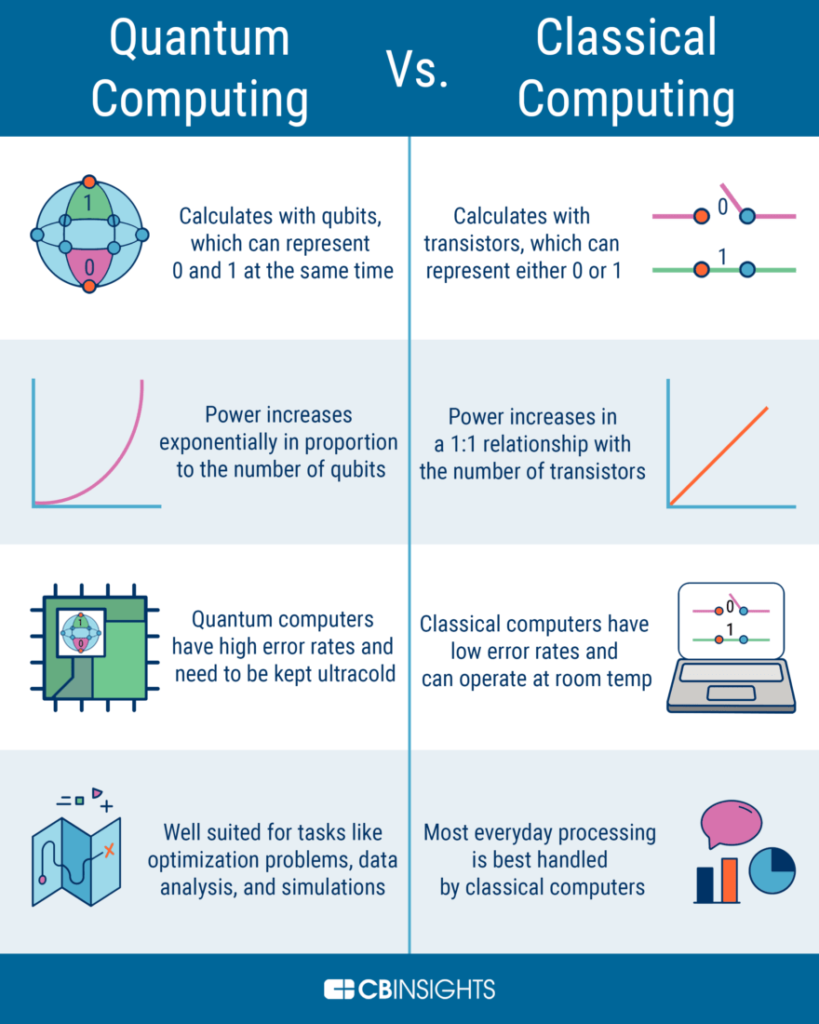
Quantum computing is a field of study that has attracted a lot of attention in recent years. It is a new approach to computing that takes advantage of the principles of quantum mechanics. Quantum computing is used to solve problems that are difficult or impossible to solve using classical computers. One of the key concepts in quantum computing is entanglement. Entanglement is a phenomenon where two particles become connected in such a way that the state of one particle affects the state of the other, even when they are separated by large distances.
Entanglement is a key ingredient in many quantum algorithms. It is used to perform quantum teleportation, quantum cryptography, and quantum error correction. Entanglement also plays a crucial role in quantum search algorithms, such as Grover’s algorithm. In this algorithm, a quantum computer can search an unsorted database of N items in O(sqrt(N)) time, which is exponentially faster than the O(N) time required by classical algorithms. Understanding entanglement is therefore essential for anyone working in the field of quantum computing. In this article, we will explore the role of entanglement in quantum algorithms, and why it is such an important concept in the field of quantum computing.
Quantum entanglement is used to create algorithms that solve complex problems faster than traditional algorithms. This is done by exploiting quantum effects like superposition and entanglement to generate more efficient algorithms. Entanglement allows two particles to become linked, meaning that their state is inextricably linked and any changes to one particle will affect the other. This means that the algorithm can be run on two particles simultaneously, greatly increasing the speed at which it can be solved.
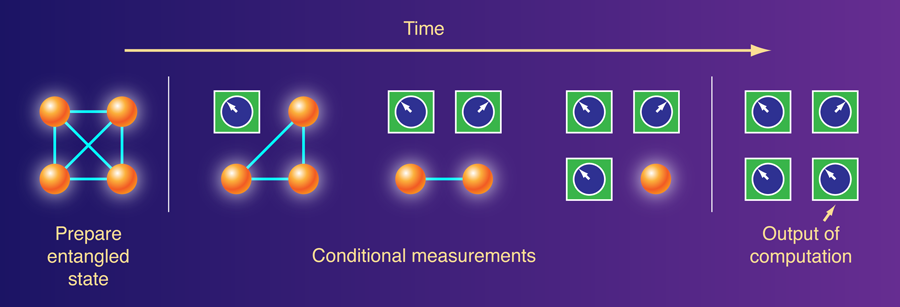
What is Entanglement Doing in Quantum Algorithms?
Entanglement is a phenomenon in quantum mechanics that has been studied for decades. It has recently been used to develop new algorithms that can solve certain problems faster than classical algorithms. In this article, we will explore what entanglement is and how it is used in quantum algorithms.
What is Entanglement?
Entanglement is a quantum phenomenon that occurs when two particles interact and become linked together. This link allows them to share properties and influence each other, even if they are separated by a large distance. It has been described as “spooky action at a distance” because the particles are able to interact without any physical connection.
Entanglement is an important concept in quantum mechanics because it allows information to be shared between particles that are not physically connected. This has implications for quantum computing, as it allows for faster processing of information.
How Is Entanglement Used in Quantum Algorithms?
Entanglement is used in quantum algorithms to speed up problem solving. By taking advantage of entanglement, quantum algorithms can solve certain problems faster than classical algorithms. For example, Google recently developed a quantum algorithm that can solve certain problems in 200 seconds, compared to the 10,000 seconds required by classical algorithms.
Entanglement also allows for the creation of quantum logic gates, which are the building blocks of quantum computers. These logic gates are able to process information faster than classical logic gates, which allows for faster processing of information.
In addition, entanglement can be used to create quantum networks, which are networks of quantum computers that can communicate with each other. This allows for faster data transfer and the ability to work on complex problems in parallel.
Conclusion
Entanglement is an important concept in quantum mechanics that has been used to develop new algorithms and create quantum logic gates. It has enabled faster processing of information and the creation of quantum networks that can communicate with each other. Entanglement is an exciting development that has the potential to revolutionize the field of quantum computing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Entanglement is an important part of quantum algorithms, and its application in quantum computing has made it a subject of great interest. This article will provide answers to the most frequently asked questions about entanglement in quantum algorithms.
What is entanglement?
Entanglement is a quantum phenomenon, in which two particles become linked in such a way that the state of one particle is dependent on the state of the other. This phenomenon is a key part of quantum mechanics, and it has been used to explain many phenomena from the behavior of atoms to the behavior of light. In quantum computing, entanglement is used to link two qubits together so that the result of one is dependent on the result of the other.
What are the benefits of entanglement in quantum algorithms?
Entanglement is used to link two qubits in a way that allows for more efficient and faster calculations. This means that it can be used to speed up calculations that would normally take a long time to complete. In addition, entanglement is used to ensure accuracy in calculations, as it ensures that the two qubits are linked in a way that results in accurate and reliable results.
What are the drawbacks of entanglement in quantum algorithms?
The main drawback of entanglement in quantum algorithms is that it requires a great deal of energy to maintain the links between the two qubits. This means that the use of entanglement can be costly in terms of energy, and this cost can reduce the efficiency of quantum algorithms. In addition, entanglement can be difficult to control and maintain, which can lead to errors in calculations.
What are the applications of entanglement in quantum algorithms?
Entanglement is used in a variety of quantum algorithms, including quantum computing and quantum information processing. In quantum computing, entanglement can be used to speed up calculations and make them more efficient. In quantum information processing, entanglement is used to securely store and transmit information, as well as to create secure communication channels.
How does entanglement work in quantum algorithms?
Entanglement works by linking two qubits together in such a way that the state of one is dependent on the state of the other. This means that when one qubit is changed, the other is affected as well. This link is maintained by a process known as entanglement, which ensures that the two qubits remain linked. This link is used to ensure the accuracy of calculations, as well as to speed up calculations by allowing the two qubits to work together.

In conclusion, entanglement is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that has proven to be incredibly useful in the development of quantum algorithms. Its ability to create strong correlations between particles, even when they are separated by large distances, has allowed quantum computers to solve problems that would be impossible for classical computers. By utilizing entanglement, quantum algorithms are able to perform calculations in parallel, leading to a significant increase in speed and efficiency.
As research in quantum computing continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of entanglement in quantum algorithms. From cryptography to machine learning, the potential applications of quantum computing are vast and exciting. While there are still challenges to be overcome, the use of entanglement in quantum algorithms provides a promising path towards a future of powerful, efficient computing.