In today’s digital age, data security has become increasingly important. With the rise of cybercrime and hacking, it is crucial to ensure that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. Full-disk encryption is one of the most effective ways to secure data and prevent it from falling into the wrong hands. But what does full-disk encryption protect against? In this article, we will explore the various threats that full-disk encryption can guard against.
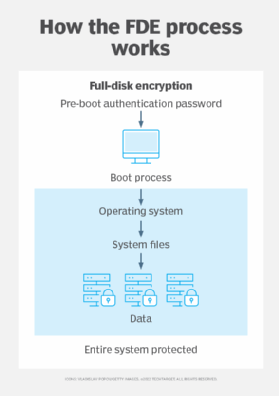
Full-disk encryption is a security measure that encrypts all the data on a computer’s hard drive. This means that even if someone gains access to the computer or the hard drive, they will not be able to read the data without the encryption key. Full-disk encryption can protect against a range of threats, including theft, hacking, and data breaches. By encrypting the entire hard drive, full-disk encryption ensures that all the data on the computer is secure, regardless of how it is accessed. Let’s dive deeper into the different types of threats that full-disk encryption can safeguard against.
Full-disk encryption protects against unauthorized access, data theft, and malicious software attacks. It is a security measure that encrypts all data stored on a hard drive, making it unreadable without the correct encryption key. This encryption prevents anyone from accessing the data stored on the disk without the encryption key, protecting against data theft and malicious software attacks. It is important to note that full-disk encryption does not protect against physical theft, as the disk itself can still be stolen.
What is Full Disk Encryption?
Full disk encryption (FDE) is a type of computer security technology that is used to encrypt the data stored on a device or hard drive. FDE works by scrambling the data stored on the disk so that it cannot be accessed without the appropriate encryption keys. This can help to protect your data from unauthorized access and protect against threats such as malware, malicious software, and data theft.
FDE is often used in corporate environments to protect sensitive data from being accessed by unauthorized individuals. It can also be used to protect personal data from being stolen or compromised. FDE can be implemented on both desktop and laptop computers, as well as on mobile devices.
What Does Full Disk Encryption Protect Against?
Full disk encryption can protect against a variety of threats, including malware, malicious software, and data theft. It can also protect against physical theft and unauthorized access to the data stored on the disk. Additionally, FDE can help to ensure that the data stored on the device is not corrupted or destroyed in the event of a disaster or power outage.
FDE is also an effective way to protect data stored on cloud-based services or remote servers. By encrypting the data stored on these services, it can help to ensure that it is not accessed by unauthorized parties or corrupted due to a security breach. Additionally, FDE can help to protect against data being stolen or compromised in the event of a data breach.
Malware and Malicious Software
Full disk encryption can protect against a variety of malware and malicious software that can damage or compromise the data stored on the disk. By encrypting the data, it makes it much more difficult for malicious software to access and exploit the data stored on the disk. Additionally, FDE can help to prevent malicious software from being installed on the device or hard drive.
Additionally, FDE can also help to protect against malicious software that is designed to steal confidential information or sensitive data. By encrypting the data stored on the disk, it can make it much more difficult for malicious software to access the data and exploit it for malicious purposes.
Data Theft
Full disk encryption can also help to protect against data theft, as it makes it much more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to the data stored on the disk. By encrypting the data, it makes it impossible for anyone to access the data without the appropriate encryption keys. Additionally, FDE can also help to protect against physical theft of the device, as the data stored on the disk cannot be accessed without the encryption key.
FDE can also help to protect against data theft in the event of a data breach. By encrypting the data stored on the disk, it can help to ensure that the data is not accessed or stolen in the event of a data breach. Additionally, FDE can also help to protect against data theft from cloud-based services or remote servers, as the data stored on these services is encrypted and cannot be accessed without the appropriate encryption keys.
Frequently Asked Questions about Full-Disk Encryption
Full-disk encryption is a computer security technique that encrypts all the data stored on a hard drive, thus protecting it from unauthorized access. It is a very effective way to protect data from hackers, thieves, and other malicious activity.
What type of data does full-disk encryption protect?
Full-disk encryption can protect all types of data stored on a hard drive, including documents, photos, music, and other files. It will also protect passwords and other sensitive information that is stored on the hard drive. Full-disk encryption will also protect data stored in the computer’s memory, as well as data that is transferred over the internet.
What types of attacks does full-disk encryption protect against?
Full-disk encryption can protect against various types of malicious attacks. It can protect against brute-force attacks, where a hacker attempts to guess the encryption key by trying various combinations. Full-disk encryption can also protect against physical attacks, where someone attempts to gain access to the hard drive by physically tampering with it. It can also protect against malware and other malicious software, which can be used to gain access to data stored on the hard drive.
How secure is full-disk encryption?
Full-disk encryption is very secure and can protect against a wide range of malicious attacks. It is important to note, however, that full-disk encryption is not foolproof and can be vulnerable to specific attacks. For example, a hacker may be able to gain access to the encryption key if they know the password used to access the hard drive. Additionally, full-disk encryption can be vulnerable to attacks that involve physical access to the hard drive, such as removing it from the computer and connecting it to another device.
Is full-disk encryption easy to use?
Full-disk encryption is generally very easy to use. Most operating systems have built-in tools for setting up full-disk encryption, and the process is usually quite straightforward. Additionally, most modern hard drives are designed to be compatible with full-disk encryption, making the setup process even easier.
What happens if I forget the encryption key?
If you forget the encryption key, you will not be able to access the data stored on the hard drive. This is why it is important to keep a secure backup of the encryption key. Additionally, some full-disk encryption solutions may offer additional security measures, such as a “backup key” that can be used to gain access to the data stored on the hard drive in case the main encryption key is lost.
AES 256-bit Self-Encrypting Drives – All you Need to Know as Fast As Possible
In conclusion, full-disk encryption is a powerful tool that offers robust protection for your sensitive data. By encrypting your entire hard drive, you can safeguard against a wide range of threats, including theft, hacking, and unauthorized access. With full-disk encryption, you can have peace of mind knowing that your data is protected, even if your device falls into the wrong hands.
In today’s digital age, data security is more important than ever. Full-disk encryption is a simple yet highly effective way to protect your sensitive data. It offers a comprehensive layer of security that can help prevent data breaches and protect your privacy. So, if you’re looking for a reliable way to secure your data, full-disk encryption is an excellent option to consider.



Thanks for sharing.