Wireless protocols such as LoRaWAN, Wi-Fi, ZigBee, and LP-WAN are commonly used by IoT and IIoT devices.
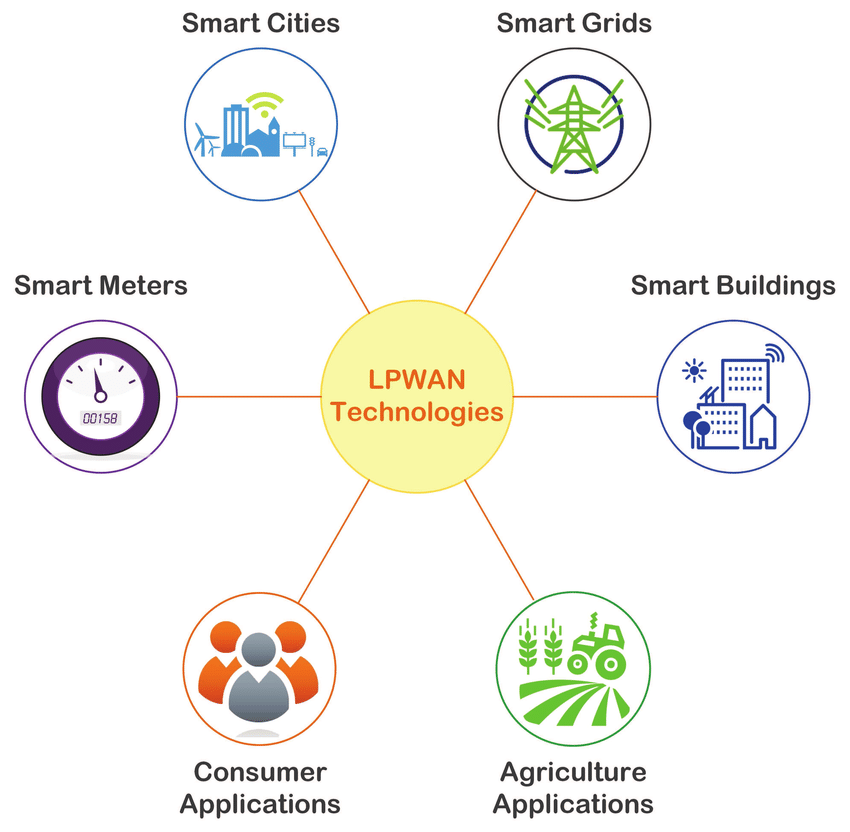
LPWAN, or Low-Power Wide-Area Network, is a wireless technology designed specifically for IoT connectivity and M2M communications. Illustrated in Figure 1, LPWAN supports a wide range of applications.
This review focuses on the advantages and limitations of LPWAN, comparing it with short-range wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), and ZigBee. It also delves into various LPWAN protocols, including Long-Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) and Long-Term Evolution for Machines (LTE-M), highlighting specific applications.
Benefits of LPWAN Protocols
While many IoT devices utilize Wi-Fi, BLE, and ZigBee radios, these short-range protocols may not efficiently support all use cases, especially for low-power or extensive IIoT and M2M deployments.
On the other hand, cellular and non-cellular LPWAN protocols (Figure 2) enable energy-efficient data transmission over distances ranging from 2 km to 1,000 km.
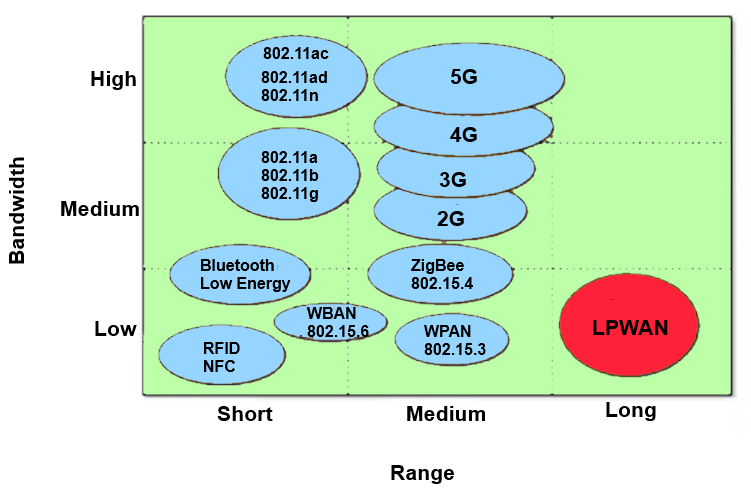
Figure 2. A comparison of wireless technologies by range and bandwidth, illustrating LPWAN’s advantages as a low-bandwidth, long-range solution. (Image: DigiKey)
Furthermore, LPWAN radio modules, like those in LoRaWAN devices (Figure 3), consume less power than short-range counterparts. They use minimal power during transmission and enter low-power sleep modes when not in use.

Figure 3. Modules like Ezurio RM1261 add LoRaWAN support to IoT devices. (Image: Ezurio)
Non-cellular LPWAN protocols operate in unlicensed frequency bands, handling small data payloads at speeds up to 200 kbps. These protocols work within specific frequency bands across different regions.
LPWAN vs. Bluetooth LE, ZigBee, and Wi-Fi
Most LPWAN protocols may not support bandwidth-intensive applications but excel in low-bandwidth, long-range communication. LTE-M offers higher data rates for enterprise applications like VoLTE.
While LPWAN ensures reliable two-way communication, some implementations face latency issues. However, LPWAN is ideal for large-scale, low-bandwidth deployments requiring long-range communication and minimal power consumption.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth LE, and ZigBee are popular in various consumer, enterprise, and industrial applications, each serving specific purposes.
Key LPWAN Protocols
LoRaWAN is widely used across different industries, operating on chirp spread spectrum (CSS) modulation within unlicensed bands. With AES-128 encryption, LoRaWAN offers data rates ranging from 0.3 kbps to 27 kbps.
Other LPWAN protocols include Sigfox, NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Weightless, each tailored for specific IoT applications.
Use Cases and Applications
LoRaWAN is ideal for applications like smart grids, water meters, and precision agriculture sensors. Sigfox excels in asset tracking and environmental sensing, while NB-IoT and LTE-M support various IoT applications.
Weightless targets smart city deployments, offering flexibility and low power consumption for infrastructure management.
Conclusion
LPWAN protocols play a crucial role in IoT and M2M applications, providing efficient data transmission over short and long distances with minimal energy consumption. LPWAN protocols like LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Weightless cater to diverse IoT needs.
References
Various LPWAN resources and guides are available from sources like Velos, AmbiMat Electronics, Soracom, Symmetry Electronics, PandoraFMS, and Abracon.