Consensus is a crucial aspect of life, whether among humans or in the digital realm. It requires a defined set of instructions to be met in order to approve and agree on something. Blockchain networks rely on Consensus protocol, which has evolved over the years to streamline and expedite processes. Among these, the Stellar consensus protocol stands out. Let’s delve into the details of this consensus and explore how the Stellar Consensus Protocol works.
What Is Consensus Protocol And Its Types?
The consensus protocol in Blockchain comprises a set of agreements that the system must reach to process and validate transactions. It involves agreements, collaborations, rights, and cooperation to reach approval. This protocol enhances overall system reliability by connecting different nodes and users in the network. With various architectures, the consensus protocol enhances network scalability and availability.
Below are different types of consensus protocols amplified in the blockchain network:
Proof of Work
Proof of Work involves nodes performing various mathematical computations to validate transactions. Miners and validators must demonstrate that their transactions meet the necessary requirements and fit within the nodes by solving complex mathematical puzzles.
Proof Of Stake
Proof of Stake is an alternative to Proof of Work that doesn’t require intricate hardware or complex math. Validators receive rewards and increase their stake based on the number of mining tokens they hold, giving them more control over the consensus process.
Stellar Consensus Protocol
The Stellar Consensus Protocol enables rapid and cost-effective transactions without relying on closed system protocols to record financial transactions accurately. It streamlines the agreement process among network participants, ensuring the validity of transactions in a timely manner.
Byzantine Agreement System
The Byzantine Agreement System enables parties within the network to agree on a specific value even in the presence of malicious nodes. It ensures that a certain minimum number of nodes must agree on a solution for it to be considered valid and added to the blockchain.
| Mechanisms | Decentralization | Less Latency | Flexibility | Asymptotic Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of Stake | Yes | Maybe | Maybe | |
| Stellar Consensus | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Byzantine Agreement | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Tendermint | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Explaining Stellar Consensus Protocol
Consensus is vital in a decentralized payment system, ensuring transaction approval, security, and preventing double-spending attacks. The SCP is built on the Byzantine Agreement, relying on trusted nodes’ agreement rather than staking power or computational abilities. Validators in SCP contribute to network security and resilience without monetary incentives.
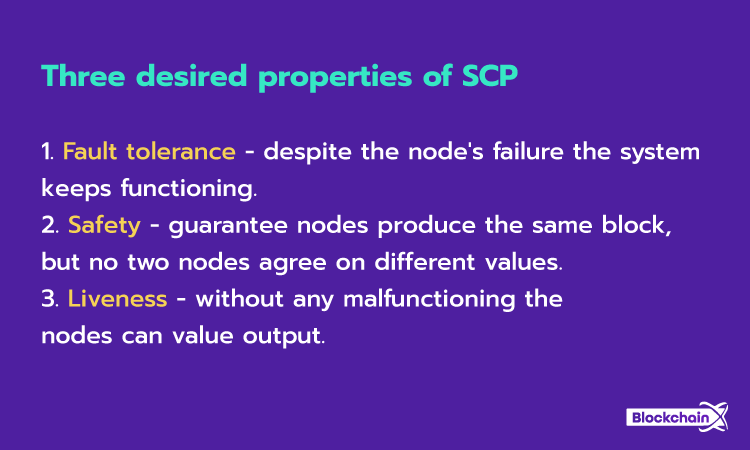
The Four Principles Of Stellar Consensus Protocol
Decentralization – Participation is not restricted, and authority is not centralized in terms of consensus approval.
Less Latency – Nodes reach consensus quickly, even for web or payment transactions, typically within seconds.
Flexibility – Users have the freedom to act and trust a combination of parties, allowing smaller entities to play a significant role alongside larger institutions.
Asymptotic Security – Digital signatures and hash families provide security against adversaries with significant computing power.
The Major Components Of Stellar Consensus Protocol
Quorum Set
Core nodes decide which nodes to trust for agreements, forming a Quorum set of trusted nodes.
Thresholds
In addition to the Quorum set, core nodes set a threshold specifying the minimum nodes required to reach consensus.
Quorum Slices
Nodes within a Quorum set that agree on a particular value form Quorum Slices.
Blocking Sets
Nodes have the power to block consensus by preventing nodes in the Quorum set from reaching agreements.
Quorum
A set of nodes sufficient to reach an agreement, consisting of nodes from Quorum slices.
Statements
Stellar expresses validation through nodes’ agreement on transaction opinions in the ledger.
Agreement System
The Byzantine agreement statement ensures fault tolerance and consistency in providing results despite errors.
What Is Federated Voting In The Working Of Stellar Consensus Protocol?
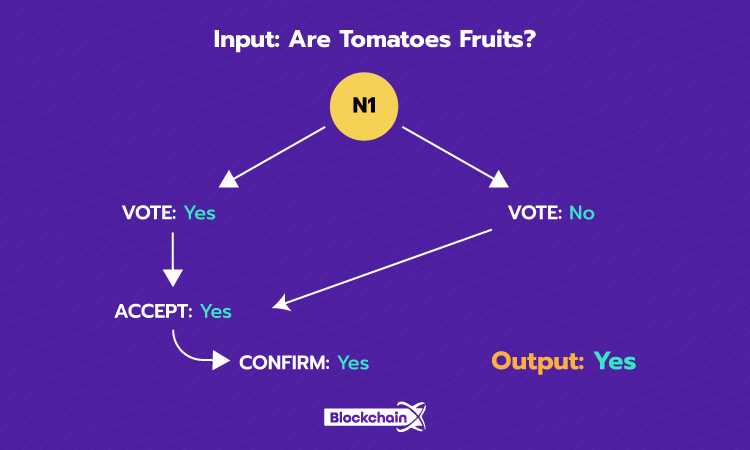
Stellar Consensus Protocol = Vote -> Accept -> Confirm
The Stellar Consensus Protocol achieves agreement through federated voting, where nodes evaluate reasons from the Quorum set before fully agreeing to the network. The process involves three main steps in federated voting:
1. Voting
2. Accepting
3. Confirming
For example, a node named ‘CAT’ may have four opinions:
1. No knowledge about CAT
2. Vote for CAT but unsure of safety
3. Support CAT based on other nodes’ agreement
4. Confirm CAT’s safety despite other nodes’ statuses
Federated voting simplifies complexities by following specific rules for voting, accepting, and confirming nodes’ decisions.
The consensus process consists of two stages:
Nomination Protocol
Under this protocol, transaction sets are selected for ledger entry. Once a candidate is confirmed, it nominates other transaction sets while still accepting and confirming previous statements. The Ballot Protocol follows the Nomination Protocol in the background.
Ballot Protocol
The Ballot Protocol unanimously confirms and applies nominated transaction sets. It includes the Prepare stage, which verifies nodes’ quorum slices, and the Commit stage, which ensures nodes’ commitment to the values.
Get Validated With Stellar Consensus Protocol
The Stellar Consensus Protocol aims to revolutionize financial transactions in the evolving web3 era. It offers a solution for efficient and secure transactions in blockchain networks. To leverage the benefits of SCP, consider partnering with a blockchain development company. Strengthen your network security and reliability with the precision of the Stellar Consensus Protocol.