The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was introduced in 2018 to protect the personal data of EU citizens and ensure that companies and organizations handling this data are compliant with the law. GDPR is a complex and far-reaching policy, and failure to comply can have serious implications.
In this article, we will look at the implications of not complying with GDPR. We will discuss the penalties that can be imposed, the potential financial and reputational damage, and the potential legal liabilities that companies and organizations may face if they fail to comply with GDPR. We will also look at the steps companies and organizations can take to ensure they are compliant with the GDPR.
Not complying with GDPR can have severe implications. Fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s annual global turnover, whichever is higher. Companies can also face reputational damage, costly legal action and penalties. Moreover, companies are also required to inform the public of any data breaches and to notify the supervisory authority within 72 hours.

What is GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU-wide regulation that sets out rules and regulations for how companies handle and process personal data. The GDPR was introduced in May 2018 and applies to all companies operating in the European Union. It sets out specific requirements for how companies must collect, store and process personal data, as well as how they must ensure that data is kept secure.
Under the GDPR, companies must obtain a person’s explicit consent before collecting any personal data. Personal data includes any information that could be used to identify an individual, such as a name, address, email address, or IP address. Companies must also provide individuals with the right to access and delete their data, as well as the right to object to their data being used for certain purposes.
What are the Implications of Not Complying with GDPR?
Financial Penalties
The most serious consequence of GDPR non-compliance is a financial penalty. According to the GDPR, companies can be fined up to 4% of their annual global turnover, or €20 million, whichever is higher. Companies can be fined for a variety of GDPR violations, including not having proper consent for collecting personal data, not having adequate security measures in place to protect data, or not providing people with the right to access and delete their data.
Fines are determined on a case-by-case basis and can be significantly higher than the maximum amount stated in the GDPR. For example, in 2019, British Airways was fined £183 million for a data breach that exposed the personal data of nearly 500,000 customers.
Damage to Reputation
In addition to financial penalties, GDPR non-compliance can also lead to reputational damage. When companies fail to comply with the GDPR, it can create a negative perception of the company in the eyes of the public. This can lead to customers and potential customers being less likely to trust the company, which can result in a decrease in sales and an overall decrease in brand loyalty.
Reputational damage can also be caused by data breaches, which can occur as a result of GDPR non-compliance. When a data breach occurs, companies risk losing the trust of their customers and potential customers, and their reputation can be damaged. This can have serious long-term consequences for a company.
Legal Action
Another consequence of GDPR non-compliance is the possibility of legal action. Individuals who believe that their personal data has been misused or mishandled can take legal action against the company. This could involve filing a civil lawsuit or a complaint to the relevant data protection authority. The individual could seek damages as a result of the GDPR violation, which could be costly for the company.
Legal action can also be taken by the relevant data protection authority. Data protection authorities can investigate companies for GDPR violations and can take action against them, including issuing fines and ordering them to take specific steps to remedy the situation.
Frequently Asked Questions About GDPR Compliance
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a legal framework set by the European Union to protect the personal data of individuals within the EU. It is important for companies to comply with GDPR in order to protect their customers’ data and to avoid costly fines.
What is GDPR and why is it important?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a legal framework set by the European Union to protect the personal data of individuals within the EU. GDPR applies to any company that collects, processes, or stores personal data of EU citizens, regardless of the company’s physical location. Compliance with GDPR is important to ensure that companies are protecting the personal data of their customers, as well as to avoid costly fines for non-compliance.
What are the implications of not complying with GDPR?
The most serious consequence of not complying with GDPR is the risk of monetary fines. Companies that are found to be in violation of GDPR can be fined up to 4% of their annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is greater. Additionally, non-compliant companies may also face reputational damage, as well as potential legal action by individuals whose data has been mishandled.
What are the requirements to comply with GDPR?
The requirements of GDPR are broad and can vary depending on the type and amount of data a company collects. In general, companies must ensure that they have appropriate technical and organizational measures in place to protect the personal data of their customers. This includes implementing processes such as data minimization, data access control, data encryption, and data deletion.
How long do companies have to comply with GDPR?
Companies had until May 25, 2018 to become compliant with GDPR. Since then, companies have been expected to comply with GDPR’s regulations, and the EU has been actively monitoring for non-compliance.
What are the penalties for non-compliance?
Companies found to be in violation of GDPR can face steep fines. The maximum fine for non-compliance is up to 4% of a company’s annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is greater. In addition to monetary fines, companies may also face reputational damage and potential legal action by individuals whose data has been mishandled.
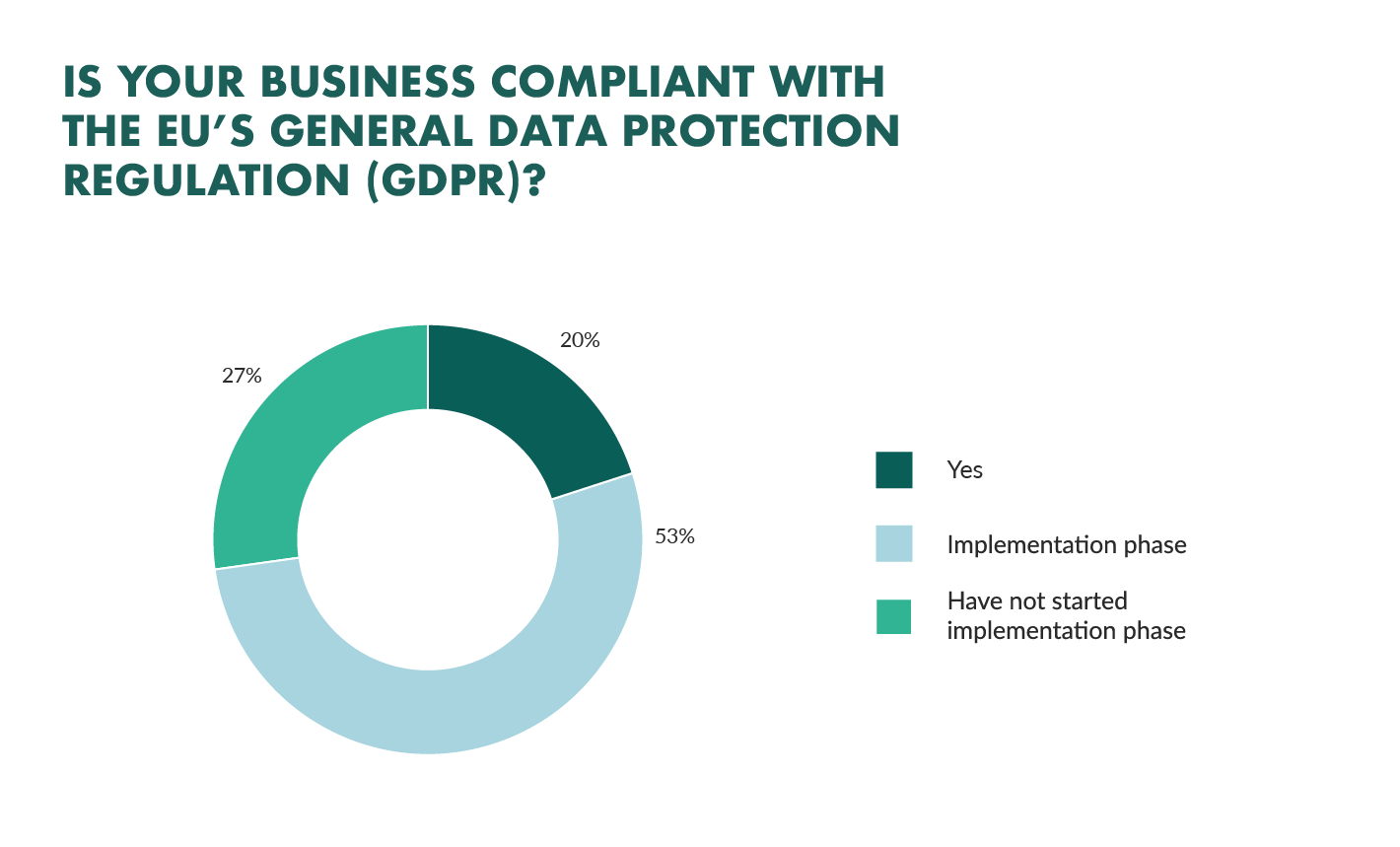
The implications of not complying with GDPR can be far reaching and serious. Companies who fail to comply can face hefty fines and a damaged reputation. Those companies who don’t comply may find that they are exposed to a greater risk of data breaches and can suffer a loss of trust from their customers. The financial repercussions of not adhering to GDPR can be substantial, and the reputational damage can be irreparable.
Overall, the importance of adhering to GDPR regulations should not be underestimated. Companies should take the time to understand the requirements and take the necessary steps to ensure their compliance. By doing so, companies can ensure that they are compliant and protect their customers, their data, and their reputation.