In today’s world, sustainability is a primary concern for many individuals and organizations. As we strive to reduce our carbon footprint and preserve the environment, we must also look to innovative technologies that can help us achieve our goals. One such technology is edge computing, which has the potential to significantly improve sustainability efforts across various industries.
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, rather than sending it to a centralized data center. This approach reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over long distances, thus minimizing energy consumption and carbon emissions. Additionally, edge computing can enable real-time monitoring and management of energy usage, allowing for more efficient and sustainable operations. In this article, we will explore how edge computing can be used to enhance sustainability in various industries and highlight some real-world examples of its successful implementation.

How Edge Computing Can Improve Sustainability
Edge computing is an emerging technology that has potential to reduce strain on the environment by cutting down on the amount of energy used by data centers. By utilizing edge computing, data can be processed closer to the source, reducing the need for energy-intensive cloud computing and reducing the environmental impact of data processing. In this article, we’ll explore how edge computing can be used to improve sustainability.
Reducing Data Center Energy Use
The biggest environmental benefit of edge computing is that it reduces the need for energy-intensive data centers. Edge computing moves processing closer to the source, allowing for data to be processed without the need for cloud computing. By reducing the need for expensive and energy-hungry data centers, edge computing can dramatically reduce the amount of energy used to process data. Additionally, by reducing the need for data centers, edge computing can reduce the amount of physical space needed for data storage, thus freeing up land for other purposes.
Another way that edge computing can reduce data center energy use is by allowing for better power management. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the need for energy-intensive cooling systems, as well as allowing for more efficient power management, such as powering down non-essential systems when not in use. This can help reduce the overall energy consumption of data centers.
Increasing Efficiency
Edge computing can also increase efficiency by allowing for more efficient data processing. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing can reduce the amount of time needed to process data, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to process the data. Additionally, edge computing can also reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be processed, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to process the data.
Edge computing can also be used to increase the efficiency of machine learning and artificial intelligence, as well as other data-intensive applications. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to process the data. Additionally, edge computing can also reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be processed, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to process the data.
Reducing Network Energy Use
Edge computing can also reduce the amount of energy needed to send data over networks. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to send the data. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be sent over the network, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to send the data.
Edge computing can also be used to reduce the amount of energy needed for data transmission over wireless networks. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent over the wireless network, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to transmit the data. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be sent over the wireless network, thus reducing the amount of energy needed to transmit the data.
Reducing Waste
Edge computing can also be used to reduce the amount of waste produced by data processing. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored, thus reducing the amount of physical space needed for data storage. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be stored, thus reducing the amount of physical space needed for data storage.
Edge computing can also be used to reduce the amount of waste generated by data centers. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of energy needed to process the data, thus reducing the amount of waste generated by data centers. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be processed, thus reducing the amount of waste generated by data centers.
Improving Security
Edge computing can also be used to improve the security of data processing. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network, thus reducing the risk of data being intercepted or stolen. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be sent over the network, thus reducing the risk of data being intercepted or stolen.
Edge computing can also be used to improve the security of data storage. By processing data locally, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored, thus reducing the risk of data being accessed without authorization. Additionally, edge computing can reduce the amount of redundant data that needs to be stored, thus reducing the risk of data being accessed without authorization.
Conclusion
Edge computing has the potential to improve sustainability in a variety of ways, from reducing data center energy use to increasing efficiency and reducing waste. Edge computing can also improve the security of data processing and storage, making it a valuable tool for organizations looking to reduce their environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
Edge computing is a technology that can be used to improve sustainability, by reducing energy and data usage and improving efficiency. Here, we answer some of the most common questions about how edge computing can be used for sustainability.
What is Edge Computing?
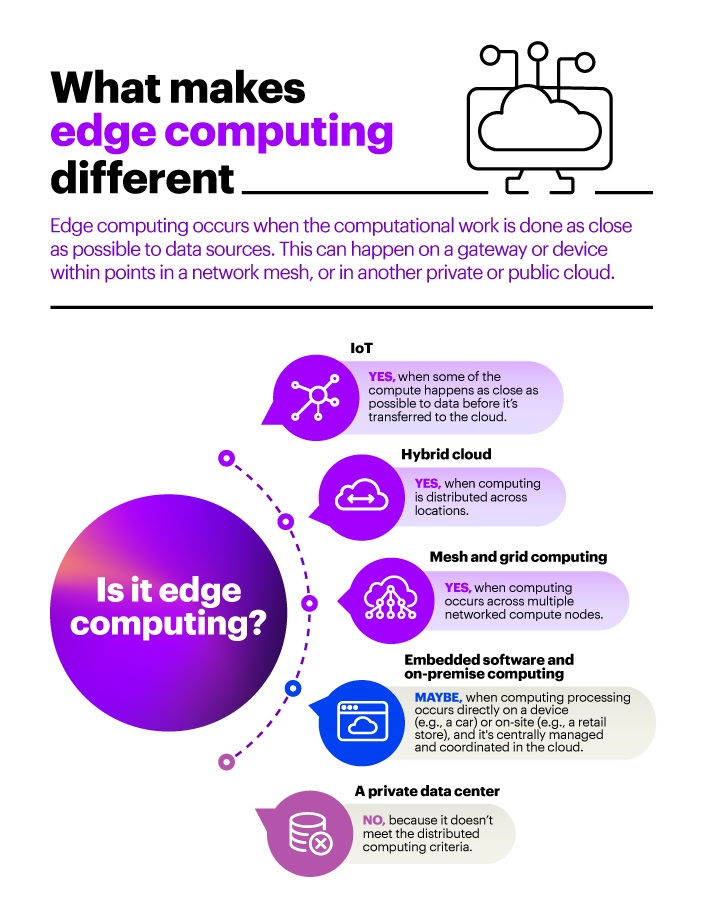
Edge computing is a type of computing that processes data closer to where it is collected or used, rather than sending it to a centralised data centre or cloud. Edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred, leading to fewer energy costs and faster response times. Edge computing also helps reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored, as it can be processed on-site, eliminating the need for centralised storage.
How Can Edge Computing Improve Sustainability?
Edge computing can improve sustainability by reducing energy consumption and data usage. By processing data closer to where it is generated, fewer resources are needed to transfer data to and from a centralised server. This can reduce energy consumption, as data does not need to be transferred over long distances. Additionally, edge computing can reduce data usage by eliminating the need for centralised storage, as data can be processed on-site. This can help reduce the number of servers needed and the amount of resources required to store data.
What Are the Benefits of Edge Computing?
Edge computing can provide a number of benefits for sustainability, including improved efficiency and lower energy costs. By processing data on-site, edge computing can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred, leading to fewer energy costs and faster response times. Additionally, edge computing can help reduce the amount of data that needs to be stored, as it can be processed on-site, eliminating the need for centralised storage.
What Are the Challenges of Edge Computing?
Edge computing can present a number of challenges for sustainability, such as security concerns, scalability issues, and a lack of standardised protocols. Additionally, edge computing can be more expensive than traditional cloud computing, as it requires additional hardware and software to be deployed. Furthermore, edge computing can be difficult to manage, as it requires dedicated resources and personnel to install, configure, and maintain the system.
What Are the Potential Uses of Edge Computing?
Edge computing can be used for a variety of applications related to sustainability, such as data analysis, energy efficiency, and smart buildings. Edge computing can be used to analyse data in real-time to make decisions about energy usage and resource management. Additionally, edge computing can be used to improve the efficiency of smart buildings by processing data on-site, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred over long distances. Finally, edge computing can be used to improve the accuracy of sensor-based systems, as data can be analysed and processed in real-time.
In conclusion, edge computing has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach sustainability. With the ability to process data closer to the source, edge computing can reduce the energy consumption and carbon footprint of large centralized data centers. Additionally, it can enable real-time monitoring and control of energy usage, allowing for more efficient and sustainable operations.
As we continue to face the pressing issue of climate change, it is crucial that we explore innovative solutions to reduce our impact on the environment. Edge computing represents a promising avenue for achieving this goal, by allowing us to harness the power of technology in a more sustainable way. By leveraging the benefits of edge computing, we can work towards a more sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.