Quantum computing is undeniably one of the most fascinating and rapidly evolving fields of computer science. As we delve deeper into the world of quantum mechanics and its applications to computing, we discover new and exciting ways to solve complex problems that were once thought to be impossible. One of the most exciting aspects of quantum computing is the potential for quantum algorithms to provide significant speedups compared to classical algorithms. But just how many quantum algorithms have been shown to be superior?
The answer to this question is not straightforward. There are a few factors to consider, such as the specific problem being solved, the size of the input, and the resources available. However, researchers have made significant progress in developing quantum algorithms that outperform classical algorithms for certain tasks. In this article, we will explore some of the most notable examples of quantum algorithms that have been shown to be superior and discuss the implications for the future of quantum computing.

Exploring Quantum Algorithms
Quantum algorithms are a type of computation that take advantage of the physical properties of quantum mechanics to solve problems faster than traditional computing methods. Quantum algorithms have been shown to be superior to traditional algorithms in terms of speed and accuracy. In this article, we will explore how many quantum algorithms have been shown to be superior and what the implications of these advances are.
Quantum Algorithms vs Traditional Algorithms
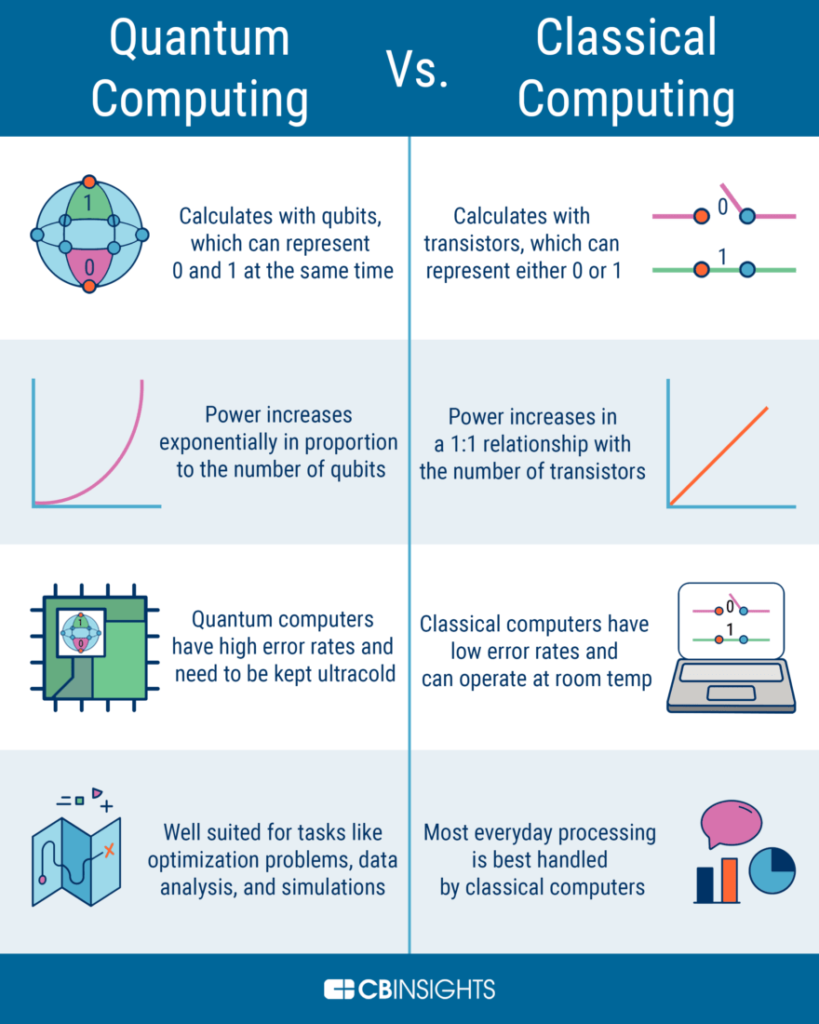
Quantum algorithms are based on the principles of quantum mechanics and are designed to exploit the properties of quantum particles. These algorithms can be used to solve complex problems more quickly than traditional algorithms. The speed of quantum algorithms is determined by the number of qubits used and the complexity of the problem. In contrast, traditional algorithms are based on classical computing principles and are limited by the speed of current processors.
Quantum algorithms are also more efficient than traditional algorithms in terms of accuracy. This is because quantum algorithms can process large amounts of data at once, allowing them to arrive at solutions more quickly and accurately. This efficiency is also seen in the way quantum algorithms can be used to solve difficult mathematical problems, such as factoring large numbers.
How Many Quantum Algorithms Have Been Shown to Be Superior?
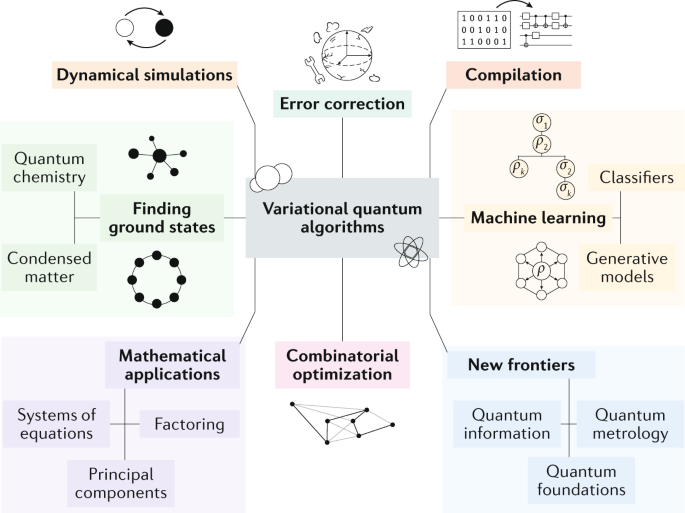
The number of quantum algorithms that have been shown to be superior to traditional algorithms is growing rapidly. In recent years, researchers have developed numerous quantum algorithms that have been shown to outperform traditional algorithms in terms of speed and accuracy. Examples of quantum algorithms that have been shown to be superior include Shor’s algorithm, Grover’s algorithm, and the HHL algorithm.
In addition to these algorithms, there are many other quantum algorithms that have been developed over the years. These algorithms have been used to solve a wide range of problems, from cryptography to image recognition. As the field of quantum computing continues to grow, more quantum algorithms are sure to be developed that outperform traditional algorithms.
Implications of Quantum Algorithms
The implications of quantum algorithms are far-reaching. As quantum algorithms become more advanced, they will be able to solve increasingly complex problems in shorter amounts of time. This could have a significant impact on areas such as medicine, finance, and security, where complex problems need to be solved quickly and accurately.
In addition, quantum algorithms could be used to help reduce energy consumption, as they are more efficient than traditional algorithms. This could help reduce the environmental impact of computing and lead to more sustainable solutions. The possibilities of quantum algorithms are endless and are sure to revolutionize the way we approach computing in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
In recent years, quantum algorithms have been shown to be superior to classical algorithms in a number of different areas. Here are the answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about quantum algorithms.
How Many Quantum Algorithms Have Been Shown to Be Superior?
Several quantum algorithms have been developed and shown to be superior in terms of speed and accuracy to their classical counterparts. Examples include the quantum Fourier transform, Grover’s algorithm, the quantum phase estimation algorithm, and the quantum approximate optimization algorithm. These algorithms have been used to solve a variety of problems, from finding the factors of large numbers to searching databases.
In addition to these algorithms, there have been a number of other quantum algorithms that have been developed and tested. These algorithms have all been shown to have some degree of superiority over classical algorithms, although the degree of superiority varies based on the problem being solved. For example, the quantum approximate optimization algorithm has been shown to be exponentially faster than the best classical algorithm for certain types of optimization problems.

In conclusion, the world of quantum computing is still in its infancy, and scientists are only beginning to understand its full potential. However, the impressive strides that have been made so far have shown that quantum algorithms have the potential to outperform classical algorithms in a range of applications. While there is still much to learn about quantum computing and its various algorithms, the future looks bright for this revolutionary technology.
As more research is conducted and more quantum algorithms are developed, we can expect to see even more examples of quantum superiority in action. From cryptography and optimization to machine learning and chemistry, quantum computing has the potential to transform numerous industries and change the way we approach complex problems. With so much promise on the horizon, it’s an exciting time to be a part of the quantum computing revolution.