Quantum cryptography ICT, the combination of quantum mechanics and information technology, is a rapidly growing field that is poised to revolutionize the way we transmit and secure information. At its most basic level, quantum cryptography is a method of encrypting information using the principles of quantum mechanics, which rely on the behavior of subatomic particles to create unbreakable codes. Unlike traditional encryption methods, which can be cracked with enough time and computing power, quantum cryptography offers a level of security that is virtually impossible to breach.
Despite its potential to transform the field of information security, quantum cryptography ICT is still in its infancy. Researchers are still working to refine the technology and develop new applications for it, but the possibilities are endless. From securing online transactions to protecting sensitive government communications, quantum cryptography is poised to become an essential part of our digital lives. In this article, we will explore the basics of quantum cryptography, its potential applications, and the challenges that researchers are facing as they work to bring this innovative technology to the mainstream.
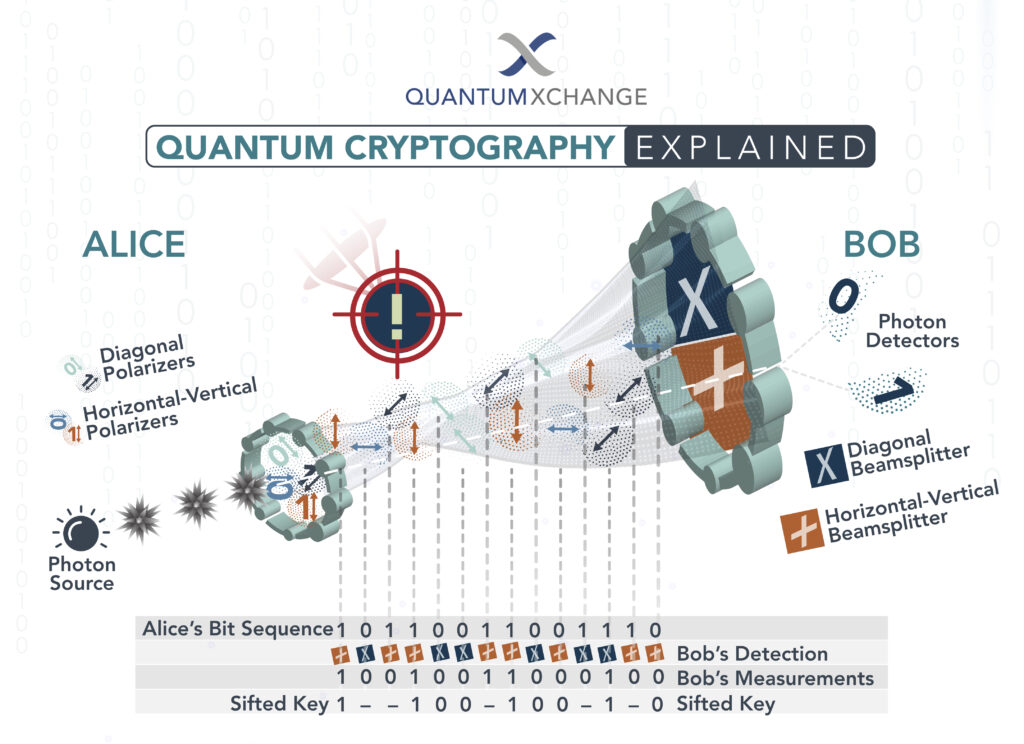
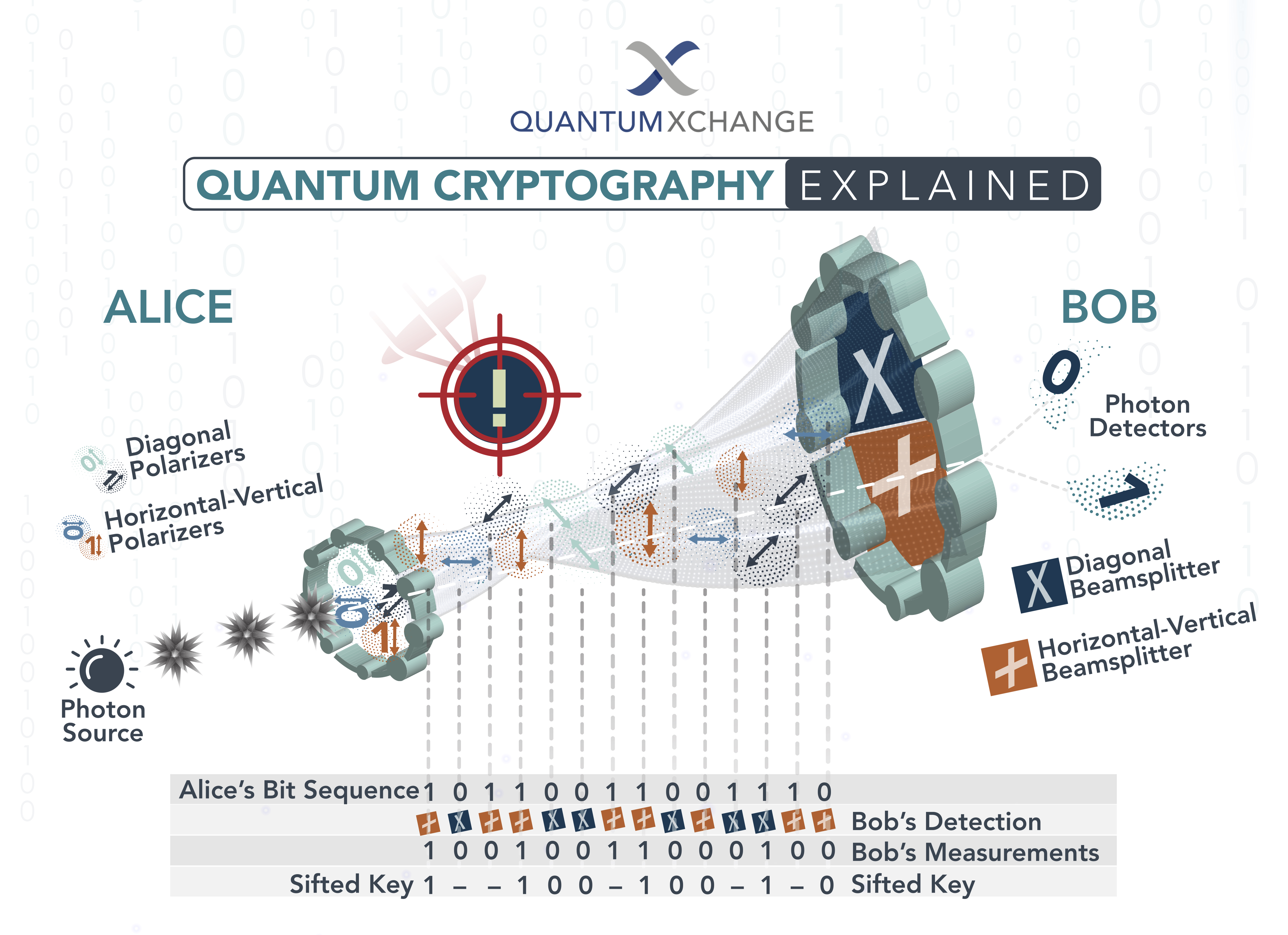
Quantum cryptography, or quantum key distribution (QKD), is a secure communication method that uses quantum mechanical properties to share a secret key between two parties. It enables two users to produce a shared, random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. QKD is considered to be one of the most secure forms of communication because it is impossible to eavesdrop without the sender and receiver noticing.
What is Quantum Cryptography ICT?
Quantum cryptography ICT is a specialized form of communication security based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is a new form of secure communication that uses the laws of quantum physics to protect data. This type of security is considered to be the most secure form of communication technology available. Quantum cryptography ICT is a branch of cryptography that uses quantum information technology to protect data.
How Does Quantum Cryptography ICT Work?
Quantum cryptography ICT works by using quantum entanglement, a phenomenon that occurs when two particles interact with each other, to establish a secure connection between two parties. In a quantum cryptography ICT system, two users exchange a series of quantum bits, or qubits, which are encoded using a quantum key. The qubits are then used to encrypt the data that is being sent between the two parties. The qubits are also used to generate a unique key that is used to decrypt the data. This key is only accessible to the two parties involved in the communication.
The quantum key is generated by the two parties exchanging a series of qubits which are then used to generate a unique key. This key is then used to encrypt and decrypt the data that is being exchanged between the two parties. The encryption and decryption process is done using an algorithm which is based on the principles of quantum mechanics. This algorithm ensures that the data is secure and cannot be intercepted or decrypted by any third-party.
Benefits of Quantum Cryptography ICT
The main benefit of quantum cryptography ICT is that it provides a high level of security for data transmission. This type of encryption is nearly impossible to break, even with the most advanced computers. This means that the data is secure and cannot be intercepted or decrypted by a third-party. Quantum cryptography ICT also provides a faster and more reliable form of communication than traditional encryption methods.
Another benefit of quantum cryptography ICT is that it can be used to communicate over long distances. This is beneficial for businesses or organizations that need to communicate securely over long distances. Quantum cryptography ICT also provides faster communication speeds than traditional encryption methods. This means that the data is transmitted faster and more securely.
Limitations of Quantum Cryptography ICT
The main limitation of quantum cryptography ICT is the cost. This type of encryption is more expensive than traditional methods, and it is not as widely available as other forms of encryption. Additionally, quantum cryptography ICT requires specialized hardware and software, which can be difficult to obtain and maintain. It also requires a high level of technical expertise to use and maintain the system.
Additionally, quantum cryptography ICT is not always suitable for all types of communication. For example, it is not suitable for voice communication or for data that is not encrypted. For these types of communication, traditional encryption methods are more suitable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum cryptography is a type of encryption that uses quantum mechanics principles to secure data. It makes use of particles of light (photons) to encode and transmit messages in such a way that they cannot be intercepted or tampered with without the sender and receiver being aware.
What is quantum cryptography?
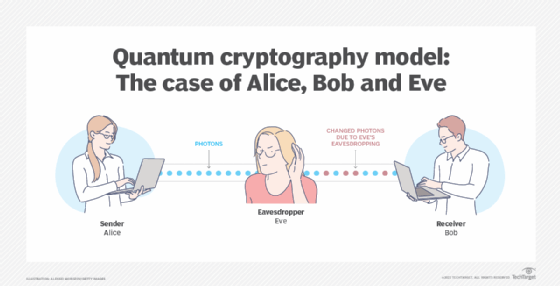
Quantum cryptography is a method of securely exchanging information using quantum mechanical properties. It is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which states that the physical properties of particles such as photons can be used to encode and transmit information. This makes it impossible to eavesdrop on the transmission without being detected, as any interference with the particles would be immediately apparent. The sender and receiver of the message can then be sure that the information being sent is secure and has not been tampered with.
How does quantum cryptography work?
Quantum cryptography works by encoding data into photons, which are particles of light. These photons are then sent via a secure channel between the sender and receiver. If any other party attempts to intercept the data, the photons will be affected and the receiver will be able to detect this. This means that the data can be transmitted securely and without the risk of it being tampered with.
What are the benefits of quantum cryptography?
The main benefit of quantum cryptography is the high level of security it provides. As any interference with the data will be immediately detected, it is impossible for a third party to access the data without the sender and receiver being aware. This means that sensitive information can be securely transmitted without the risk of it being compromised.
What is the difference between quantum cryptography and traditional cryptography?
The main difference between quantum cryptography and traditional cryptography is the level of security it provides. Traditional cryptography relies on mathematical algorithms to encrypt data, which can be broken if the right methods are applied. Quantum cryptography, on the other hand, relies on the physical properties of particles to transmit data securely and without the risk of interception or tampering.
Who uses quantum cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is used by a wide range of organisations and individuals who need to securely transmit sensitive information. This includes government agencies, financial institutions, and even individuals who wish to protect their data from being accessed by unauthorised parties. Quantum cryptography provides a high level of security and is an effective way of ensuring that data is kept safe from interception and manipulation.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is an emerging technology that offers a high level of