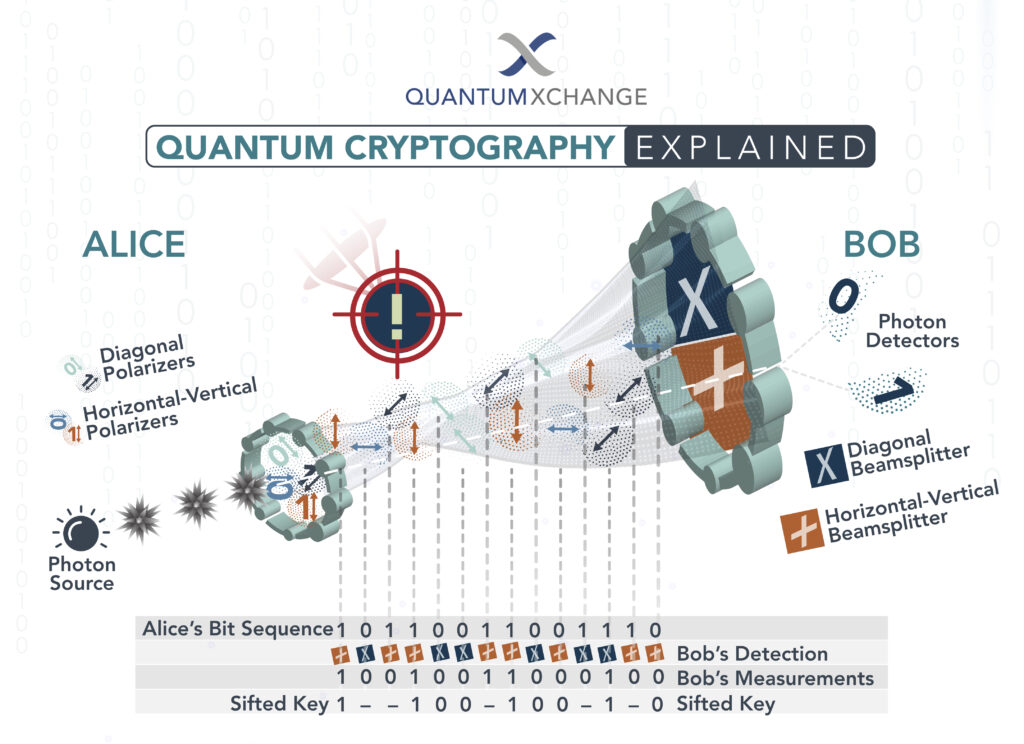
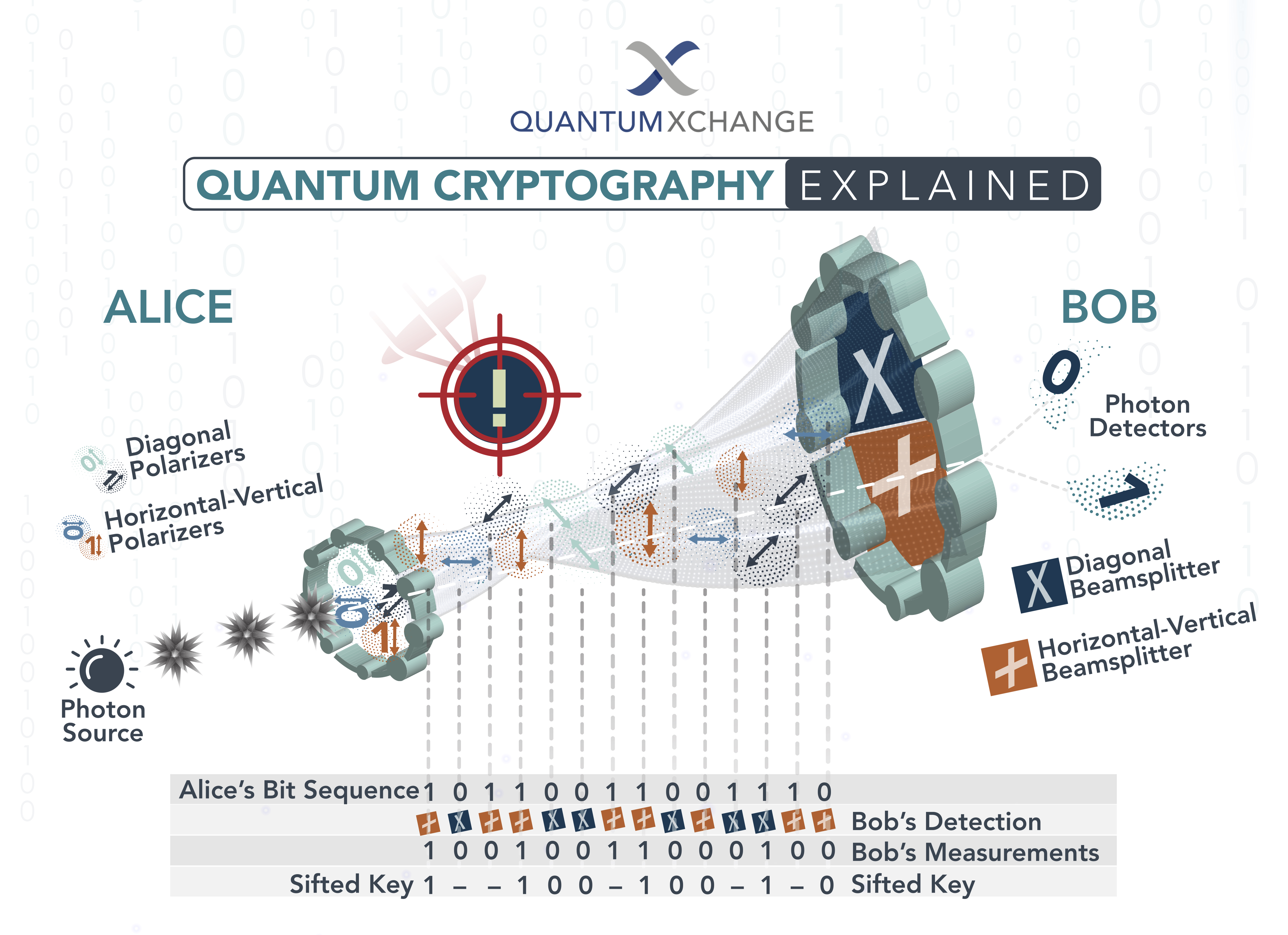
Quantum cryptography is a field that has emerged as a result of the limitations of classical cryptography. Classical cryptography uses mathematical algorithms to encode messages and protect sensitive information. However, advances in computing power have made these algorithms vulnerable to sophisticated attacks. This has led to the development of quantum cryptography, which relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to secure communication channels.
The purpose of quantum cryptography is to create unbreakable encryption methods that cannot be cracked by any known method, even with the most advanced computing technology available. The key to this unbreakable security lies in the principles of quantum mechanics, which allow for the creation of encryption keys that are impossible to intercept or copy. As a result, quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize the way we secure our communication channels, from banking transactions to military communications.
Quantum cryptography is a security technique that uses quantum mechanics to secure cryptographic communications. It allows two parties to generate a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. In addition, quantum cryptography provides an extra layer of security by using quantum mechanics to detect any attempts of interception. Quantum cryptography is also known as quantum key distribution.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a form of cryptography that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to securely transmit data. It relies on the fact that any attempt to intercept or eavesdrop on a quantum communication will disrupt the quantum state of the system, making it impossible to read the data without detection.
Unlike traditional encryption methods, which rely on mathematical algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data, quantum cryptography uses the principles of quantum physics to create and transmit data securely. This makes it much more difficult to break, since it is based on the laws of physics rather than mathematical algorithms.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by sending a stream of photons, or particles of light, over a secure channel between two endpoints. These photons are encoded with a specific quantum state, which can only be read by the intended recipient. If an eavesdropper attempts to intercept the data, the quantum state of the photons will change and the data will be unreadable.
This makes quantum cryptography much more secure than traditional encryption methods, as it is impossible to intercept the data without detection. The quantum state of the photons can also be used to detect any attempts to tamper with the data, further increasing the security of the system.
What is the Purpose of Quantum Cryptography?
The primary purpose of quantum cryptography is to provide a secure means of communication. Quantum cryptography is used to protect sensitive data, such as financial transactions and military secrets. It can also be used to protect internet traffic and ensure privacy in online communications.
Another important use for quantum cryptography is in the field of quantum computing. Quantum computers use principles of quantum physics to perform calculations at much higher speeds than traditional computers. To ensure the security of these systems, quantum cryptography can be used to protect the data from being intercepted or tampered with.
Frequently Asked Questions About Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a secure communication technique that utilizes quantum mechanics principles to protect data. It is used in a variety of applications, including banking, military, and medical records. Quantum cryptography is considered one of the most secure forms of encryption available.
What is the Purpose of Quantum Cryptography?
The purpose of quantum cryptography is to provide a secure form of communication. It uses the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure that the data being sent between two points is secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with. This makes it one of the most secure forms of encryption available.
Quantum cryptography is used in a variety of applications, such as banking, military, and medical records. The encryption used in quantum cryptography makes it virtually impossible for third parties to intercept or tamper with the data being sent between two points. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where security is of the utmost importance.
What are the Advantages of Quantum Cryptography?
The primary advantage of quantum cryptography is its security. The principles of quantum mechanics used in quantum cryptography make it virtually impossible for third parties to intercept or tamper with the data being sent between two points. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where security is of the utmost importance.
Another advantage of quantum cryptography is its speed. The use of quantum mechanics allows for data to be transferred quickly and securely. This makes it faster than traditional encryption techniques, which can be slow and unreliable. Additionally, quantum cryptography is not susceptible to the same vulnerabilities as traditional encryption techniques, making it a more secure form of communication.
What is Quantum Key Distribution?
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a form of quantum cryptography that is used to securely distribute a key between two parties. The key is used to encrypt and decrypt data sent between two parties. QKD utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure that the key is secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with.
QKD is considered one of the most secure forms of encryption available. It is used in a variety of applications, such as banking, military, and medical records. The use of QKD ensures that the data being sent between two points is secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with.
What are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
The primary limitation of quantum cryptography is its cost. The equipment used to implement quantum cryptography is expensive and requires a high degree of technical expertise to operate. Additionally, the data transfer rate is limited by the speed of the quantum particles used in the encryption process.
Another limitation is the distance over which quantum cryptography can be used. The distance between two points must be relatively short in order for the quantum particles to remain secure. As a result, quantum cryptography is typically used for point-to-point communication over relatively short distances.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by using the principles of quantum mechanics to encrypt data sent between two points. This is done by using two keys, one public and one private. The private key is known only to the sender, and the public key is known to both the sender and the receiver.
When data is sent between two points, the sender encrypts the data using the public key. The receiver then decrypts the data using the private key. This ensures that the data is secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with. The use of quantum mechanics in quantum cryptography makes it one of the most secure forms of encryption available.
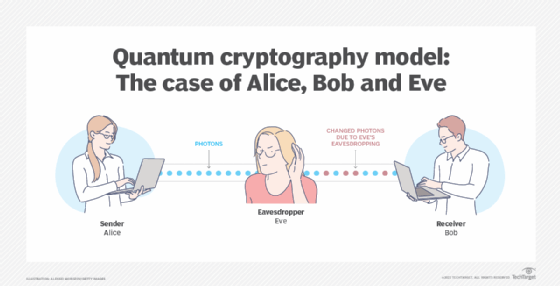
In conclusion, the purpose of quantum cryptography is to provide a secure way of transmitting sensitive information without the risk of interception or hacking. With the advancements in technology, traditional encryption methods have become more vulnerable to attacks. Quantum cryptography is based on the laws of physics and uses the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure the security of information. It has the potential to revolutionize the field of cybersecurity, making it possible to protect data from even the most advanced cyber threats.
As the world becomes more connected, the need for secure communication and data transfer will only increase. Quantum cryptography offers a promising solution to this challenge, making it possible to safeguard information in a way that was once thought impossible. While the technology is still in its early stages, it has already shown great promise, and researchers are working tirelessly to improve its capabilities. As we move forward into a more digital world, quantum cryptography will undoubtedly play a vital role in keeping our information safe and secure.