Quantum cryptography is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to change the way we think about data security. It is a highly advanced form of cryptography that is based on the principles of quantum mechanics. Unlike traditional encryption methods, which rely on mathematical algorithms, quantum cryptography uses the properties of quantum physics to ensure that data is secure.
At its core, quantum cryptography is all about using the strange and mysterious properties of the quantum world to create unbreakable codes. It works by using particles of light, known as photons, to transmit information in a way that is completely secure. This is because the act of measuring a quantum particle changes its state, which means that any attempt to intercept a quantum message will be immediately detected. As a result, quantum cryptography promises to provide a level of security that is unparalleled in the world of data encryption.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is an emerging field of cryptography that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to secure communication. It is a form of secure communication which uses the properties of quantum particles, such as photons, to send encrypted messages. Quantum cryptography is used to ensure that the data sent between two parties remains secure and cannot be intercepted or altered without being detected.
How Quantum Cryptography Works
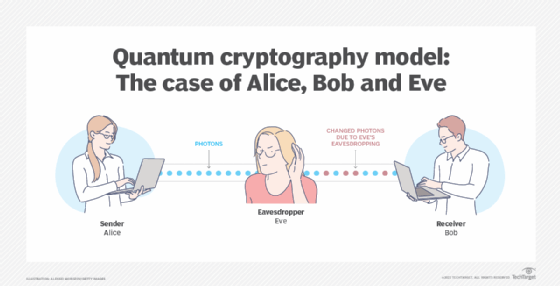
Quantum cryptography works by using quantum particles to transmit messages between two parties. When a message is sent between two locations, the sender and the receiver, the particles are encoded with a secret key which is known only to the sender and the receiver. This key is used to encrypt the message, meaning that only the sender and the receiver can understand the message. This makes it impossible for an eavesdropper to intercept and decode the message, as they do not possess the secret key.
In addition to encrypting the message, quantum cryptography also utilizes quantum entanglement. This is a phenomenon where two particles are linked together and any changes in one of the particles will have an effect on the other. This ensures that any changes to the message, such as an interception or alteration, will be detected by the sender and the receiver.
Advantages of Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography has several advantages over traditional cryptography. Firstly, it is much more secure than traditional methods as it is impossible for an eavesdropper to intercept and decode the message. Furthermore, quantum cryptography is resistant to attack from quantum computers, which are able to crack traditional cryptography methods. Finally, quantum cryptography is also much faster than traditional methods, as it does not require the use of large amounts of computing power.
The main disadvantage of quantum cryptography is its cost. Quantum cryptography requires specialized hardware, such as photon detectors, which can be expensive. Furthermore, it is not yet widely available, meaning that it is not suitable for use in all applications.
Applications of Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography has numerous potential applications. It could be used to secure financial transactions, as well as to secure data stored in the cloud. It could also be used to secure military communications, as well as to secure data sent over the internet. Finally, it could be used to securely transmit data between two locations, such as between two offices or between two countries.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize the way we secure our data. It is much more secure than traditional methods and is resistant to attack from quantum computers. Furthermore, it is also much faster than traditional methods. However, it is not yet widely available and is expensive to implement.
Frequently Asked Questions about Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a secure method of communication that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to protect information. Quantum cryptography is considered to be one of the most secure forms of encryption due to its ability to detect any tampering with the data being sent.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
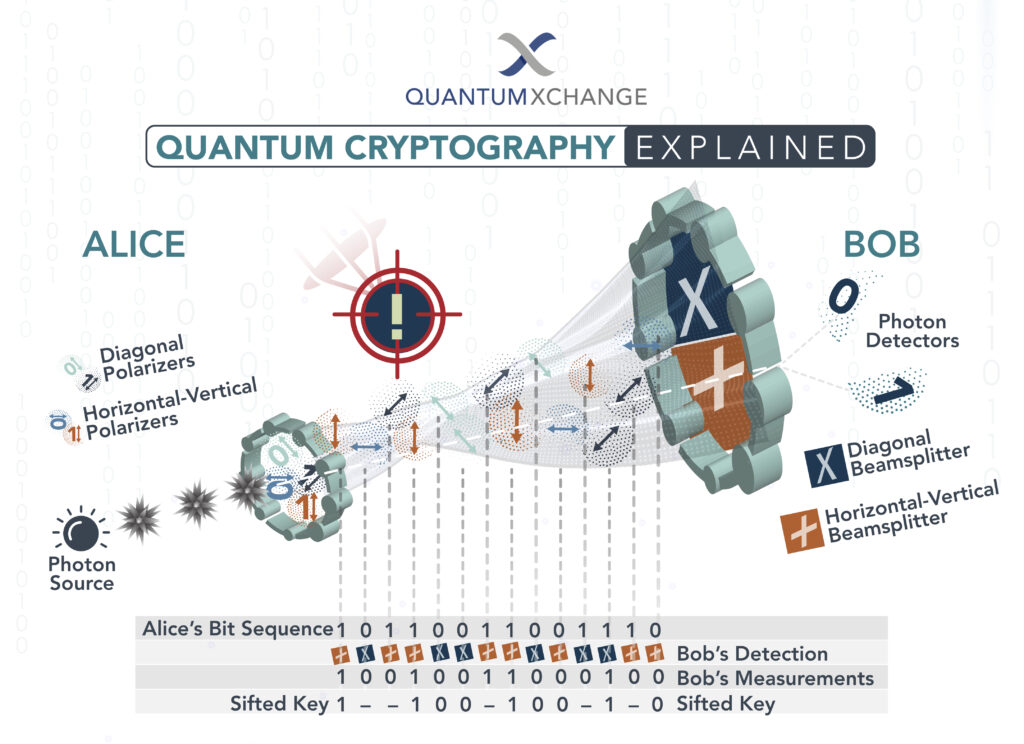
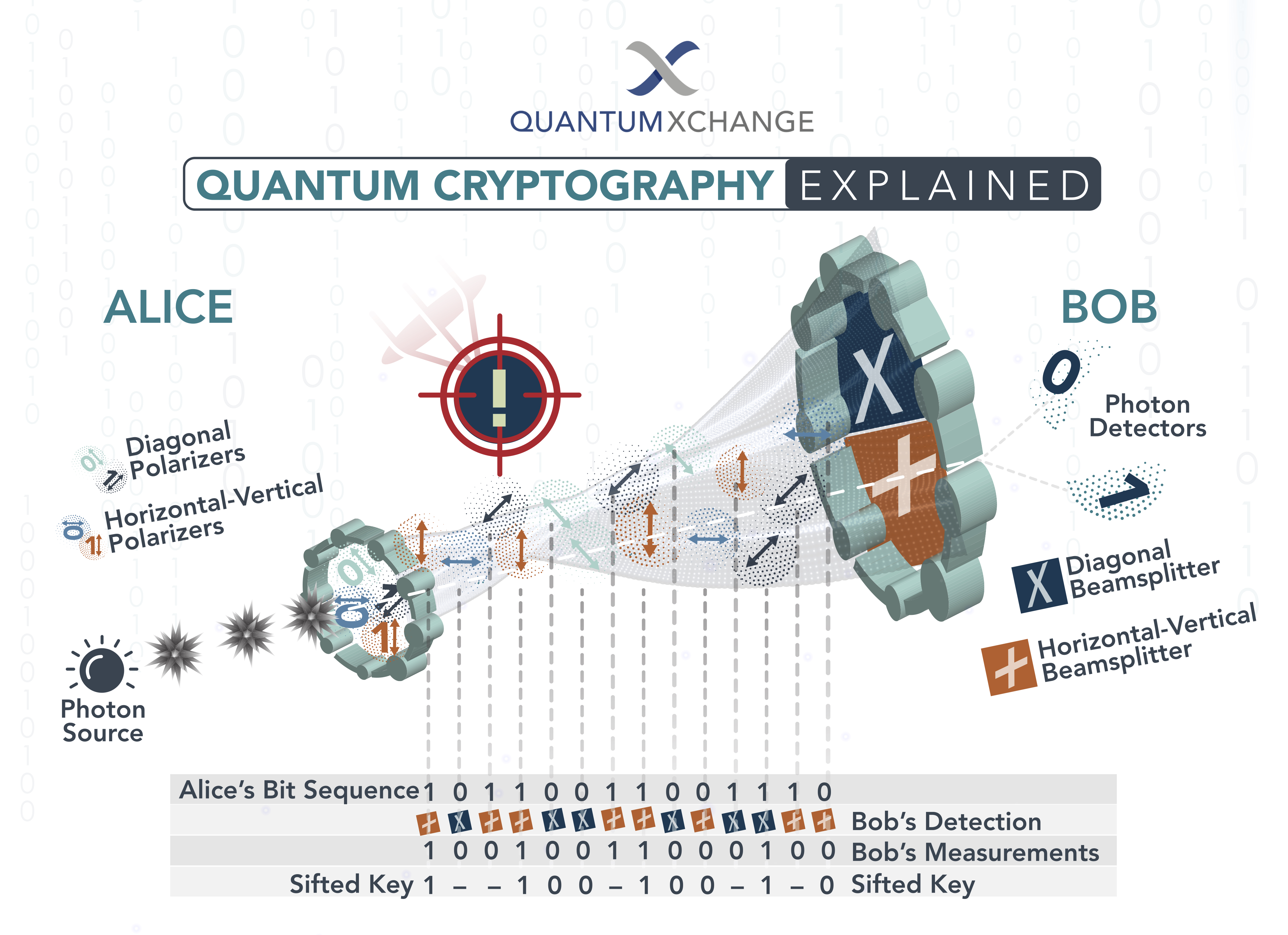
Quantum cryptography is a type of encryption that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to protect data. It is considered to be one of the most secure forms of encryption available today due to its ability to detect any tampering with the data being sent. Quantum cryptography is based on a process called quantum key distribution (QKD), which allows two parties to securely exchange a secret key. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data.
The QKD process works by sending particles of light along an optical fiber. The particles of light are in a quantum state and any attempt to intercept the data will cause a change in the state of the particles. This change is detected by the two parties and the data is not exchanged.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by sending particles of light along an optical fiber. These particles of light are in a quantum state and any attempt to intercept the data will cause a change in the state of the particles. This change is detected by the two parties and the data is not exchanged.
The two parties then use a mathematical algorithm to generate a secret key. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data. The key is also used to verify the integrity of the data, ensuring that it has not been tampered with. The key is destroyed after it has been used, making it impossible to reuse the same key again.
What Are the Advantages of Quantum Cryptography?
One of the main advantages of quantum cryptography is its security. Since the particles of light are in a quantum state, any attempt to intercept the data will cause a change in the state of the particles. This change is detected by the two parties, making it impossible for anyone to access the data without authorization.
Another advantage of quantum cryptography is that it allows for greater privacy. Since the key is destroyed after it is used, it is impossible for anyone to reuse the same key again. This makes it extremely difficult for anyone to gain access to the data without authorization.
What Are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
One of the main limitations of quantum cryptography is its cost. Implementing a quantum cryptography system can be expensive, especially if the system needs to be scaled up. Additionally, quantum cryptography systems require powerful computers to generate and communicate the key, adding to the cost.
Another limitation of quantum cryptography is its speed. Quantum cryptography systems can be slow and the process of generating a key can take some time. This can be a problem when dealing with large amounts of data that needs to be securely transmitted quickly.
What Are Some Examples of Quantum Cryptography?
One of the most popular examples of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution (QKD). QKD is a process that allows two parties to securely exchange a secret key. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data. Other examples of quantum cryptography include quantum signature schemes and quantum privacy amplification.
Quantum cryptography is rapidly becoming more popular as a form of secure communication. Companies are increasingly turning to quantum cryptography to protect their data from unauthorized access. As the technology continues to improve, we can expect to see quantum cryptography used in a variety of different applications.
What is Quantum Cryptography? An Introduction
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a revolutionary technology that promises to provide an unparalleled level of security to our digital world. By harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics, it allows for the creation of unbreakable encryption keys that cannot be intercepted or decoded by any outside party.
As we continue to rely more and more on digital communication, the need for secure and reliable encryption methods becomes increasingly crucial. Quantum cryptography is a game-changing technology that has the potential to transform the way we secure our digital networks, making them virtually impenetrable to even the most sophisticated cyber attacks. While it is still in its infancy, the future of quantum cryptography is bright, and we can expect to see it playing an increasingly important role in our daily lives in the years to come.