When it comes to machine learning, data is the key fuel in driving progress. But what happens when you have limited labeled data and a vast amount of unlabeled data at your disposal? This is where Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) steps in.
Semi-Supervised Learning strikes a balance between supervised and unsupervised learning, enabling models to make accurate predictions while minimizing the cost of data labeling.
In this post, we will delve into the concept of semi-supervised learning, its significance, how it operates, real-world applications, and the challenges associated with working with it.
What Is Semi-Supervised Learning?
Semi-Supervised Learning is a machine learning technique that utilizes a small set of labeled data along with a large pool of unlabeled data for model training. Unlike supervised learning that relies solely on labeled datasets and unsupervised learning that doesn’t use labels at all, semi-supervised learning finds a middle ground.
Why is this important?
Labeling data can be costly, time-consuming, and often requires expertise in the domain. Conversely, gathering raw, unlabeled data is relatively easier. Semi-supervised learning bridges this gap, enabling us to maximize model performance with minimal labeled data.
Also Read: What is Data Collection?
How Does Semi-Supervised Learning Work?
The typical process of semi-supervised learning involves the following steps:
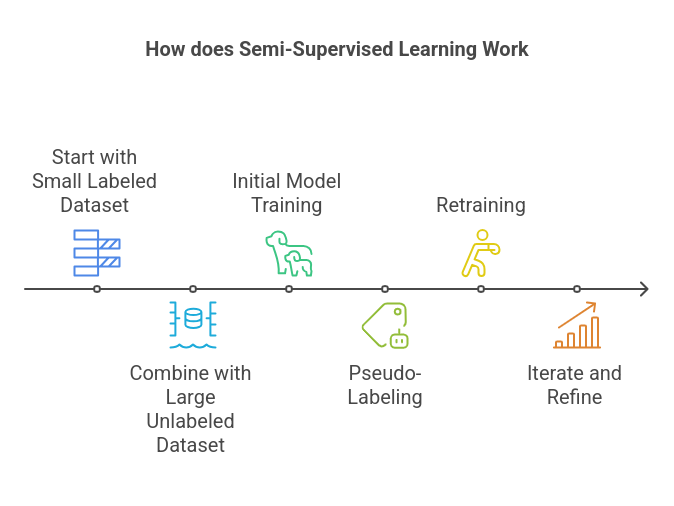
- Start with a small labeled dataset: These are your “ground truths” from which the model can learn directly.
- Combine with a large unlabeled dataset: These are the data points you have but without labels.
- Initial model training: The model is trained on the labeled data.
- Pseudo-labeling: The trained model predicts labels for the unlabeled data.
- Retraining: The model is retrained using both the original labeled data and the pseudo-labeled data.
- Iterate and refine: This loop continues until performance stabilizes or reaches a desired level.
This approach leverages the model’s ability to generalize from a small, high-quality labeled dataset and scale its learning with abundant unlabeled data.
Why Use Semi-Supervised Learning?
Here are some key reasons why semi-supervised learning has gained attention:
- Reduced labeling costs: You don’t need massive labeled datasets.
- Improved model accuracy: When labeled data is scarce, SSL often outperforms purely supervised models.
- Scalability: With so much unlabeled data being generated daily, SSL provides a practical way to put that data to use.
- Works well with natural datasets: SSL is highly effective for text, images, speech, and other real-world data formats.



