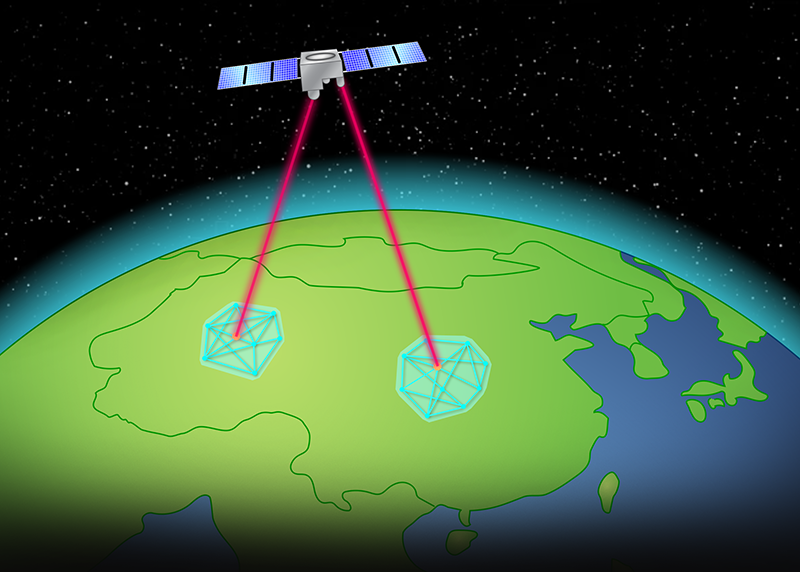
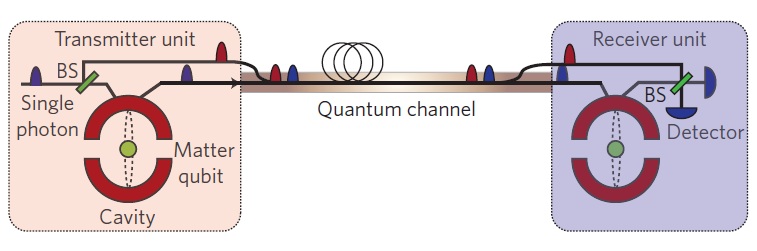
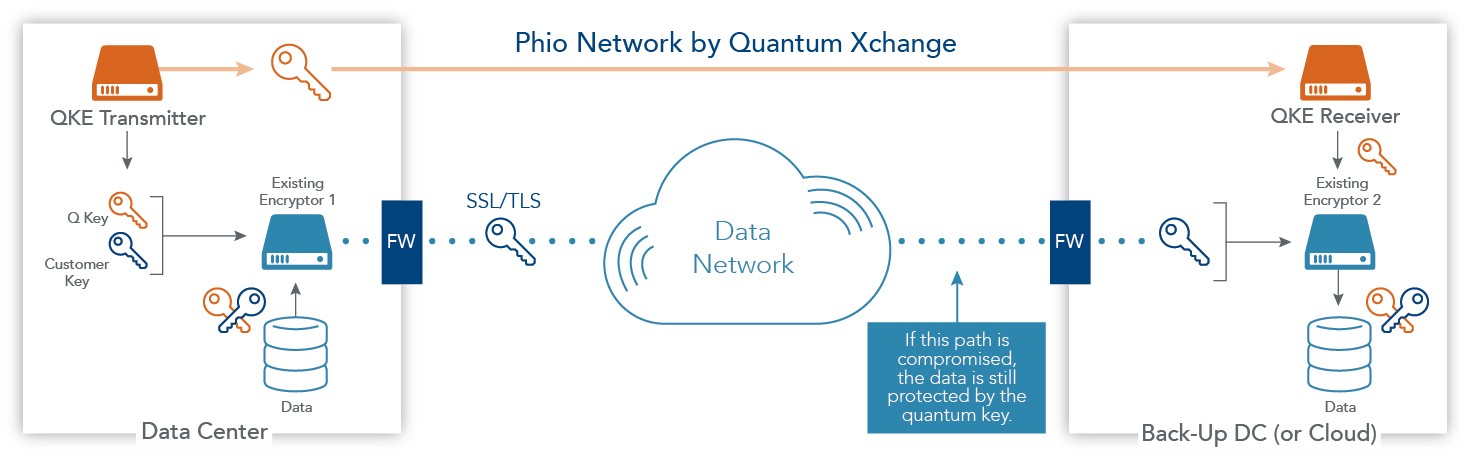
Quantum communication is a revolutionary technology that promises to transform the way we communicate and share information. It is a branch of science that deals with the transfer of information using the principles of quantum mechanics. Unlike classical communication, which is based on the exchange of bits, quantum communication is based on the exchange of qubits. Qubits are quantum bits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously, making them much more powerful than classical bits.
The concept of quantum communication is fascinating, and its potential applications are vast. It offers a level of security that is impossible to achieve using classical communication methods. Even the most advanced encryption techniques can be broken with enough computing power, but quantum communication uses the laws of physics to ensure that any attempted interception is immediately detected. In this article, we will explore the basics of how quantum communication works and the potential impact it could have on our future.
Quantum communication works by exchanging information encoded in the form of quantum particles. It relies on the transmission of single photons, or particles of light, over fiber-optic networks. These particles travel through a vacuum, allowing for the secure transmission of data. By using quantum entanglement, two particles can be linked together, so that any changes in the state of one particle will result in an immediate change in the state of the other particle.
What is Quantum Communication?
Quantum communication is a form of communication which utilizes the properties of quantum mechanics to transmit information from one point to another. It is based on the principles of quantum entanglement, allowing for a secure transmission of data across large distances. It is also referred to as quantum cryptography, as it is used to protect the privacy of data during transmission.
Quantum communication has the potential to transform the way we communicate and exchange data. It is considered to be one of the most secure forms of data transmission, as it is practically impossible to intercept or decipher the data being transmitted.
How Does Quantum Communication Work?
Quantum communication relies on the principles of quantum entanglement. This principle states that two particles can become entangled and share the same state, regardless of the distance between them. This means that if the state of one particle is changed, the other particle will also change its state. This allows for the transmission of data through a quantum channel, which is virtually impossible to intercept.
To send data, two particles are entangled and the data is encoded onto one of the particles. The encoded particle is then sent from one point to another. When the particle arrives at its destination, the receiver can measure the state of the particle and obtain the encoded data. Since the particles are entangled, the receiver can be certain that the data has not been tampered with during transmission.
Advantages of Quantum Communication
Quantum communication has numerous advantages over traditional forms of communication. Firstly, it is much more secure than traditional communication methods. As the data is encoded onto entangled particles, it is virtually impossible to intercept or decipher the data. This makes it ideal for secure communication applications, such as military and government communications.
Secondly, quantum communication is much faster than traditional methods. This is because the data is transmitted through a quantum channel, which does not suffer from noise or interference. This means that the data can be transferred much faster than traditional communication methods. Finally, quantum communication is much more efficient than traditional methods, as it requires less energy to transmit the data. This makes it ideal for applications where energy efficiency is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Quantum Communication Works
Quantum communication is a type of communication that uses the properties of quantum mechanics to send data. It makes use of the unique properties of quantum particles to securely transmit data over long distances. Here are some frequently asked questions about how quantum communication works.
What is Quantum Communication?
Quantum communication is a field of quantum mechanics that uses the properties of quantum particles to send data over long distances. Quantum communication works by encoding information into the quantum states of particles and then transmitting them over a communication channel. The particles carry the information, which can be decoded at the other end to reconstruct the original data. This process is secure because any interference with the particles will cause them to change their quantum state, alerting the receiver that the data has been compromised.
How Does Quantum Communication Work?
Quantum communication works by encoding information into the quantum states of particles and transmitting them over a communication channel. The sender encodes the information into the quantum state of the particles and then sends them over the channel. At the receiver’s end, the particles are decoded to reconstruct the original data. This process is secure since any interference with the particles will cause them to change their quantum state, alerting the receiver that the data has been compromised.
What Are the Benefits of Quantum Communication?
The main benefit of quantum communication is its security. Because any interference with the particles will cause them to change their quantum state, it is practically impossible to access the data without the receiver’s knowledge. This makes it ideal for secure communication applications such as banking, military, and government. Additionally, quantum communication allows for faster data transmission than traditional methods, which is beneficial for applications like video conferencing and streaming services.
What Are the Limitations of Quantum Communication?
The main limitation of quantum communication is its distance. Currently, quantum communication can only be used for distances up to a few hundred kilometers. In addition, quantum communication is sensitive to noise and other environmental factors, which can affect the accuracy of the data. Finally, quantum communication requires specialized equipment, which can be expensive.
What Are Some Examples of Quantum Communication?
Quantum communication is being used in a variety of applications. For example, quantum key distribution (QKD) is being used to securely transmit information over long distances. Additionally, quantum teleportation is being used to transport quantum information from one place to another. Finally, quantum communication is being used in the banking sector to securely transmit financial data.
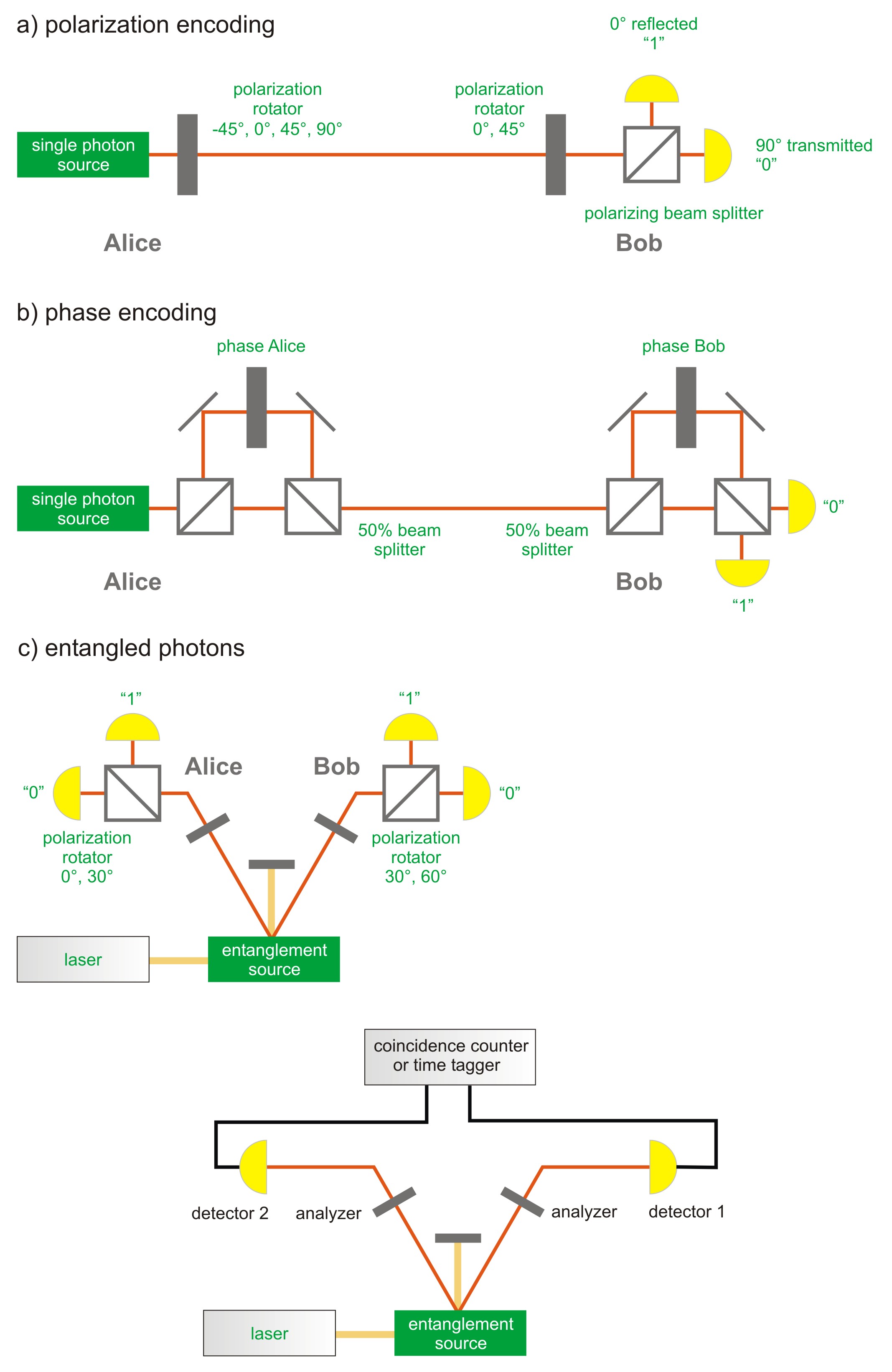
In conclusion, quantum communication is a fascinating field with immense potential for revolutionizing the way we transmit information. Using the principles of quantum mechanics, scientists have been able to develop techniques that guarantee the security and privacy of data transmission. Although the technology is still in its infancy, it has already been used in various applications, including military communications and financial transactions. With continued research and development, quantum communication may soon become the standard for secure communication, transforming the way we interact with each other and with technology.
In summary, quantum communication is a complex and sophisticated system that has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate. By harnessing the power of quantum mechanics, scientists have developed techniques that guarantee the security and privacy of data transmission. Although the technology is still in its nascent stages, it has already demonstrated its potential in various applications. As further research is conducted, we can expect to see continued advancements in quantum communication, leading to a future where secure communication is the norm. As a professional writer, I am excited to see what the future holds for this exciting field.