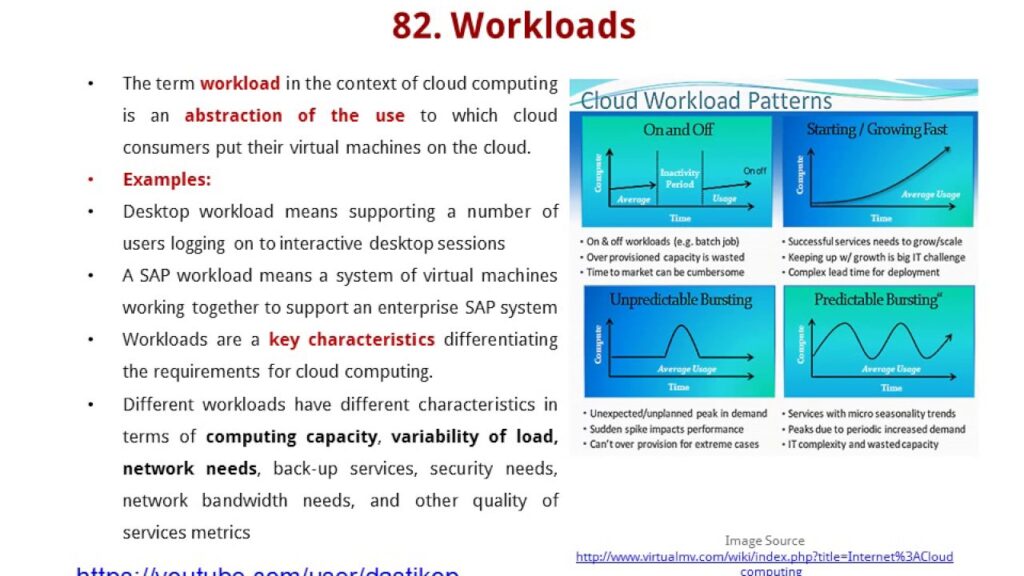
Google Cloud serverless projects are being utilized by a financially motivated threat group in Latin America, known as FLUXROOT, to coordinate credential phishing campaigns, as reported by The Hacker News.
This incident is part of a larger trend where cybercriminals are exploiting cloud computing services for malicious purposes, presenting a significant challenge for IT and cybersecurity professionals.
Google’s biannual Threat Horizons Report delves into the rise of serverless architecture and offers insights into the phenomenon. The report highlights how cybercriminals are leveraging the same benefits of serverless technology that legitimate businesses enjoy – flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and simplicity – to carry out malicious activities. Threat actors are using serverless infrastructure to distribute malware, host phishing pages, and execute serverless-compatible scripts.
FLUXROOT, for example, used Google Cloud container URLs to host sophisticated phishing pages targeting Mercado Pago, a popular online payments platform in Latin America. By impersonating the platform’s login interface, FLUXROOT aimed to steal users’ login credentials for unauthorized access to their financial accounts.
However, FLUXROOT is not the only threat actor exploiting Google Cloud. Another group, PINEAPPLE, has been observed using Google Cloud to disseminate the Astaroth malware, which primarily targets Brazilian users.
PINEAPPLE’s tactics involved compromising existing Google Cloud instances and creating new projects to generate container URLs on legitimate Google Cloud serverless domains. These URLs directed unsuspecting victims to malicious infrastructure, leading to the deployment of the Astaroth malware.
To combat these threats, Google has taken swift action by shutting down malicious Google Cloud projects and updating its Safe Browsing lists. Nevertheless, the incident underscores the ongoing battle between cybersecurity defenders and threat actors in the cloud environment.
The abuse of cloud services by cybercriminals extends beyond phishing and malware distribution to include activities like illicit cryptocurrency mining and ransomware attacks. The widespread adoption of cloud technologies across industries has fueled this trend.
One of the major challenges posed by this trend is the difficulty in detecting malicious activities due to threat actors blending their operations with normal network traffic. This makes it crucial for cloud providers and users to prioritize security audits, robust authentication methods, and advanced threat detection systems to maintain a secure cloud environment.
As cloud adoption continues to surge, both cloud providers and consumers must remain vigilant against evolving cyber threats. The attacks of the future will require innovative defense measures to stay ahead of cybercriminals.