As computer networks become more complex, it becomes increasingly important to have tools and technologies that can help manage these systems efficiently. One such technology is the Switch Virtual Interface (SVI), which is a powerful feature of Cisco switches. SVI allows network administrators to create virtual interfaces on a switch that can be used to route traffic between VLANs, simplify network management, and provide a layer of security. In this article, we will explore what SVI is, how it works, and why it is an important tool for managing modern computer networks.
To understand SVI, it is important to first understand what a switch is and how it functions in a network. A switch is a networking device that connects devices on a local network, allowing them to communicate with each other. Each device connected to the switch is assigned a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address, which the switch uses to determine where to send data packets. SVI allows administrators to create virtual interfaces on the switch that can be used to route traffic between VLANs, which are logical groups of devices that are defined by their function or location. By creating these virtual interfaces, administrators can simplify network management, improve network security, and create a more efficient and scalable network infrastructure.
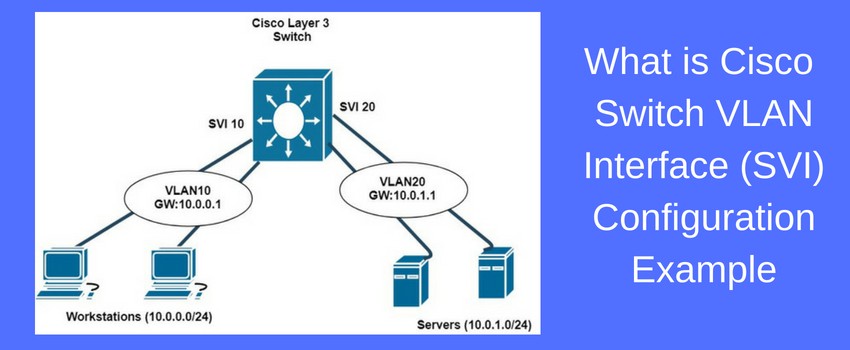
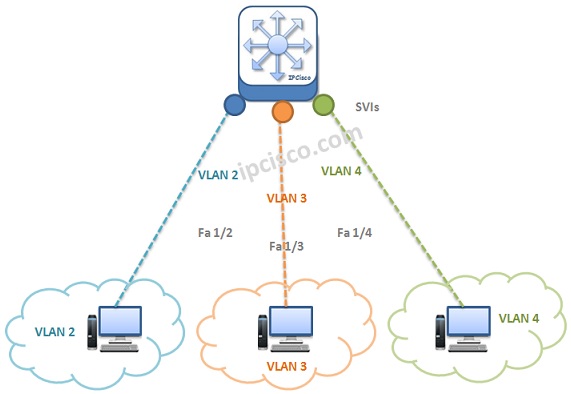
Switch virtual interface (SVI) is a virtual Layer 3 interface that is configured on a switch, allowing the switch to forward traffic to and from a Layer 3 IP network. It is used to provide inter-VLAN routing, allowing communication between different VLANs on the same physical switch.
What Is a Switch Virtual Interface (SVI)?
A switch virtual interface (SVI) is a type of virtual interface used in network switches. It is a virtual connection point between the switch and other devices, such as routers and other switches, as well as hosts connected to the switch. The SVI is used to manage and route traffic between the switch and other devices on the network.
An SVI is also known as a VLAN interface, as it is typically used to create virtual local area networks (VLANs). VLANs allow networks to be logically segmented, which can help improve security, reduce broadcast traffic, and simplify network management.
How Does an SVI Work?
An SVI is a virtual interface that is configured on the switch itself. It is typically configured with an IP address and subnet mask, and it serves as a gateway for traffic entering and leaving the switch. Any traffic destined for devices connected to the switch is routed to the SVI, which then forwards the traffic to the appropriate device.
When a packet is received from a connected device, the SVI will forward the packet to the appropriate device on the network. If the packet is destined for a device outside the network, the SVI will forward the packet to the default gateway, which is typically a router or another switch.
Advantages of SVIs
SVIs offer a number of advantages over physical connections. For example, they are easier to manage and configure than physical connections, as they can be configured and managed through the switch’s command line interface (CLI).
In addition, SVIs can be used to create VLANs, which can improve network security, reduce broadcast traffic, and simplify network management. They can also be used to isolate traffic from different departments or applications, which can help to improve network performance and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Finally, SVIs can be used to connect multiple switches together, creating a larger and more robust network. This can be useful for businesses that need to connect multiple locations or expand their networks.
Disadvantages of SVIs
While SVIs offer a number of advantages, they also have some drawbacks. For example, they require additional configuration and management, which can be time-consuming and complex. In addition, they can increase the complexity of the network, as they require additional routing protocols and services to be configured.
Finally, SVIs can increase the risk of security breaches, as they can be used to bypass security measures put in place on physical connections. For this reason, it is important to ensure that SVIs are properly configured and managed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a component of a Layer 3 switch that provides a gateway for traffic between different VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and IP networks. It enables communication among different VLANs without the need for a physical router.
What is Switch Virtual Interface?
Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a component of a Layer 3 switch that provides a gateway for traffic between different VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and IP networks. It enables communication among different VLANs without the need for a physical router. An SVI is a virtual Layer 3 interface configured on the switch, which provides the same function as a physical router connected to the switch. It allows inter-VLAN communication by routing traffic between VLANs.
How Does SVI Work?
When a packet arrives at the switch, the SVI inspects its header and determines the VLAN to which the packet belongs. The SVI then forwards the packet to the appropriate VLAN or IP network. This process is known as routing. The SVI also acts as a gateway, allowing communication between different VLANs and IP networks.
What Are the Benefits of Using SVI?
The main advantage of using SVI is that it reduces the cost of network infrastructure. It eliminates the need for physical routers, which can be expensive to purchase and maintain. SVI also simplifies network configuration and management, since all routing and switching needs are handled by the SVI.
Are There Any Drawbacks to Using SVI?
The main drawback of using SVI is that it can be more complex to configure and maintain than a physical router. It also requires a Layer 3 switch, which can be more expensive than a Layer 2 switch. Additionally, SVI is not as secure as a physical router, since it is not able to provide packet filtering.
How Do I Configure SVI?
Configuring SVI is relatively straightforward. The first step is to create a VLAN, which is done using the switch’s VLAN commands. Then, the SVI is created using the switch’s interface command. The SVI is then assigned an IP address and other parameters such as the VLAN ID. Finally, routing protocols are configured to allow communication between different VLANs.
video demonstration on how to configure a switch virtual interface
In conclusion, Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a powerful tool for network administrators to manage their networks with ease. It allows for the creation of a virtual interface on a switch that is associated with a VLAN. Thus, SVI provides a gateway between the VLANs and enables communication between them. This feature is particularly useful in large-scale networks where multiple VLANs are implemented to segregate traffic and improve network performance.
In summary, switch virtual interface is an essential component of modern networking that offers numerous benefits to network administrators. It simplifies network management, improves security, and enhances network performance. Therefore, businesses and organizations that rely on robust and efficient networks should consider implementing SVI on their switches to reap its full benefits.