AI has completely changed our interaction with technology, with Large Language Models (LLMs) at the forefront of this transformation. These AI models can understand, process, and generate human-like text, playing a crucial role in chatbots, search engines, content creation tools, and virtual assistants.
ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity AI are some of the leading LLMs revolutionizing industries by automating tasks, improving communication, and enhancing user experiences. But what exactly are Large Language Models? How do they function? And what are their limitations?
In this post, we’ll delve into everything you need to know about LLMs, from their structure and applications to the obstacles they encounter and their future in the realm of artificial intelligence.
Understanding LLMs
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI models that can comprehend and generate text similar to human language patterns. These models are trained on vast datasets comprising books, articles, and online content, allowing them to recognize language structures and produce text-based responses.
LLMs leverage deep learning techniques for prediction and text generation, enabling them to adapt to context and handle various linguistic tasks.
Popular LLMs
Some of the commonly used Large Language Models include:
- ChatGPT– A conversational AI model developed by OpenAI.
- Gemini – An advanced LLM designed for multimodal interactions.
- Perplexity AI – A chatbot offering real-time, factual responses.
These models utilize sophisticated AI algorithms to interpret queries, respond to prompts, and generate text that resembles human language.
Explore the top open-source LLMs and discover their features, applications, and significance in AI development.
Operation of Large Language Models
The functioning of large language models involves several steps. These models rely on deep learning techniques, particularly Transformer-based neural networks.
The self-attention mechanism in LLMs evaluates word relationships while generating responses that maintain context accuracy.

Steps in Processing by LLMs:
- Tokenization – Breaking down input text into smaller tokens for processing.
- Training on Extensive Datasets – Learning from large text datasets to enhance language understanding.
- Attention Mechanisms – Determining the significance of each word in a sentence relative to others.
- Text Generation – Generating coherent and contextually relevant text through probability-based predictions.
The Transformer architecture, introduced by Google in 2017, significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of these models, serving as the basis for modern AI-powered language processing.
Architecture of LLMs
The processing and text generation in LLMs are dependent on a complex multi-layer architectural design encompassing various functional components.
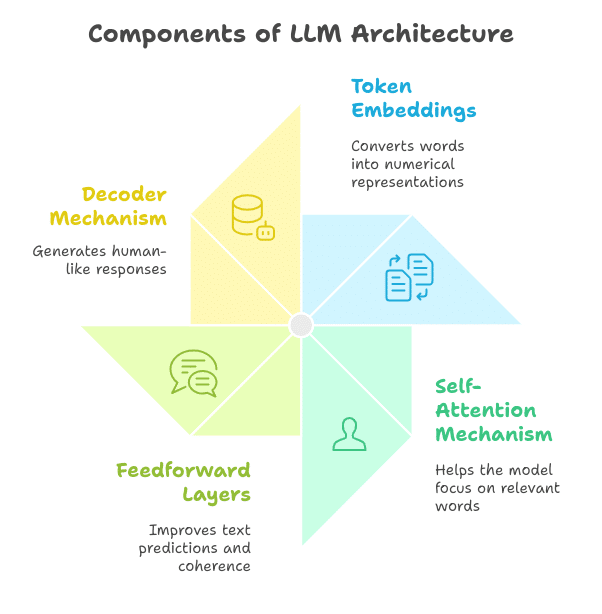
Key Components of LLM Architecture:
✔ Token Embeddings – Converting words into numerical representations for processing by the AI model.
✔ Self-Attention Mechanism – Assisting the model in focusing on the most relevant words in a sentence.
✔ Feedforward Layers – Enhancing text predictions and sentence coherence.
✔ Decoder Mechanism – Generating human-like responses based on context.
This architecture empowers LLMs to produce high-quality text, address complex queries, and even create creative content like poems, essays, and code.
Applications of Large Language Models
Various industries benefit from the diverse enterprise applications of LLMs. These models are impacting critical areas as outlined below.
1. Chatbots & Virtual Assistants
- AI-driven chatbots such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini deliver human-like interactions, aiding in customer service, issue resolution, and general inquiries.
2. Content Generation
- LLMs function as programmed tools for generating blog content, reports, summaries, and social media posts, enhancing the efficiency of writers and businesses.
3. Code Generation & Debugging
- Platforms like GitHub Copilot support programmers by generating code snippets, identifying errors, and boosting productivity.
4. Language Translation & Processing
- Several language models operate in services like Google Translate and DeepL, as well as AI-based transcription tools, improving global communication.
5. Healthcare & Research
- AI models aid in medical diagnosis, drug discovery, and research documentation, assisting doctors and researchers in analyzing vast data sets.
6. Education & E-Learning
- AI tutors and personalized learning assistants offer explanations, create study materials, and support students in understanding complex topics.
7. Creative Writing & Art
- LLMs help authors, poets, and artists in generating ideas, crafting stories, and even producing AI-assisted poetry and artwork.
LLMs are versatile tools that continue to evolve and expand into new domains.
Challenges of LLMs
Despite their benefits, Large Language Models face several challenges:
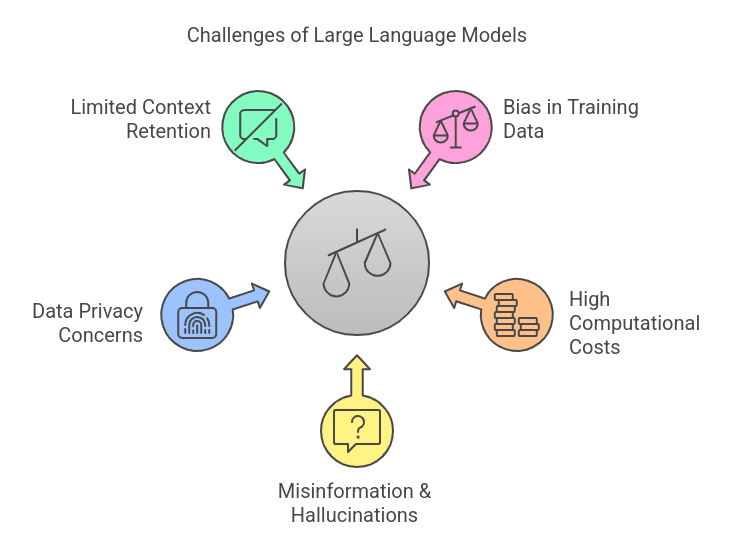
- Bias in Training Data – LLMs may inherit biases from their training data.
- High Computational Costs – Training and running LLMs require significant computing resources, making them costly to maintain.
- Misinformation & Hallucinations – LLMs may generate incorrect or misleading information.
- Data Privacy Concerns – Handling sensitive user data raises ethical and legal issues.
- Limited Context Retention – Some LLMs struggle with maintaining long-term coherence in conversations.
Experts are continuously working to improve these models, enhancing their accuracy, reducing bias, and strengthening security measures.
Learn the best practices for managing and deploying LLMs to optimize performance and scalability in AI applications.
The Future of LLMs in Artificial Intelligence
As artificial intelligence progresses, LLMs will evolve to offer more sophisticated functionalities. Some key future trends include:
- More Efficient Training Methods – Researchers are exploring ways to reduce the energy consumption and cost of training LLMs.
- Better Personalization – Future models will tailor responses to individual users, enhancing user experience.
- Hybrid AI Models – Combining LLMs with other AI technologies for enhanced problem-solving.
- Multimodal AI – Integrating text with images and audio processing capabilities for a comprehensive AI experience.
These advancements will make LLMs smarter, faster, and more ethical, transforming industries and everyday interactions.
Conclusion
Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping artificial intelligence, revolutionizing our interaction with technology. While they pose challenges, ongoing enhancements in AI ethics, efficiency, and personalization will make them even more potent in the future.
Interested in delving deeper into AI and Machine Learning?
Enhance your career with the UT Austin AI & Machine Learning course. Gain comprehensive knowledge of AI, Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning while earning dual certificates from top-tier faculty and industry experts.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can LLMs replace human writers?
No, while LLMs aid in writing, human creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence remain irreplaceable.
2. Do LLMs comprehend language like humans?
Not precisely. LLMs predict words based on statistical patterns but do not truly grasp meaning as humans do.
3. How are LLMs fine-tuned for specific industries?
LLMs can be fine-tuned with industry-specific data for sectors like healthcare, law, and finance.
4. Can LLMs handle multilingual processing?
Yes, numerous LLMs are trained in multiple languages, but their accuracy depends on the available data for each language.
5. What ethical concerns are associated with LLMs?
Bias, misinformation, and job displacement are key concerns, prompting the development of more responsible AI systems.



