In today’s digital age, wireless networks have become an integral part of our daily lives. From streaming movies to browsing the internet, we rely heavily on wireless networks to stay connected. However, with the rise of wireless networks comes a number of unique challenges and problems that can occur. These problems can range from security breaches to signal interference, and can have serious consequences for businesses and individuals alike.
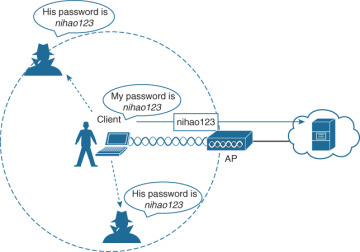
One of the most significant challenges facing wireless networks is security. With the ability to access wireless networks from anywhere, it can be difficult to ensure that the network remains secure. Hackers and cybercriminals can easily gain access to wireless networks and steal sensitive information, such as credit card numbers and passwords. In addition, signal interference can also pose a problem, as the wireless signal can be disrupted by other devices or structures, causing a loss of connection or slow internet speeds. These and other special problems associated with wireless networks require careful consideration and management to ensure their continued success and reliability.
Wireless networks can suffer from security risks, interference, lack of coverage and speed issues. Security risks can include eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, spoofing attacks, and more. Interference can be caused by other wireless networks, cordless phones and microwaves. Lack of coverage can occur when the wireless signal is blocked by walls and other objects. Speed issues can be caused by a variety of factors, such as network congestion, distance from the access point, and more.
Wireless Network Problems
Wireless networks are convenient, but they can be prone to certain problems that wired networks don’t have. Special problems can occur with wireless networks that can affect their performance and reliability. In this article, we will discuss the different types of special issues that can occur with wireless networks and how to troubleshoot them.
Interference
Interference is one of the most common problems associated with wireless networks. Interference can occur from a variety of sources, including other wireless networks, microwaves, cordless phones, and even neighboring wireless devices. When interference occurs, it can cause slow speeds, dropped connections, and other issues. To troubleshoot interference, you should first try moving your wireless devices away from other wireless devices and changing the channel on your router. You can also try using a higher-quality wireless router with better antennas to help reduce interference.
Security Concerns
Wireless networks also have the potential to be vulnerable to security breaches. Without proper security measures in place, it’s possible for hackers or malicious users to gain access to your network and compromise your data. To ensure your wireless network is secure, you should use the latest encryption protocols and make sure your router has a strong password. You should also use a firewall and antivirus software to help protect your network.
Range Limits
Wireless networks are typically limited in range, which can cause problems if you need to cover a large area with your network. To extend the range of your wireless network, you can use a range extender or access point. These devices can help increase the range of your network, allowing you to cover a larger area with your wireless network.
Power Issues
Power issues can also affect your wireless network. If your router is not getting enough power, it can cause slow speeds or dropped connections. To troubleshoot power issues, you should check the power adapter to make sure it is working properly and plugged in correctly. If you are using a battery-powered router, make sure the battery is charged and the power adapter is plugged in.
Network Congestion
Network congestion can also cause problems with wireless networks. If too many devices are connected to your network, it can cause slow speeds and dropped connections. To troubleshoot network congestion, you should try disconnecting some of your devices and limiting the number of devices connected to your network.
Hardware Issues
Hardware issues can also cause problems with wireless networks. If your router or other hardware is malfunctioning, it can cause slow speeds and dropped connections. To troubleshoot hardware issues, you should check your router and other hardware to make sure they are working properly. If necessary, you should replace any hardware that is not functioning properly.
Software Issues
Software issues can also affect your wireless network. If your router or other software is not up to date, it can cause slow speeds and dropped connections. To troubleshoot software issues, you should check your router and other software to make sure they are up to date. If necessary, you should update any software that is not up to date.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also affect your wireless network. If your router is located in an area with poor signal reception, it can cause slow speeds and dropped connections. To troubleshoot environmental factors, you should try moving your router to a different location with better signal reception. You should also make sure there are no obstacles blocking the signal, such as walls or furniture.
Frequently Asked Questions
This page provides answers to questions about the potential risks and problems associated with wireless networks.
What are the security risks associated with wireless networks?
Wireless networks can be vulnerable to security threats due to the use of radio waves to transmit data. Unencrypted data can be intercepted by anyone within range of the wireless signal, allowing an attacker to access confidential information such as passwords and credit card numbers. Additionally, wireless networks can be subject to spoofing attacks, where an attacker can impersonate a legitimate wireless network and deceive users into connecting to it.
To mitigate these risks, it is important to ensure that wireless networks are protected with strong encryption and authentication protocols, such as WPA2. Additionally, it is important to regularly monitor network activity for any suspicious activity.
What special problems can occur with wireless networks?
Wireless networks are susceptible to interference from other wireless networks, as well as from physical obstructions such as walls and furniture. Interference can lead to reduced performance, slow data speeds, and intermittent connection problems. Additionally, wireless networks can be subject to signal attenuation, which is when the signal becomes weaker as it travels farther from the router.
To minimize these issues, it is important to ensure that the router is positioned in a central location with minimal interference and obstructions. Additionally, it is important to use high quality equipment that is designed to reduce interference and signal attenuation.
What is the difference between a wired and a wireless network?
A wired network is a type of computer network that uses physical cables, such as Ethernet cables, to connect devices together. These cables are used to transmit data between devices, and require a physical connection between each device. A wired network is typically more reliable than a wireless network, as it is not susceptible to interference or signal attenuation.
A wireless network, on the other hand, is a type of computer network that uses radio waves to transmit data between devices. Wireless networks are typically more convenient than wired networks, as they do not require physical connections between devices. However, they can be more vulnerable to security threats, interference, and signal attenuation.
What is the difference between a Wi-Fi and a cellular network?
Wi-Fi is a type of wireless network that uses radio waves to transmit data between devices. Wi-Fi is typically used to provide an internet connection to devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. Wi-Fi networks are typically short range and require a physical connection to a router in order to access the network.
A cellular network, on the other hand, is a type of wireless network that uses radio waves to transmit data between devices. Cellular networks are typically used to provide an internet connection to devices such as smartphones and tablets. Cellular networks are typically long range and do not require a physical connection to a router in order to access the network.
What is the difference between WEP and WPA encryption?
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a type of encryption used to secure wireless networks. WEP uses a shared secret key to encrypt data, and is typically considered to be less secure than other encryption protocols.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a type of encryption used to secure wireless networks. WPA uses an encryption key that is unique to each device, and is typically considered to be more secure than WEP. Additionally, WPA supports the use of more advanced authentication protocols, such as EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol).
In conclusion, wireless networks have revolutionized the way we communicate and access information. However, they come with unique challenges that require careful management to ensure optimal performance. The most common problems associated with wireless networks include congestion, interference, security, and range limitations.
To mitigate these challenges, it’s essential to invest in high-quality networking equipment, implement strong security protocols, and conduct regular network audits. Additionally, it’s crucial to stay updated with the latest wireless technologies and industry best practices to enhance the performance and reliability of your network. In doing so, you can maximize the benefits of wireless networks while minimizing their potential drawbacks, ultimately enabling you to achieve your goals more efficiently and effectively.