Blockchain technology has taken the world by storm, revolutionizing the way we conduct transactions and store data. It has become an essential part of many industries, including finance, healthcare, and logistics, to name a few. At the heart of this technology lies a complex system of mathematical algorithms that ensure the security and integrity of the data stored on the blockchain. If you’re interested in learning more about blockchain and how it works, one of the fundamental concepts to understand is the three primary components of a blockchain.
In simple terms, a blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that is maintained by a network of computers. It is made up of three primary components: blocks, nodes, and miners. Each block contains a set of transactions that are verified by the nodes on the network, and once verified, the block is added to the blockchain. The role of the miners is to solve complex mathematical algorithms that enable them to validate transactions and earn rewards for their work. By understanding the three primary components of a blockchain, you will gain a deeper appreciation of how this technology works and why it has become such a critical part of our digital world.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary new way to store data with enhanced security and transparency. It is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable digital ledger system that can record virtually any kind of transaction or activity. The technology is used to create and maintain a growing list of records, or blocks, which are linked together using cryptography. Each block is connected to the previous block, creating an unbroken chain of data that is constantly updated and maintained.
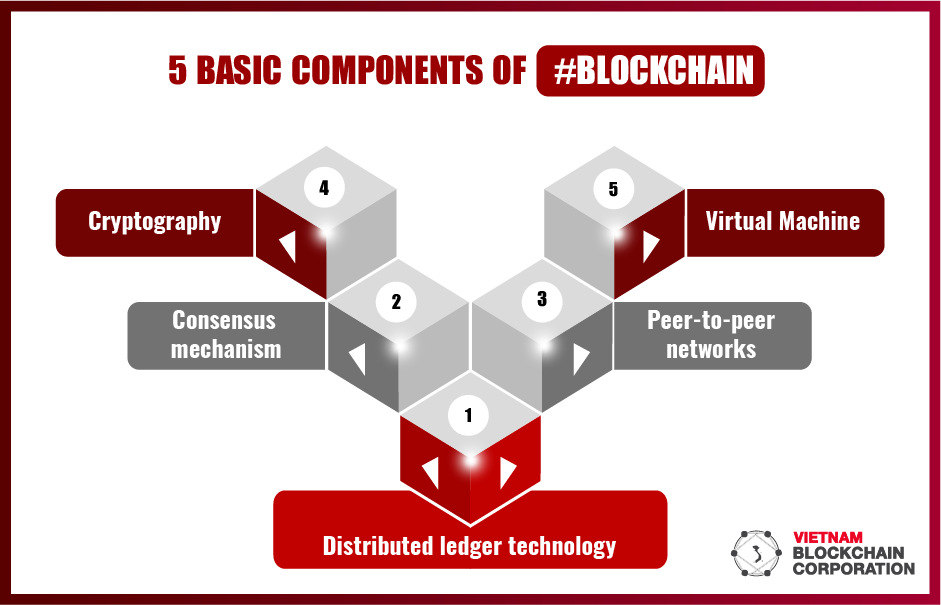
What are the Three Primary Components of Blockchain?
1. Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
A distributed ledger is a digital database that is shared across multiple computers or nodes. This ledger can be used to store data in a secure, distributed, and immutable way. Each node in the network maintains a copy of the ledger and any changes to the ledger are validated by all the other nodes. This ensures that the data stored on the ledger is accurate and up-to-date.
The data stored on the ledger is secure and tamper-proof, as the ledger is cryptographically secured and is replicated across all nodes. This makes it virtually impossible for any one user or entity to alter or delete the data stored on the ledger.
2. Cryptography
Cryptography is the process of encoding and decoding data using mathematical algorithms. Cryptography is used to secure the data stored on the blockchain ledger and to ensure that only authorized users can access the data. It also ensures that the data stored on the ledger is accurate and cannot be tampered with.
Cryptography is used to create digital signatures, which are used to authenticate the identity of users and to ensure that transactions are valid and secure. Cryptography also ensures that the data stored on the blockchain is immutable and cannot be changed or deleted.
3. Consensus Mechanism
A consensus mechanism is a set of rules that all users in a blockchain network must adhere to in order to validate a transaction. Consensus mechanisms are used to ensure that all users in the network agree on the same set of facts and that all transactions are valid. The most common consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks is the proof-of-work algorithm, which requires users to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate a transaction.
In addition to proof-of-work, there are other consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-stake and delegated proof-of-stake that can be used to validate transactions. Each consensus mechanism has its own set of rules and requirements that must be followed in order for a transaction to be validated.
Frequently Asked Questions about Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed database technology that keeps records of digital data or events in a way that is secure, immutable, and auditable. It is the underlying technology for many digital currencies and smart contracts.
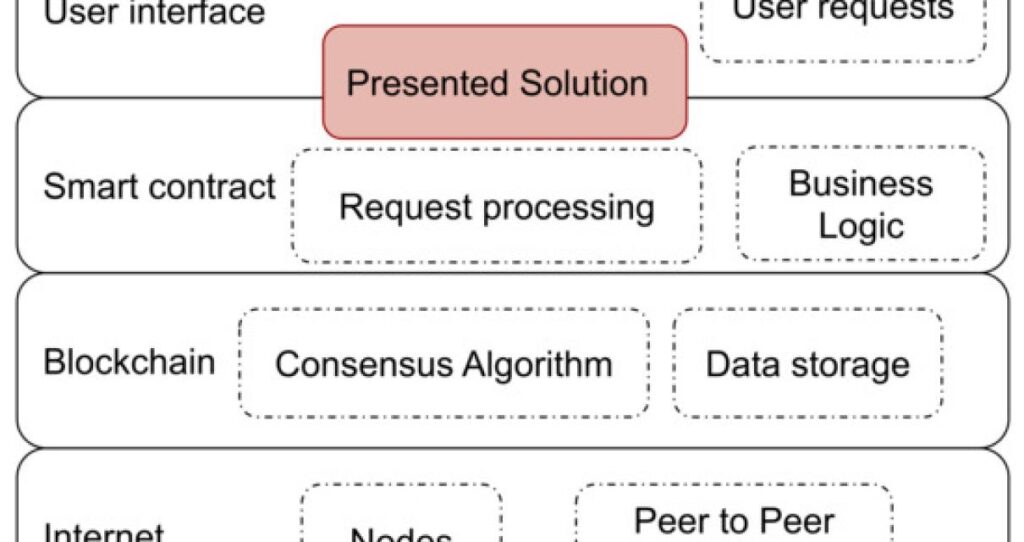
What are the three primary components in a blockchain?
The three primary components in a blockchain are the data, the blocks, and the nodes. The data is the information stored on the blockchain, such as a transaction or a smart contract. The blocks are the containers that store the data. They are cryptographically linked together in a chain so that the data cannot be altered or removed. The nodes are the computers or devices that make up the blockchain network and validate the data stored in the blocks.
The nodes verify the data by making sure it follows the set rules of the blockchain, such as the consensus protocol. Once verified, the data is added to the blockchain and the nodes are rewarded for their work. This is how the blockchain technology works and how it is able to remain secure and immutable.
Components In A Blockchain
In conclusion, the three primary components in a blockchain are the network, the blocks, and the consensus algorithm. Together, these components work seamlessly to ensure that transactions are secure, transparent, and immutable. The network provides the infrastructure for transactions to take place, while the blocks house the information about each transaction. The consensus algorithm ensures that all parties involved in the transaction are in agreement and that no one can alter the information contained within the blockchain.
As blockchain technology continues to gain popularity, it is essential to understand the three primary components that make it possible. By grasping these key elements, individuals and organizations can leverage blockchain to implement secure and transparent transactions that are resistant to tampering or fraud. As we move towards a more digitized world, blockchain technology is poised to transform the way we conduct business, and understanding its core components is a crucial step in harnessing its potential.