When it comes to the ever-changing realm of deep learning and computer vision, certain architectures stand out for their simplicity, effectiveness, and scalability. One such influential model is VGG, developed by the Visual Geometry Group at the University of Oxford.
If you are delving into convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or searching for a robust, well-established model for image recognition, understanding VGG is essential.
This post will delve into what VGG is, its architecture, advantages, disadvantages, real-world applications, and frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive view of why VGG continues to shape the field of deep learning.
What is Visual Geometry Group (VGG)?
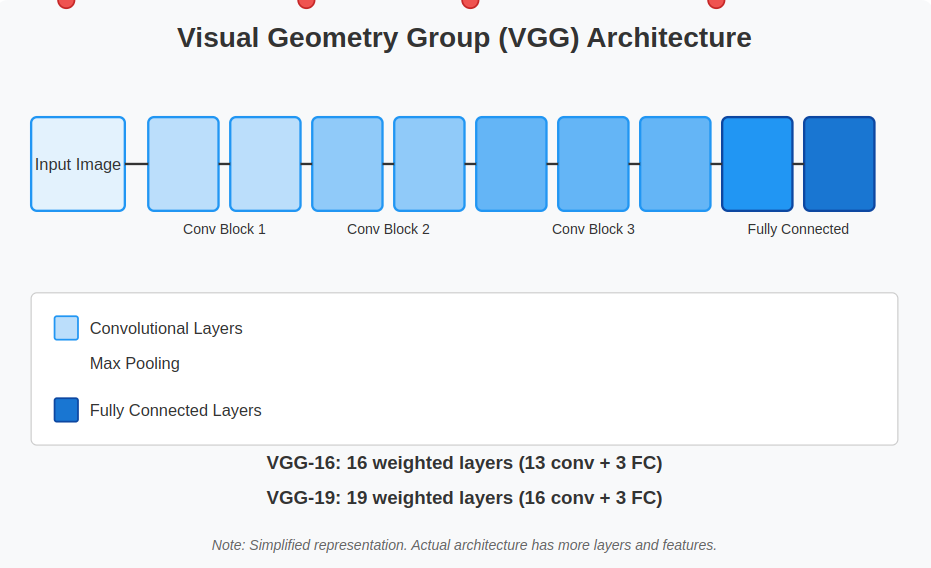
VGG, which stands for Visual Geometry Group, is a widely used deep convolutional neural network architecture known for its numerous layers. The term “deep” signifies the network’s large number of layers, with VGG-16 and VGG-19 consisting of 16 and 19 convolutional layers, respectively.
VGG has played a pivotal role in advancing object recognition models and has outperformed many baseline models across various tasks and datasets, including ImageNet.
Despite its age, VGG remains one of the most popular architectures for image recognition due to its efficiency and structured design.
Why is VGG Important?
VGG’s success stems from its simplicity and effectiveness:
- It utilizes only 3×3 convolutional layers stacked on top of each other.
- It increases depth to enhance accuracy.
- It is highly adaptable to various vision tasks like object detection, segmentation, and style transfer.
Although newer architectures like ResNet and EfficientNet have surpassed VGG in efficiency, VGG remains a foundational model in computer vision education and practice.
VGG Architecture Explained in Detail
The VGG architecture stands out for its elegant simplicity and systematic design. The key concept revolves around using small convolutional filters (3×3) and layering them more deeply to capture intricate features from images.
Let’s break down the structure step by step:



