As technology continues to advance, so does the demand for faster and more efficient computing. One of the most significant developments in recent years has been the emergence of edge computing. This innovative approach to computing allows data processing to take place closer to the source, reducing latency and improving overall performance. But what factors have made edge computing cheaper and easier to implement?
The answer lies in a combination of technological advancements and changing business needs. As more and more devices become connected, the demand for real-time data processing has increased exponentially. This, combined with the rise of cloud computing and the need for more efficient data management, has led to the development of edge computing solutions that are both more affordable and easier to implement. In this article, we will explore some of the key factors that have contributed to the rise of edge computing and the benefits it offers for businesses of all sizes.
The three main factors driving the growth of edge computing are cost reduction, faster data processing, and improved security. Cost reduction has been achieved through cloud computing, which enables companies to pay only for the resources they need. Faster data processing is possible because data can be processed closer to where it originates, reducing latency. Improved security is achieved through the use of encryption and authentication technologies.

Edge Computing: The Emerging Technology Revolutionizing the Way We Work
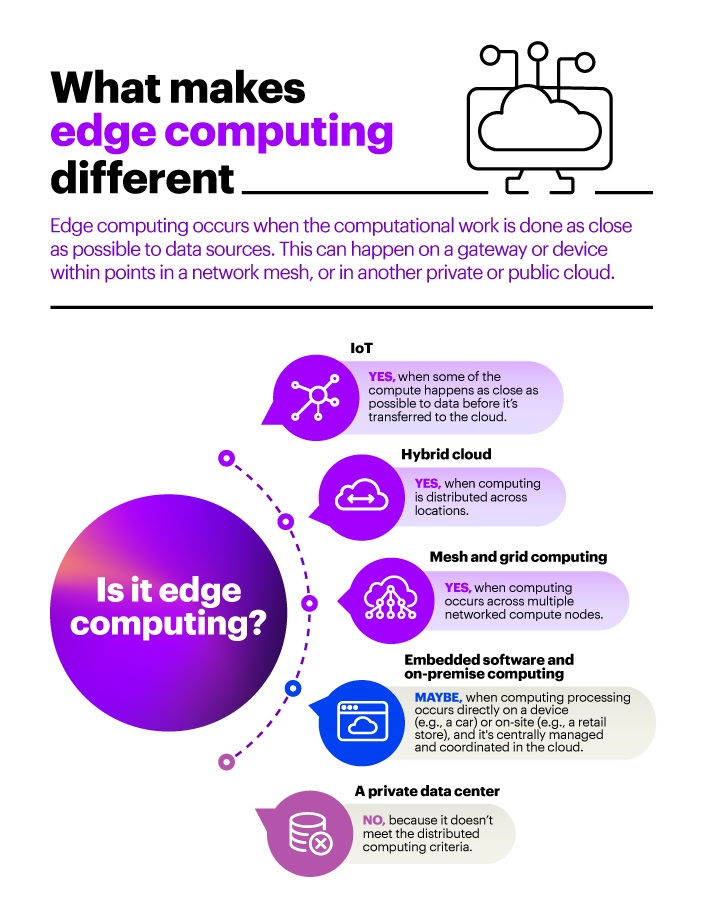
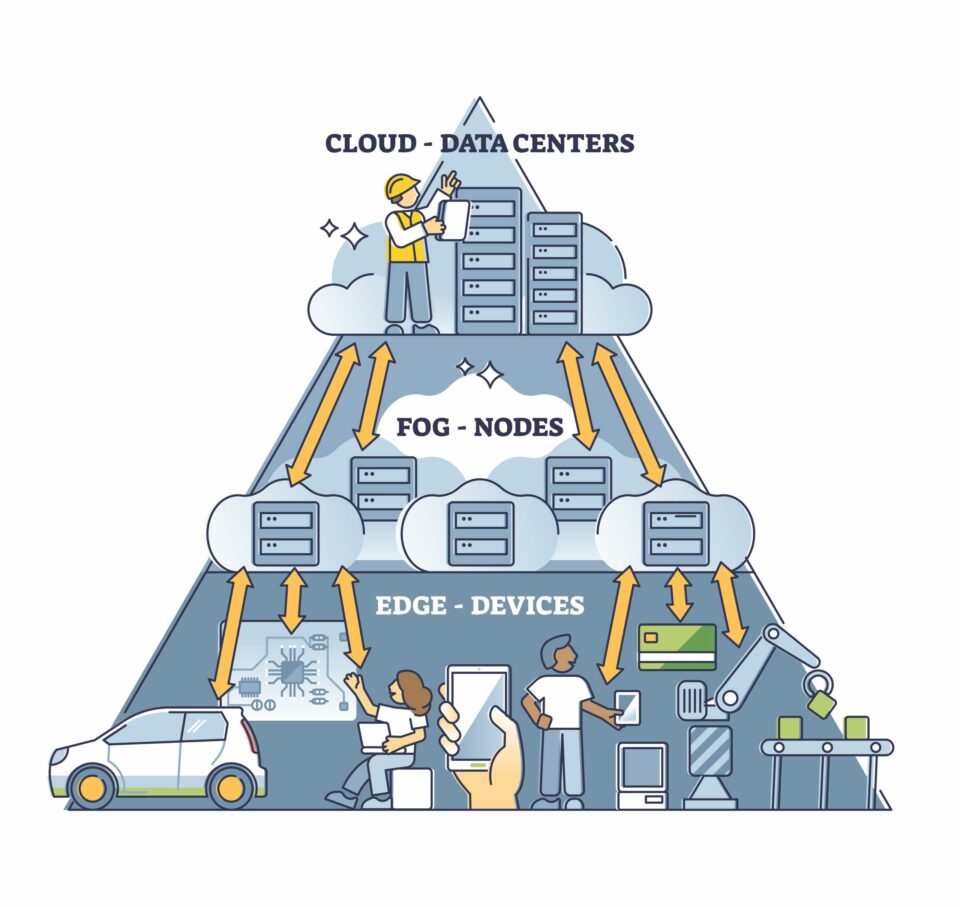
Edge computing is an emerging technology that is revolutionizing the way we work. It involves the processing of data at the edge of the network, as opposed to in centralized data centers. This type of computing is becoming increasingly popular due to its ability to provide real-time, low-latency data processing, as well as its cost-effectiveness and scalability. In this article, we will explore the factors that have made edge computing cheaper and easier.
Faster Data Processing
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is its ability to process data much faster than traditional methods. By performing the data processing at the edge of the network, instead of in centralized data centers, edge computing drastically reduces the latency associated with data transmission. This means that data can be processed in real-time, rather than having to wait for it to be sent to a central data center. This is especially beneficial for applications that require fast response times, such as self-driving cars and drones.
Another benefit of edge computing is its scalability. By performing the data processing at the edge of the network, it can easily scale up or down as needed, depending on the demands of the application. This makes it much more cost-effective than traditional data centers, which require expensive hardware and software upgrades in order to scale up.
Reduced Costs
Edge computing also offers significant cost savings. By eliminating the need for expensive infrastructure, such as data centers, edge computing can drastically reduce costs. Additionally, since edge computing uses less power than traditional methods, it also reduces energy costs.
In addition to reducing infrastructure costs, edge computing also eliminates the need for expensive software licenses. By running the processing at the edge of the network, it eliminates the need for costly licenses, which can add up quickly. This makes edge computing a much more cost-effective option for businesses.
Edge computing also eliminates the need for expensive hardware. By processing the data at the edge of the network, it eliminates the need for expensive servers and other hardware, which can be costly to maintain. This makes edge computing a much more affordable option for businesses.
Increased Security
Edge computing also provides increased security. By performing the processing at the edge of the network, it eliminates the need for data to be transmitted over long distances, which can be vulnerable to attack. Additionally, since the data is processed locally, it is much more secure than traditional methods. This makes edge computing a much more secure option for businesses.
Finally, edge computing is also much easier to deploy and maintain than traditional methods. By running the processing at the edge of the network, businesses can quickly and easily deploy the technology, without having to worry about managing a large, complex data center. This makes edge computing a much more attractive option for businesses.
In conclusion, edge computing is revolutionizing the way we work and is becoming increasingly popular due to its ability to provide real-time, low-latency data processing, as well as its cost-effectiveness and scalability. By reducing the need for expensive infrastructure, software licenses, and hardware, edge computing has made the technology much cheaper and easier to deploy. Additionally, edge computing provides increased security, making it a much more secure option for businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
Edge computing is a method of decentralizing computing power and data storage closer to the devices and people that need it. This has helped to make edge computing much cheaper and easier to use than before.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that enables data processing and storage closer to the device or user that needs it. This helps to reduce latency and increase reliability. Edge computing can be used for a variety of applications, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI).
Edge computing is different from traditional cloud computing, as it does not rely on a centralized server or data center. Instead, data and processing power is distributed across a network of devices, which are located close to the user or device that needs it. This helps to reduce network latency, improve reliability, and make edge computing much cheaper and easier to use.
What Are the Benefits of Edge Computing?
Edge computing offers a number of benefits over traditional cloud computing. Firstly, edge computing can reduce latency, as data and processing power is located closer to the device or user that needs it. This can help to improve the user experience and make applications more responsive. Secondly, edge computing can be more reliable, as distributed data and processing power can be used to ensure that applications and services remain available even if some parts of the network fail. Thirdly, edge computing can be much cheaper than traditional cloud computing, as it does not require expensive infrastructure and hardware to maintain.
What Factors Have Made Edge Computing Cheaper and Easier?
There are a number of factors that have made edge computing much cheaper and easier to use than before. Firstly, advances in technology have made it easier to deploy edge computing solutions. This includes the development of low-power hardware, such as microcontrollers, which can be used to power edge computing devices. Secondly, the rise of cloud computing and the increasing availability of high-speed internet have made it easier to transfer data between devices. Finally, the emergence of open source software and development platforms has made it easier for developers to develop and deploy edge computing applications.
What Are Some Examples of Edge Computing Applications?
Edge computing can be used for a variety of applications, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI). For example, edge computing can be used to power IoT devices, such as smart home appliances, which can be connected to the internet and used to monitor and control them remotely. Edge computing can also be used to power cloud computing applications, such as streaming services and online gaming. Finally, edge computing can be used to power AI applications, such as facial recognition and natural language processing.
What Are the Challenges of Edge Computing?
Although edge computing offers many benefits, there are also some challenges that need to be addressed. Firstly, edge computing can be more complex to deploy and manage than traditional cloud computing, as it requires a distributed network of devices. Secondly, edge computing can be more vulnerable to security threats, as the data is stored and processed on a distributed network of devices. Finally, edge computing requires more robust networks, as data and processing power needs to be transferred between devices in real-time.
In conclusion, the advent of edge computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate in the digital age. The emergence of cheaper and more accessible hardware components, coupled with the increasing availability of cloud-based services and software, has made edge computing more cost-effective and easier to implement. Additionally, the growing demand for real-time data processing and the need to reduce network latency has further driven the adoption of edge computing technology.
Furthermore, the advancements in edge computing have paved the way for new applications and use cases, from autonomous vehicles and smart cities to industrial automation and healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more innovations and breakthroughs in the future. With the increasing focus on data privacy and security, edge computing may also provide a more secure and decentralized alternative to traditional cloud-based solutions. Overall, the future of edge computing looks promising, and it is an exciting time for businesses and individuals alike to explore the possibilities of this transformative technology.