In the world of networking, there are several different types of topologies that engineers use to connect their devices. One of the most common is the bus topology, which is a network design that connects all devices to a single cable. This topology has been around for decades and is still widely used in many settings, from small businesses to large organizations.
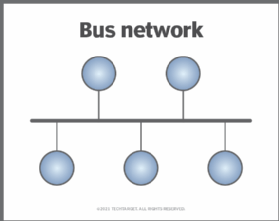
A defining characteristic of a bus topology-based network is that all devices on the network are connected to a single cable. This cable acts as a backbone, carrying data signals from one device to another. Because all devices are connected to the same cable, they share the same bandwidth, which can sometimes lead to congestion if too many devices are connected. However, bus topology networks are known for their simplicity and ease of use, making them a popular choice for many organizations.
What is a Bus Topology-Based Network?
A bus topology-based network is a type of computer network which is characterized by the use of a single shared communication line and a single host computer. The bus topology is the simplest type of network topology available and is often used in small office or home networks. In a bus topology-based network, all the computers connected to the network share the same data bus. All messages sent between the computers travel along this single bus.
Advantages of a Bus Topology-Based Network
A bus topology-based network is an easy and cost-effective way to set up a computer network. It is simple to set up and maintain, as there is no need for complex wiring or additional hardware, such as hubs and switches. Furthermore, the data bus is relatively inexpensive and easy to replace should it ever become damaged or corrupted. In addition, due to the single data bus, the network is very reliable and efficient as all data travels along a single path.
Cost-Effective
One of the main advantages of a bus topology-based network is that it is a cost-effective way to set up a computer network. As mentioned, there is no need for complex wiring or additional hardware, such as hubs and switches. Furthermore, the data bus is relatively inexpensive and easy to replace should it ever become damaged or corrupted. This makes the bus topology-based network an ideal choice for small office or home networks.
Easy to Set Up and Maintain
Another advantage of a bus topology-based network is that it is easy to set up and maintain. This is due to the fact that there is no need for complex wiring or additional hardware. Furthermore, since the data bus is relatively inexpensive, it can be easily replaced if it becomes damaged or corrupted. This makes the bus topology-based network an ideal choice for small office or home networks.
Reliable and Efficient
The bus topology-based network is also a reliable and efficient way to set up a computer network. This is because all the data travels along a single data bus. This eliminates the need for complex wiring and additional hardware, as all the data is sent along the same data bus. Furthermore, since the data bus is relatively inexpensive and easy to replace, the network is highly reliable and efficient.
Ideal for Small Networks
The bus topology-based network is ideal for small office or home networks. This is because it is relatively inexpensive and easy to set up and maintain. Furthermore, the data bus is relatively inexpensive and easy to replace should it ever become damaged or corrupted. This makes the bus topology-based network an ideal choice for small office or home networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bus topology-based networks are used to link multiple computers and devices together. This type of network is characterized by its linear shape, with all devices connected to a single cable known as the backbone.
What is a Bus Topology?
A bus topology is a type of network that is characterized by a single, linear cable or backbone, to which all computers and other network devices are connected. This type of network is very common in small networks, such as those found in home offices or small businesses. It is easy to set up and is relatively inexpensive. The main disadvantage of a bus topology-based network is that if the backbone fails, then all of the devices connected to it will be unable to communicate.
What Are the Advantages of a Bus Topology?
The primary advantage of a bus topology-based network is its cost. It is inexpensive to install and maintain, and it is also easy to set up. Additionally, it is easy to extend the network by simply adding additional devices to the backbone.
Another advantage of a bus topology-based network is its flexibility. It allows for the easy inclusion of new devices or the removal of existing devices. Additionally, it can accommodate a variety of different types of devices, from computers to printers and other peripherals.
What Are the Disadvantages of a Bus Topology?
The primary disadvantage of a bus topology-based network is that if the backbone fails, then all of the devices connected to it will be unable to communicate. Additionally, it is limited in terms of its scalability, as it cannot easily accommodate large numbers of devices. Furthermore, it is not suitable for use in large networks, as it is not robust enough to handle heavy traffic.
What Are the Alternatives to a Bus Topology?
There are several alternatives to a bus topology-based network, such as star, ring, and mesh topologies. A star topology is characterized by a central hub to which all devices are connected. A ring topology is characterized by a continuous loop of cables, with each device connected to two other devices. Finally, a mesh topology is characterized by a network of interconnected devices, with each device connected to several other devices.
What Are the Benefits of a Bus Topology?
The primary benefit of a bus topology-based network is its simplicity and low cost. Additionally, it is easy to set up and maintain, and it is also relatively reliable. Additionally, it is suitable for use in small networks, as it can easily accommodate a limited number of devices. Furthermore, it is also relatively easy to extend the network by simply adding additional devices to the backbone.
Network Topologies (Star, Bus, Ring, Mesh, Ad hoc, Infrastructure, & Wireless Mesh Topology)
In conclusion, the defining characteristic of a bus topology-based network is its simplicity and ease of use. With a linear structure that connects all devices to a single cable, the bus topology allows for efficient communication and easy troubleshooting. However, its limitations in terms of scalability and potential for network congestion should be considered when implementing this type of network.
Despite its drawbacks, the bus topology remains a popular choice for small to medium-sized networks due to its affordability and practicality. As technology continues to evolve, it is important for network administrators to stay informed about the various types of network topologies and choose the one that best meets their organization’s needs. Whether it is a bus topology or a more advanced topology, a well-designed network can greatly enhance communication and productivity within an organization.