Computer vision, like many areas of artificial intelligence (AI), has seen exponential growth in recent years. According to data from recruiting platforms, job listings seeking artificial intelligence or computer vision specialists have doubled from 2021 to 2023. This growth presents an exciting time for those involved in AI.
While there is a high demand for computer vision specialists, it’s not just engineers who are driving growth in this sector. Both the business and technical sides require individuals who can contribute to the success of the field.
This article introduces various positions within the realm of computer vision (CV) beyond the traditional roles of computer vision engineers or AI/machine learning/data science specialists.
About us: Viso Suite offers businesses an industry-agnostic, comprehensive solution for addressing business challenges through computer vision infrastructure. This end-to-end platform streamlines application development, deployment, management, and scaling. To learn more about enterprise-grade AI, schedule a demo with our team to explore Viso Suite.
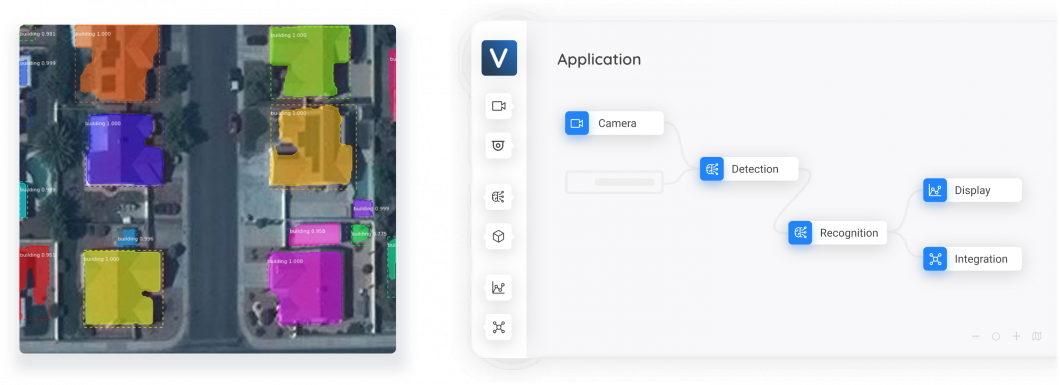
The Current Landscape of Tech Jobs
Computer vision roles are highly technical, requiring specific skills. A computer vision engineer or CV specialist typically needs the following skills:
- A bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as computer science, applied mathematics, electrical engineering, artificial intelligence, or similar.
- Experience with various computer vision techniques like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurring Neural Networks (RNN), transformers, diffusion models, and radionics.
- Familiarity with classical computer vision tools including OpenCV, object detection, image segmentation, and data annotation.
- Proficiency in programming languages like Python or C++, and tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- Hands-on experience with specific image formats (e.g., DICOM) and collaboration with subject-matter experts.
In addition to core computer vision roles, many job listings seek candidates for less technical CV positions. Our analysis will delve into these career opportunities in computer vision that go beyond the traditional roles of CV engineers or AI/ML specialists.
It’s important to note that most of these jobs are concentrated in North America, Western Europe, India, and East Asia, with some positions allowing for remote work.
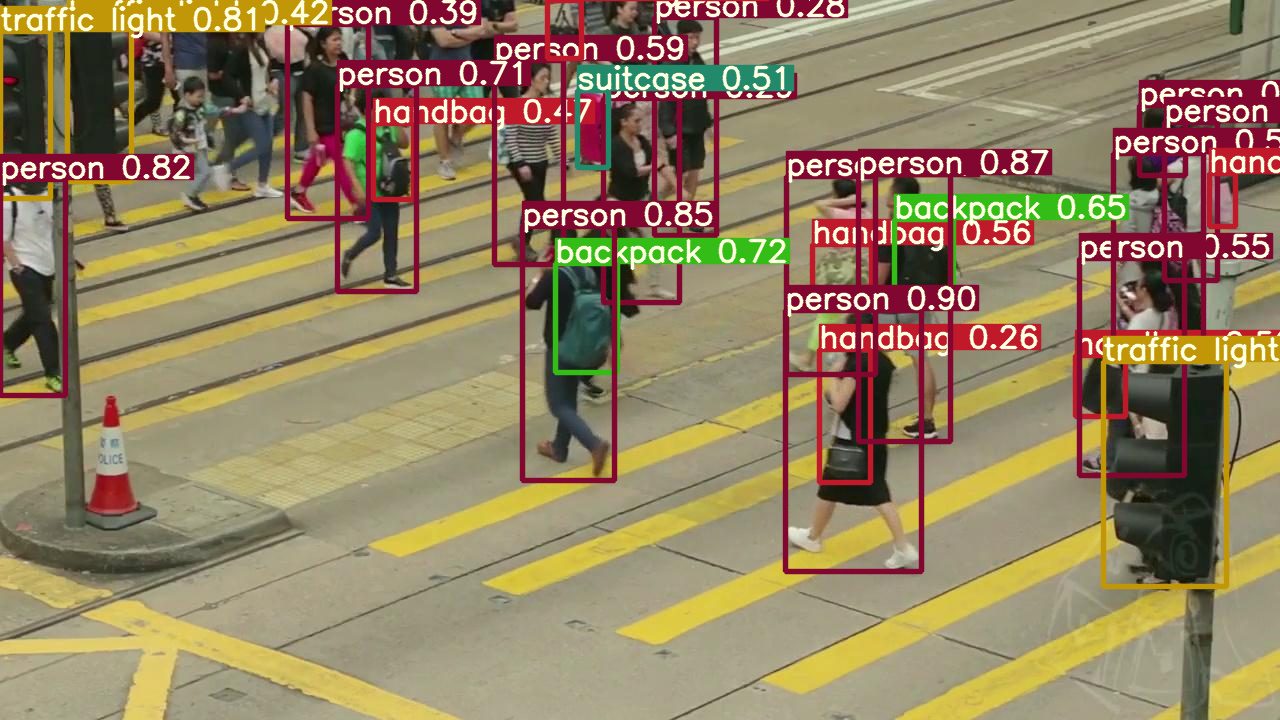

Computer Vision Roles in the Global Market
This section outlines various computer vision jobs that are considered auxiliary roles in the industry but still require specific skills and expertise.
Image Annotation Position
Skills required for this role include:
- Proficiency in using different image annotation tools and software efficiently.
- Collaborating with CV scientists, engineers, and researchers to understand annotation requirements and project objectives.
- Experience in utilizing various annotation tools (e.g., bounding boxes, polygons), software for 2D image annotation, and 3D point cloud annotation.
- Annotating and labeling 2D images and 3D clouds to identify objects of interest, such as cars in traffic or medical conditions in healthcare.
- Verifying and validating annotations to ensure high data quality and reliability.
- Understanding spatial data, 2D and 3D geometry, and coordinate systems.
- Following annotation instructions and specifications to ensure accuracy and consistency across annotated datasets.
- Providing feedback and suggestions to enhance annotation processes and workflows.
- Maintaining records of annotation tasks, including documentation of steps, specifications, and any encountered issues.
- Staying informed about advancements in computer vision and image technology relevant to annotation tasks.
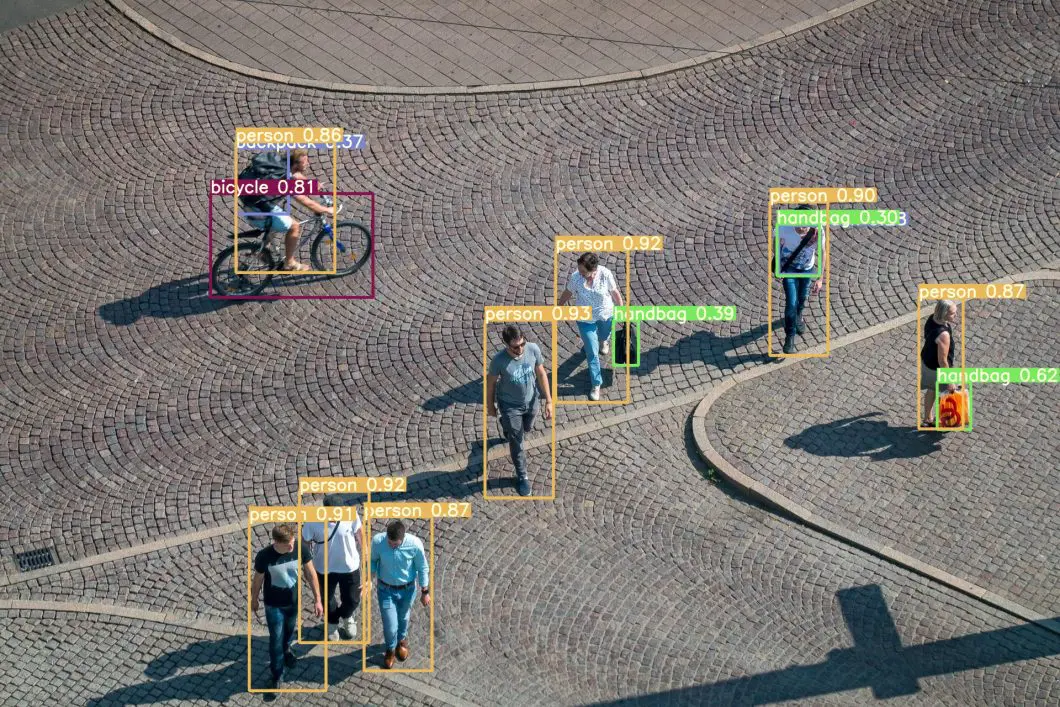
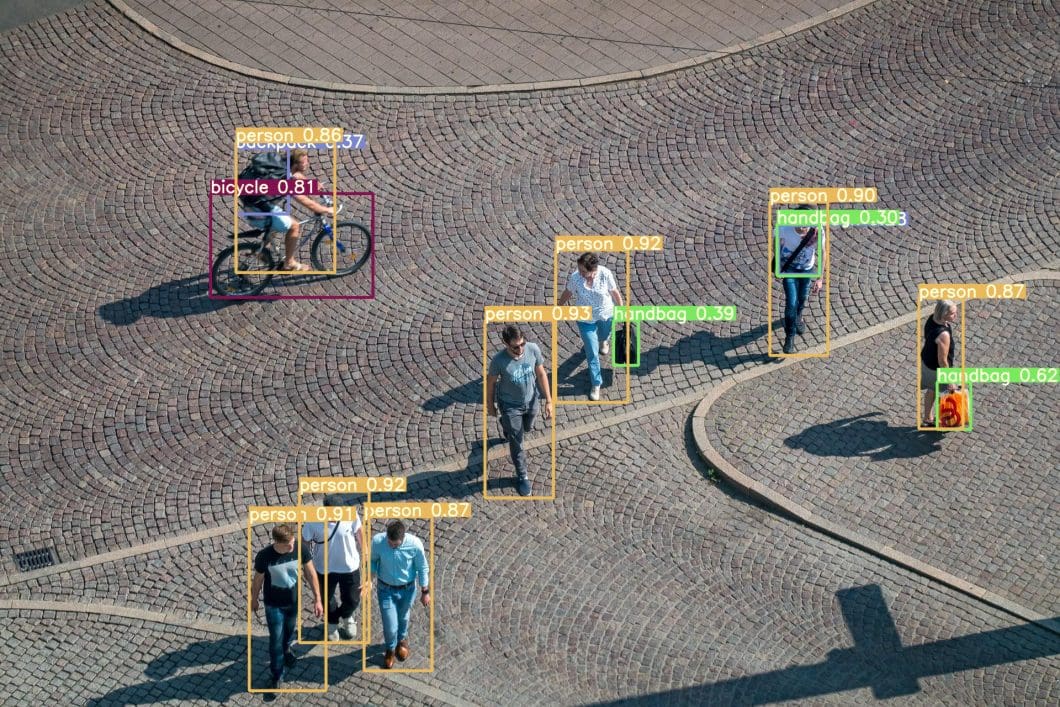
AI / Data Annotation Role
Aside from image annotation, there is data annotation related to AI and machine learning applications, such as in natural language processing (NLP) or retail.
- Providing input examples for training content.
- Supplying training data to machine learning and computer vision engineers to define ground truth data.
- Identifying gaps in training data and proposing enhancements.
- Developing and maintaining annotation guidelines and best practices.
- Completing the labeling process, including updating previously labeled data if definitions or guidelines change.
- Labeling data based on predefined business frameworks.
- Reviewing and annotating data to ensure quality standards and project requirements are met.
- Offering feedback to improve data accuracy and quality for machine learning engineers.
- Understanding how labeling choices impact the final quality of the trained AI model.
- Collaborating internally to optimize model performance based on annotated data.
- Thoroughly reviewing meeting transcripts and related highlights (notes).
- Making informed decisions in ambiguous situations requiring careful analysis.

Image Processing Technician
Image processing technicians perform tasks such as:
- Image acquisition – capturing images with scanners or digital cameras, or importing from external sources.
- Image enhancement – improving visual quality by reducing noise, enhancing contrast, and removing artifacts.
- Image restoration – restoring degraded images by eliminating noise, distortion, and blurring.
- Image segmentation – dividing images into segments representing different objects or features.
- Image description and representation – expressing image features concisely and meaningfully, and representing images for computer analysis and manipulation.
- Image analysis – extracting information from images using mathematical models and algorithms to identify objects, patterns, and features.
 Post navigation
Post navigation



