Paragraph 1:
Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs) are vital pieces of equipment that have saved countless lives in emergency situations. These small devices are designed to transmit a distress signal on a specific frequency when activated, helping rescue teams locate planes or vessels in distress in remote or inaccessible areas. The ELT transmits a unique code that can be picked up by search and rescue teams, allowing them to pinpoint the location of the distress and respond quickly with life-saving aid.
Paragraph 2:
In aviation, ELTs are mandatory for all aircraft and are typically installed in the tail section of the plane. When activated, ELTs transmit on 406 MHz, the international frequency for distress signals, and can also transmit on 121.5 MHz, an older emergency frequency that is still monitored by some search and rescue teams. The activation of an ELT is typically triggered by an impact or g-force sensor, but can also be manually triggered by the pilot or passengers in an emergency situation. ELTs have been instrumental in saving lives in search and rescue missions, making them an essential component of any aircraft’s safety equipment.
When activated, an emergency locator transmitter (ELT) transmits a distress signal on the international emergency frequency of 406 MHz. It is also able to transmit on 121.5 MHz and 243 MHz, which are the frequencies used for search and rescue operations. All ELTs are equipped with an antenna and an emergency beacon transmitter. The beacon transmits the distress signal, which is detected by satellites and search and rescue teams. An ELT also has a GPS receiver, which helps in locating the exact location of the aircraft in distress. By using the ELT, the search and rescue teams can easily locate the aircraft and take the appropriate action.
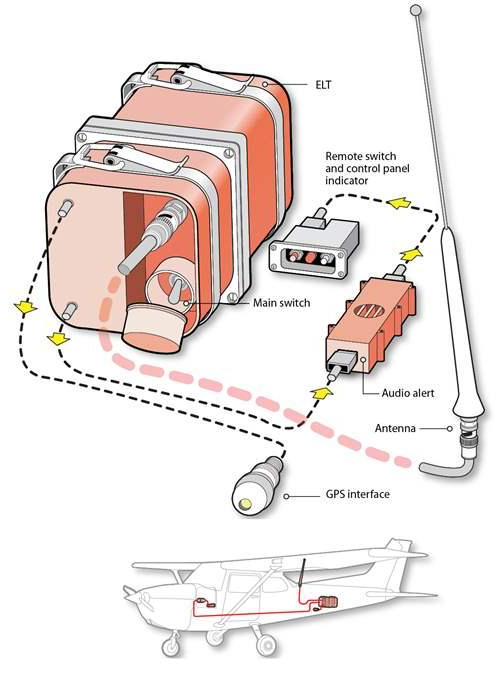
Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT)
An emergency locator transmitter (ELT) is a device that is used to send out a distress signal in the event of an emergency. The signal is picked up by satellites and is relayed to the nearest rescue coordination center (RCC). The ELT is typically found on aircraft but can also be found on other types of vehicles, such as boats and cars.
How ELT Works
An ELT is typically a device that is activated manually or automatically when an emergency situation arises. In the event of an aircraft crash, the ELT will be triggered and will begin transmitting a distress signal. This signal is picked up by satellites and is then relayed to the nearest RCC. The signal will contain information such as the plane’s position, altitude, and speed.
Once the signal has been received by the RCC, they will then be able to send out a rescue team to the location of the crash. The ELT is designed to run on its own power source, usually a battery, so that it can continue transmitting even if there is a power failure. The ELT will also have a GPS receiver, so that the signal can be tracked in real-time.
When Activated, an ELT Transmits On?
When activated, an ELT will typically transmit on the 121.5 MHz frequency, which is the international distress frequency for aviation. This frequency is monitored by the RCC and is used for search and rescue operations. In addition to this, the ELT will also transmit on the 406 MHz frequency. This frequency is monitored by the Cospas-Sarsat satellite system, which is used to detect and locate emergency beacons.
The ELT will also transmit a digital signal on the 406 MHz frequency. This signal contains encoded information such as the beacon’s identification number, the date and time of activation, and the location of the beacon. This information can then be used by the RCC to more quickly and accurately locate the beacon and send out a rescue team.
Frequently Asked Questions
An Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) is an electronic device that is used to alert search and rescue personnel in the event of an aircraft crash.
What is an Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT)?
An Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) is an electronic device that is used to alert search and rescue personnel in the event of an aircraft crash. An ELT is installed in an aircraft and is designed to be activated automatically in a crash or manually in an emergency situation. The ELT is designed to transmit a distress signal on either 121.5 MHz or 243.0 MHz, depending on the type of ELT installed.
The signal is picked up by Search and Rescue personnel and the signal can be used to help locate the aircraft. ELTs are usually equipped with a GPS receiver, which can be used to help pinpoint the location of the aircraft in the event of an emergency.
How does an ELT work?
An ELT is designed to send out a distress signal upon activation. The signal is transmitted on 121.5 MHz or 243.0 MHz, depending on the type of ELT installed. The signal is picked up by Search and Rescue personnel and can be used to help locate the aircraft. ELTs are usually equipped with a GPS receiver, which can be used to help pinpoint the location of the aircraft.
The ELT is designed to be activated automatically in the event of a crash or manually in the event of an emergency. The ELT is activated by a switch in the cockpit or by a shock sensor in the event of a crash. The ELT is also equipped with an antenna that is designed to deploy in the event of a crash, allowing for the signal to be transmitted over a greater range and for a longer period of time.
What frequency does an ELT transmit on?
An ELT transmits on either 121.5 MHz or 243.0 MHz, depending on the type of ELT installed. The signal is picked up by Search and Rescue personnel and can be used to help locate the aircraft. ELTs are usually equipped with a GPS receiver, which can be used to help pinpoint the location of the aircraft.
The ELT is designed to be activated automatically in the event of a crash or manually in the event of an emergency. The ELT is activated by a switch in the cockpit or by a shock sensor in the event of a crash. The ELT is also equipped with an antenna that is designed to deploy in the event of a crash, allowing for the signal to be transmitted over a greater range and for a longer period of time.
Is there a way to test an ELT?
Yes, there is a way to test an ELT. The ELT should be tested on a yearly basis in order to ensure that it is functioning properly. The test should include a visual inspection of the ELT, a check of the power connections, and a test of the ELT’s transmitter.
The ELT should be tested in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and the applicable regulations. The ELT should also be tested with a suitable test set to ensure that the ELT is transmitting properly and that the signal is being received by Search and Rescue personnel.
What is the range of an ELT signal?
The range of an ELT signal depends on the type of ELT installed and the conditions at the time of transmission. The signal can be received up to 400 miles away in ideal conditions, however the range is usually much less. The signal is usually received within a range of 20-30 miles in most cases.
An ELT is also equipped with an antenna that is designed to deploy in the event of a crash, allowing for the signal to be transmitted over a greater range and for a longer period of time. The ELT can also be equipped with a GPS receiver, which can be used to help pinpoint the location of the aircraft in the event of an emergency.
HOW ELT HELPS IN SEARH AND RESCUE OF LOST AIRCRAFT | EMERGENCY LOCATOR TRANSMITTER | EASA
In conclusion, an emergency locator transmitter (ELT) is a crucial device that can save lives in emergency situations. This small but powerful device is designed to automatically transmit distress signals when activated, providing rescuers with the precise location of the emergency. Whether it is a plane crash or a stranded hiker, the ELT can make all the difference in ensuring a successful rescue operation.
As technology continues to advance, the ELT is becoming even more sophisticated and reliable. With the introduction of newer and more advanced models, rescue operations are becoming more efficient and effective. It is important for individuals and organizations to invest in high-quality ELTs and ensure they are properly maintained to ensure they are ready to activate in the event of an emergency. By doing so, we can help ensure the safety of those in need and increase the chances of a successful rescue operation.



