In today’s fast-paced digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives. From social media to online shopping, we rely on the internet to connect us to the world. However, have you ever wondered how the internet actually works? What makes it possible for us to access information from all over the world instantly? The answer lies in the complex network of interconnected computers and servers that form the backbone of the internet.
At the heart of this network lies the internet backbone, a term commonly used to refer to the high-speed data transmission lines that connect internet service providers (ISPs) and other network operators. These backbone networks are responsible for transmitting vast amounts of data across the globe, allowing us to access information from anywhere in the world. In this article, we will delve deeper into the backbone of the internet and explore the different tiers that make it possible. So, let’s dive in and discover which network tier forms the backbone of the internet.
Which Network Tier Forms the Internet Backbone?
The internet is a complex network of computers and devices that provides us with vast amounts of information and services. This global network consists of different tiers, where each tier is responsible for a different purpose. The backbone of the internet refers to the tier that is the most essential for providing the highest-level communication services.
What is the Internet Backbone?
The internet backbone is the tier of the internet that serves as the primary highway of data transfer between networks. It is composed of high-speed data lines that are connected to a large number of networks around the world. This tier is the “core” of the internet, providing the most reliable and highest-speed connection between networks. It is the most essential component of the internet, as it is responsible for providing the highest-level communication services.
The internet backbone is made up of several types of networks, including fiber-optic lines, satellite networks, and terrestrial networks. Each of these networks has its own advantages and disadvantages. Fiber-optic lines are the most reliable and fastest type of network, but they are also the most expensive. Satellite networks provide a wide coverage area but are not as reliable as the other types of networks. Terrestrial networks are the least expensive option but are not as reliable or fast as the other types of networks.
Who Owns the Internet Backbone?
The internet backbone is owned and operated by various companies, organizations, and governments around the world. These companies typically own and operate the infrastructure, including the fiber-optic lines and other types of networks. Governments and organizations around the world also have a hand in the ownership of the internet backbone, as they may own and control parts of the infrastructure.
The ownership of the internet backbone is important, as it determines who can access, control, and manage the data that is transferred across the networks. For example, certain organizations may have exclusive access to certain parts of the internet backbone. This allows them to manage and control the data that is transferred across the internet, as well as to monitor the traffic on the networks.
The ownership of the internet backbone is also important for security purposes. Organizations that own and manage parts of the internet backbone can monitor the data that is transferred across the networks and can prevent malicious activities. This can help to ensure that the internet remains secure and reliable for all users.
Conclusion
The internet backbone is the tier of the internet that is responsible for providing the highest-level communication services. It is composed of high-speed data lines that are connected to a large number of networks around the world. The internet backbone is owned by various companies, organizations, and governments around the world, and it is important for providing reliable and secure data transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Internet backbone is the tier of a telecommunication network that interconnects other, smaller networks and provides long-distance transmission of data. It forms the core of the Internet and many other large networks.
What is the Internet backbone?
The Internet backbone is the tier of a telecommunication network that interconnects other, smaller networks and provides long-distance transmission of data. It is composed of the high-speed data lines, fiber optic cables, and network nodes that transfer data from one network to the next, making it possible for the interconnected networks to communicate. It is the core of the Internet and many other large networks.
What is the purpose of the Internet backbone?
The purpose of the Internet backbone is to connect multiple networks together and provide a means for data to be transmitted over large distances. It enables communication, information sharing, and collaboration between networks that are geographically dispersed. Without it, large networks such as the Internet would not be possible.
Who controls the Internet backbone?
The Internet backbone is controlled by various organizations such as Internet service providers, educational institutions, government agencies, and corporations. These organizations are responsible for managing the infrastructure of the Internet and ensuring that data is transmitted between networks efficiently.
How is the Internet backbone maintained?
The Internet backbone is maintained by the organizations that control it. They are responsible for ensuring that the infrastructure is up to date and capable of handling the large volumes of data that are transmitted across it. This includes upgrading equipment, monitoring network performance, and troubleshooting any issues that arise.
How is the Internet backbone used?
The Internet backbone is used to transmit data between networks, allowing different organizations and individuals to communicate and collaborate. It is used to connect computers and other devices to the Internet, as well as to connect different networks and share data. It is also used for the transmission of voice and video communications, streaming media, and other forms of data.
Backbone Computer Network Explained
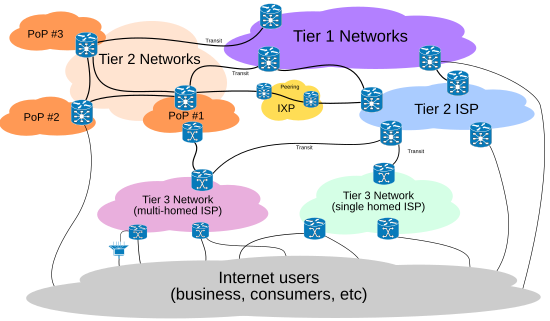
In conclusion, the internet backbone is formed by Tier 1 networks, the highest level of the global internet hierarchy. These networks are responsible for carrying the vast majority of internet traffic and providing connectivity to other networks, including Tier 2 and Tier 3 networks. While Tier 2 and Tier 3 networks may also play a role in the internet backbone, it is Tier 1 networks that form the core infrastructure on which the internet relies.
The importance of Tier 1 networks cannot be overstated, as they are the backbone of the internet that connects millions of people and devices around the world. Without these networks, the internet as we know it today would not exist. As technology continues to evolve and the demand for internet connectivity grows, Tier 1 networks will continue to play a critical role in supporting the global digital economy and keeping the world connected.