Testing as a Service (TaaS) can optimize deployment and boost efficiency for dependable Open RAN networks
The race to establish 5G networks has been ongoing for several years, expanding coverage and offering access to advanced services. Initiatives like Open RAN contribute to the development of high-performing, resilient, and flexible mobile infrastructures that benefit consumers, businesses, and the overall economy.
Open RAN provides network-equipment vendors with the flexibility to introduce new products and accelerate progress. By promoting modularity, Open RAN allows both established players and new market entrants — particularly smaller, specialized companies like startups and scale-ups — to take advantage of new business opportunities, cost savings, and flexibility.
Compliance and Compatibility
Open RAN network elements must deliver expected features and performance, including compatibility with equipment from different vendors. However, testing and certifying Open RAN components pose challenges due to the complexity and diversity of the ecosystem. The disaggregated architecture of Open RAN, which interconnects network elements via standardized interfaces while separating hardware from software, necessitates thorough compatibility testing to ensure smooth integration across multi-vendor environments. Key challenges include maintaining consistent performance, managing diverse hardware setups, and adhering to evolving standards.
Vendors must prioritize comprehensive compliance and compatibility testing, robust security measures, and the potential impact of hardware variations on network performance. They must also navigate the evolving certification processes, which require collaboration with industry organizations and adherence to strict regulatory guidelines. Addressing these challenges is essential for network equipment manufacturers to deliver dependable, scalable, and secure Open RAN networks.
The O-RAN Alliance has outlined certification requirements, confirming adherence to specifications, and badging that encompasses interoperability (or end-to-end functionality for a complete O-RAN solution). Testing is conducted at an Open Testing and Integration Center (OTIC) approved by the Alliance.
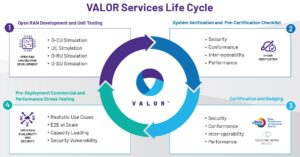
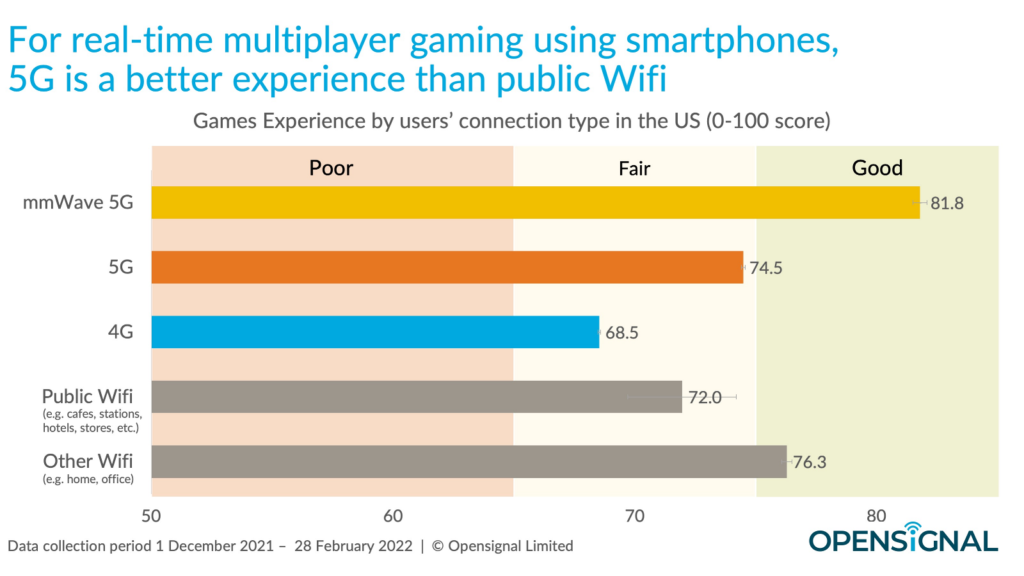
Figure 1. Open RAN equipment testing lifecycle includes development, verification, certification, and stress testing.
Prior to formal compliance testing and at various stages of development, product manufacturers must test their equipment to evaluate performance, interoperability, and security, addressing any vulnerabilities and meeting industry security standards. Additionally, approved equipment must undergo testing in a real-world environment before deployment, including large-scale stress testing. Figure 1 illustrates the testing lifecycle.
Eliminating the Open RAN Testing Gap
Establishing suitable in-house testing, encompassing equipment, facilities, and personnel, can be costly for smaller companies that are a key focus of the Open RAN initiative. Conversely, access to testing services is limited. These factors together create a barrier. The availability and affordability of continuous testing services, crucial during product development, and ultra-high-capacity load and stress testing typically required pre-deployment, are inadequate.
The emergence of hybrid physical and cloud-based Lab-as-a-Service (LaaS) models like VALOR — VIAVI Automated Lab-as-a-Service for Open RAN — is addressing these challenges. The U.S. National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) granted a $21.7 million award from the Public Wireless Supply Chain Innovation Fund (PWSCIF) to establish the test lab. VALOR is an “on-demand” test lab that supports engineers in product development and pre-compliance testing, as well as pre-deployment testing in authentic operational conditions. Services range from cloud-based environments for initial testing to comprehensive multi-cell load and stress testing, which were previously inaccessible to smaller firms.

Figure 2. The VALOR Lab in Chandler, Arizona consists of network equipment and test equipment.
Testing is highly automated and includes a cloud-based lab portal and access to a physical lab in Chandler, Arizona (Figure 2). Physical testing time can be scheduled through an online portal with the hardware shipped in advance. Software testing is cloud-based, completely virtual, and accessible 24/7.
The LaaS model complements existing industry testing labs. VALOR was the first service authorized by the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) for their system performance certification program. By assisting vendors in preparing for certification, badging, and acceptance tests at Open Testing and Integration Centers (OTICs) and approved labs, LaaS alleviates strain on services and accelerates the time-to-market for new products.
Accessible and Cost-Effective
Funded by the NTIA PWSCIF, VALOR will make functional/conformance testing affordable through cloud-based access to VIAVI’s node emulators, such as the multi-user equipment (UE) emulator, O-RU (radio unit), O-DU (distributed unit), O-CU (centralized unit), and Core emulators, enabling testers to conduct functional tests as they advance in product implementation. Figure 3 illustrates the testing process.
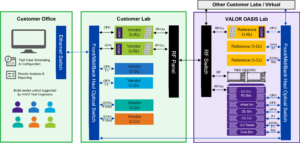
Figure 3. VALOR process for a device under test includes the ability to emulate radio units (O-RU), distributed units (O-DU), and centralized units (O-CU), which form an Open RAN network.
The platform offers an on-demand test suite for managing the complete product lifecycle from functionality to high-capacity stress tests. Test equipment covers compliance and performance testing for radio units (O-RU), distributed units (O-DU), centralized units (O-CU), end-to-end testing, and interoperability testing. The lab utilizes emulated equipment or real reference units in line with test specifications from relevant O-RAN Alliance working groups. Security tests encompass all 3GPP and O-RAN working group specifications and include O-RAN pre-badging as well as extensive vulnerability assessments like denial of service (DoS), fuzzing, open fronthaul (OFH) interface testing, port scanning, and O-CLOUD security. Testing with a large number of emulated user equipment (UEs), under various channel conditions and traffic patterns, is also available.

Figure 4. The VAMOS Dashboard provides access to test functions.
Figure 4 demonstrates how VALOR leverages VIAVI Automation Management and Orchestration System (VAMOS). Integrated with the VIAVI NITRO Wireless portfolio, VAMOS automates test campaigns, cases, and executions within a single cloud-based platform.
Customizable workspaces and configurations streamline the testing process and enhance resource utilization across teams and lab locations. Shared tool testbeds and individual sandboxes cater to various testing requirements, while the platform’s analytics and reporting capabilities optimize test resource utilization and enhance test accuracy.
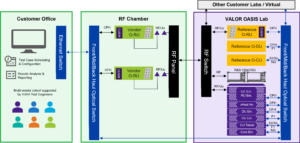
Figure 5. The VALOR OTA testing process includes an RF chamber to isolate radio units from the ambient RF environment.
VALOR offers subsystem testing for compliance, performance, and interoperability. Additionally, end-to-end testing with core emulation and RIC tests covering compliance and performance validation, as well as training of rApps and xApps, are available. The service will eventually feature over 500 test cases compliant with O-RAN WG4 (Working Group 4), WG5, WG11, and TIFG (Test & Integration Focus Group) specifications (refer to O-RAN Alliance specification pages for documentation) as well as 3GPP specifications. Furthermore, a large (25′ x 35′) anechoic chamber from ETS-Lindgren and RF testing equipment from Rohde & Schwarz will be accessible for Massive MIMO and beamforming over-the-air (OTA) performance testing, as depicted in Figure 5.
Enhancing Certification and Deployment Test Success Rates
Open RAN introduces modularity to the mobile radio-access network infrastructure, making the market more inclusive for companies of all sizes. While disaggregation can foster competition and expedite progress, practical hurdles can deter smaller companies from entering the market. Establishing a lab for development, pre-certification, badging, and pre-deployment testing can be costly. Conversely, access to commercial lab services is limited.
Hybrid on-demand Lab-as-a-Service models address these challenges. By combining online and physical services, these models mitigate access barriers and reduce costs while supporting O-RAN Alliance and 3GPP specifications for testing in alignment with relevant industry standards for security, compliance, interoperability, and performance.
Additionally, engineers can take proactive measures to identify and resolve issues even before engaging a professional lab like VALOR. The following outlines six steps that can enhance the likelihood of passing the rigorous certification and deployment tests:
- Conduct Initial Compliance Tests
Validate O-RU, O-DU, and O-CU against baseline specifications, conducting functional tests to ensure basic device operation. - Emphasize Interoperability
Set up small-scale tests to verify basic interoperability between multi-vendor components, such as fronthaul communication between an O-RU and O-DU. Open-source testing tools or emulators can facilitate this process. - Perform Preliminary Security Checks
Scan for common vulnerabilities like port scanning or basic denial-of-service scenarios, validating compliance against foundational O-RAN security requirements. - Conduct Low-Scale Stress Testing
While large-scale simulation may not be feasible, some O-RAN developers can simulate a limited number of user equipment (UEs) to assess system performance under specific traffic loads. Where feasible, experiment with various channel conditions and traffic patterns to identify performance bottlenecks. - Leverage Virtualized Tools
Utilize software-based emulators and simulators to test core functionalities before physical deployment. It is crucial to ensure seamless operation of software components across virtualized environments. - Document Results
Maintain detailed records of testing methodology, results, and configurations used, which will be invaluable during professional lab testing and validation.