As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, network topology has become a critical topic for anyone interested in computer networks. Network topology refers to the arrangement of network components, such as computers, servers, and routers, and the way they are connected. There are several common types of network topology, including bus, ring, star, mesh, and tree. However, not all network topologies are created equal, and some are more common than others.
In this article, we will explore the topic of network topology and answer the question, “which of the following is not a common network topology?” We will delve into each type of network topology, examining its advantages and disadvantages, so that you can determine which is best suited to your needs. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of network topology and be able to make an informed decision when it comes to setting up your own network.
Answer: Starbus Network Topology Starbus Network Topology is not a common network topology. It is a hybrid of the star and linear bus network topologies. Starbus combines the advantages of both topologies. It is a complex network topology that requires a large number of nodes to be connected in order to form a network. It is not suitable for small networks, as it is difficult to maintain and manage.
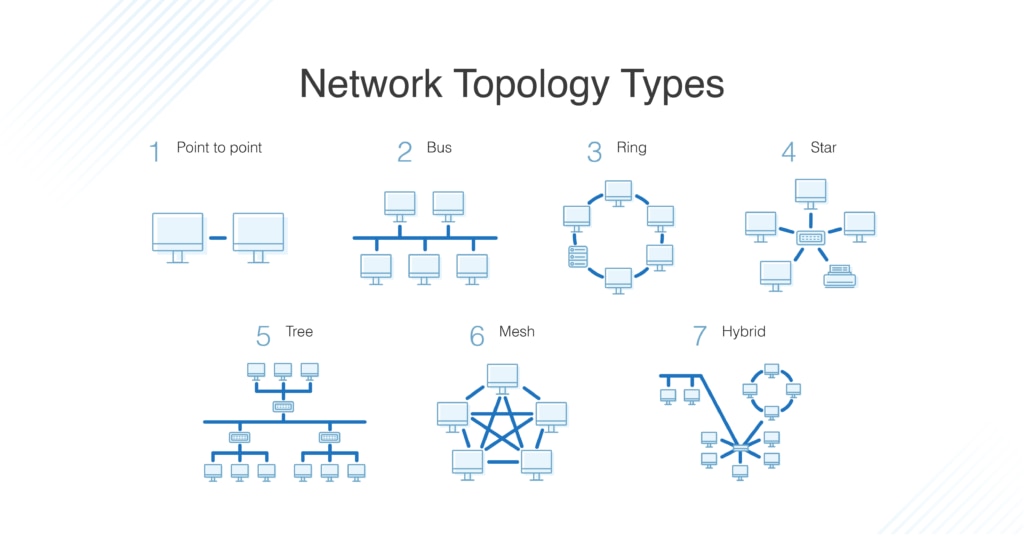
Which Of The Following Is Not A Common Network Topology?
Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. It refers to the physical and logical layout of interconnected devices and the paths that signals can take between them. In this article, we’ll explore which of the following is not a common network topology.
Point-to-Point Topology
Point-to-point topology is a type of network topology in which each node is connected to exactly one other node. This type of topology is typically used when connecting two locations over a wide area, or when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In point-to-point topology, data is transmitted directly from one node to another, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable but expensive, as it requires dedicated links for each connection.
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology is a type of network topology in which each node is connected to every other node in the network. This type of topology is typically used when connecting multiple locations over a wide area, or when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In mesh topology, data is transmitted from one node to the next until it reaches its destination, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable, but expensive, as it requires dedicated links for each connection.
Bus Topology
Bus topology is a type of network topology in which all nodes are connected to a single cable or bus. This type of topology is typically used when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In bus topology, data is transmitted from one node to the next along the bus, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable and cost-effective, as it requires only one cable for all the nodes.
Star Topology
Star topology is a type of network topology in which all nodes are connected to a single central node. This type of topology is typically used when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In star topology, data is transmitted from one node to the next via the central node, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable and cost-effective, as it requires only one cable for all the nodes.
Tree Topology
Tree topology is a type of network topology in which nodes are arranged in a hierarchical structure. This type of topology is typically used when connecting multiple locations over a wide area, or when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In tree topology, data is transmitted from one node to the next along the tree structure, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable and cost-effective, as it requires only one cable for all the nodes.
Ring Topology
Ring topology is a type of network topology in which all nodes are connected in a circular arrangement. This type of topology is typically used when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In ring topology, data is transmitted from one node to the next in a circular manner, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable and cost-effective, as it requires only one cable for all the nodes.
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is a type of network topology in which two or more different topologies are combined. This type of topology is typically used when connecting multiple locations over a wide area, or when connecting two or more devices in a local area network (LAN). In hybrid topology, data is transmitted from one node to the next along the different topologies, without passing through any intermediate nodes. This type of topology is reliable and cost-effective, as it combines the advantages of different topologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the most common network topologies are Point-to-Point, Mesh, Bus, Star, Tree, and Ring. Hybrid topology is not a common network topology. It is a combination of two or more different topologies and is typically used in wide area networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
This page provides answers to commonly asked questions about the different types of network topologies.
Which of the following is not a common network topology?
The answer to this question is the Star-Shaped Network Topology. This type of network topology does not exist as it is not a common network topology. The most common network topologies are the star topology, bus topology, ring topology, mesh topology and tree topology.
The star topology is the most commonly used network topology. In this type of network, each device is connected to a central hub or switch. The hub or switch acts as the central point of communication and manages the flow of data between each device. This type of topology is easy to install and maintain.
The bus topology is another common network topology. In this type of network, all of the devices are connected to a single line called a bus. This type of topology is cost effective and easy to install, but can be difficult to maintain.
The ring topology is a network topology in which all of the devices are connected to each other in a closed loop. This type of topology allows for the data to be routed from one device to another without the need for a central hub or switch.
The mesh topology is a network topology in which each device is connected to every other device in the network. This type of topology is more reliable and secure than other topologies, but is more expensive and difficult to maintain.
The tree topology is a network topology in which each device is connected to a central hub or switch in a hierarchical structure. This type of topology is more reliable and secure than other topologies, but is more expensive and difficult to maintain.
Common Network Topologies – CompTIA Network+ N10-006 – 1.6
In conclusion, network topology plays a crucial role in determining the performance, scalability, and reliability of a network. Choosing the right topology can make all the difference in the success of an organization’s communication and data infrastructure. While there are several common network topologies, it’s essential to remember that not all topologies are created equal. Understanding the differences between each topology and their advantages and disadvantages can help organizations make informed decisions when designing and implementing their network infrastructure.
In summary, the answer to “which of the following is not a common network topology?” is a point-to-point topology. While it may not be as commonly used as other topologies, it still has its place in certain scenarios, such as connecting remote locations or devices. Ultimately, choosing the right topology requires careful consideration of an organization’s specific needs and goals, and a professional network administrator can help ensure that the network is optimized for performance, security, and scalability.