Quantum cryptography is a term that has been making waves in the world of cybersecurity for a while now. It is a cutting-edge technology that promises to revolutionize the way we transmit sensitive information across the internet. In simple terms, quantum cryptography is a technique that uses quantum mechanics to protect the privacy of digital communications. It is based on the principle that the act of observing a quantum system changes it, which makes it possible to detect any attempts to eavesdrop on a communication channel.
The concept of quantum cryptography may sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but it is very real and has already been implemented in some secure communication systems. With the rise of cybercrime and the increasing need for secure communication channels, the importance of this technology cannot be overstated. In this article, we will delve deeper into what quantum cryptography is, how it works, and why it is such a game-changer in the world of cybersecurity. So, fasten your seatbelts, and let’s take a journey into the fascinating world of quantum cryptography.
Quantum Cryptography is a method of securely sending and receiving data using quantum-based techniques. It uses the principles of quantum mechanics to generate encryption keys, which are then used to encrypt and decrypt data. Quantum cryptography is considered to be more secure than traditional encryption methods, as it is resistant to hacking and other forms of interception.
Quantum cryptography is an emerging technique for secure communication. It leverages the laws of quantum mechanics to generate and exchange secret keys, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages. This method is more secure than traditional cryptography, as it is resistant to hacking and interception.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography, also known as quantum key distribution (QKD), is a method of secure communication that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to protect data from malicious attack. It is a form of encryption that is based on the principle of quantum entanglement, which allows two parties to securely exchange information without it being intercepted by a third party. Quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize secure communication, as it is nearly impossible to break.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
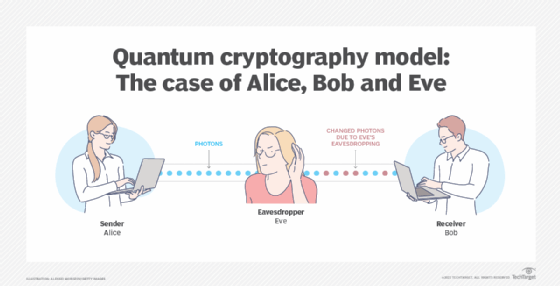
Quantum cryptography works by using a quantum channel to securely exchange a cryptographic key between two parties. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt messages sent over the channel. The security of the key is ensured by the laws of quantum mechanics, as any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication would cause the quantum system to collapse, alerting the two parties to the intrusion. As a result, quantum cryptography can provide a much higher level of security than traditional cryptographic methods.
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
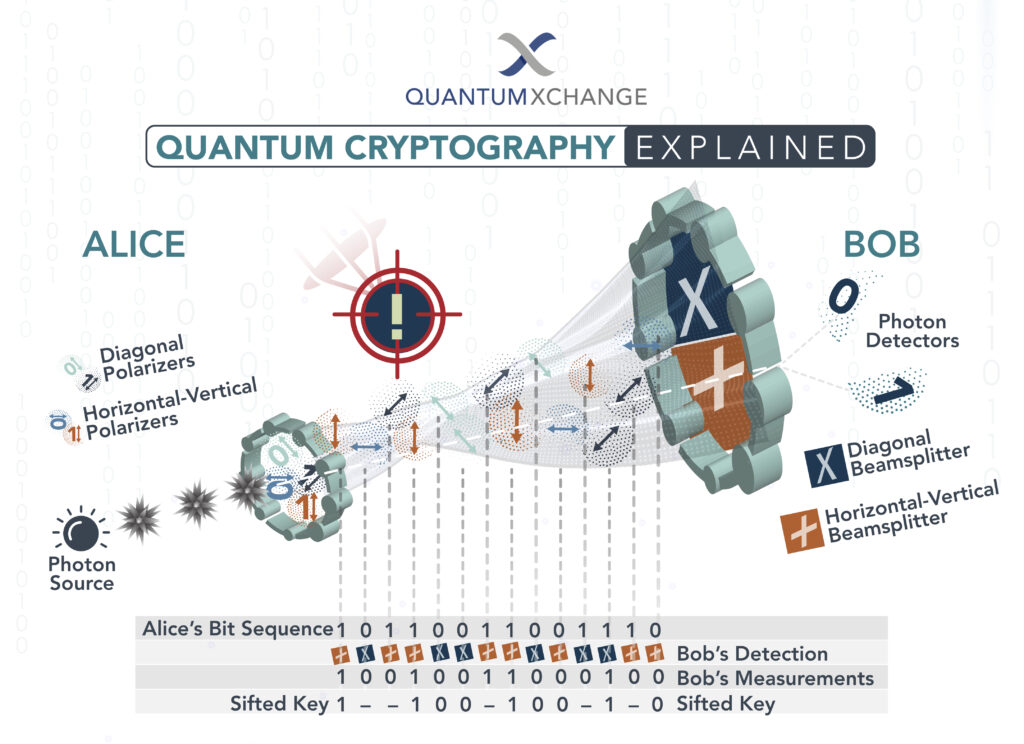
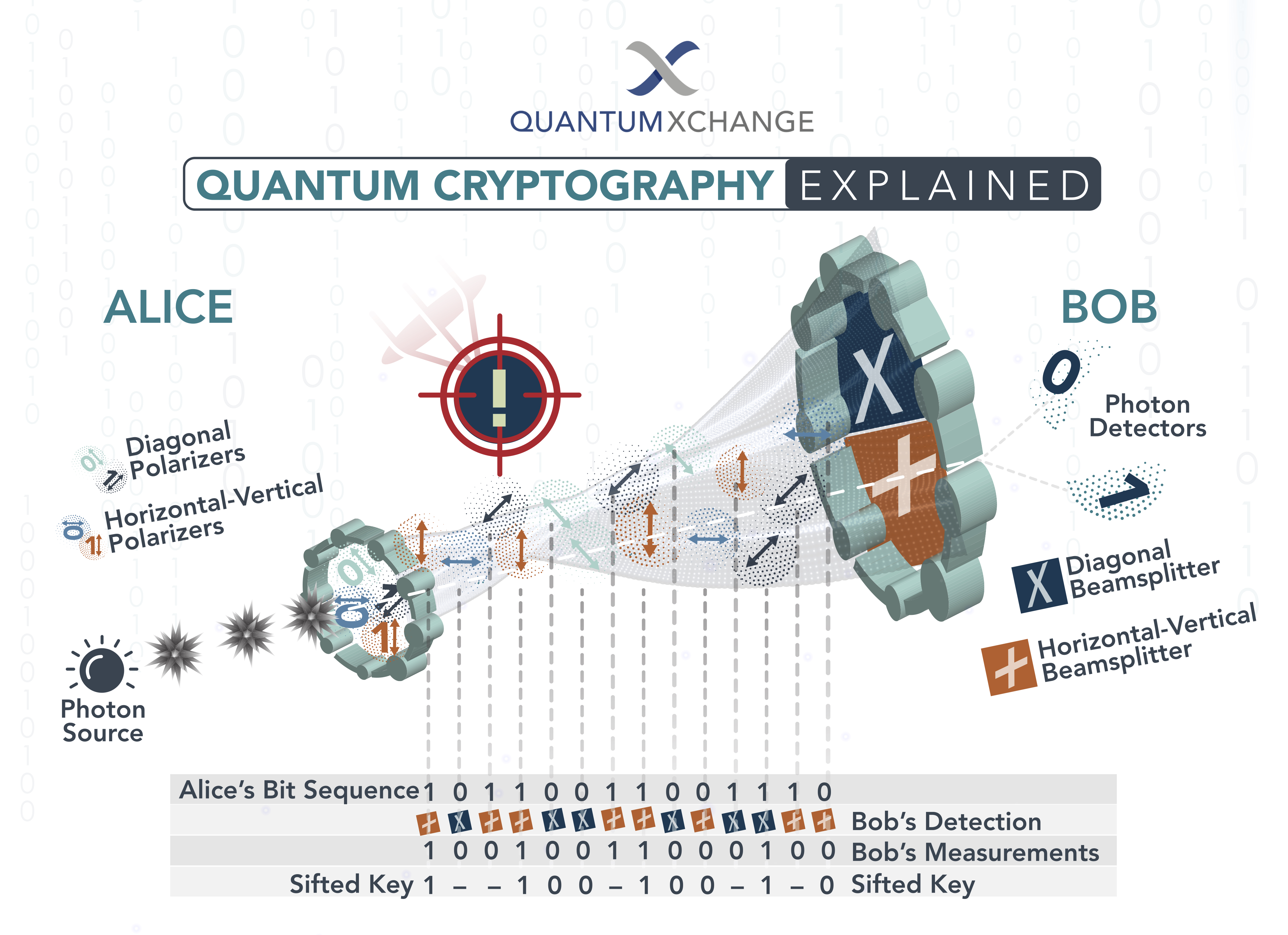
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is the most common implementation of quantum cryptography. In this process, two parties communicate using a quantum channel to securely exchange a cryptographic key, which is used to encrypt and decrypt messages sent over the channel. The security of the key is ensured by the laws of quantum mechanics. In order for a third party to eavesdrop on the communication, they would need to break the laws of quantum mechanics, which is virtually impossible.
QKD works by sending a stream of quantum bits, or qubits, between two parties. The two parties then measure the qubits and use the results to generate a random cryptographic key. This key is then used to encrypt and decrypt messages sent over the quantum channel. As any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication would cause the quantum system to collapse, the two parties are alerted to the intrusion and can take countermeasures against it.
The Benefits of Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography offers a number of benefits over traditional cryptographic methods. Firstly, quantum cryptography is virtually impossible to break, as any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication would cause the quantum system to collapse. This makes it the most secure form of encryption available. Additionally, quantum cryptography is much faster than traditional methods, as it does not require complicated computations or mathematical operations.
Furthermore, quantum cryptography can be used to securely exchange large amounts of data. As the security of the key is ensured by the laws of quantum mechanics, it can be used to securely send large amounts of data without the risk of interception. As a result, quantum cryptography is becoming increasingly popular for secure communication over long distances.
Frequently Asked Questions about Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is the science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to secure communications. It allows two parties to produce a shared random secret key known only to them, which can then be used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is an application of quantum mechanics that allows two parties to securely communicate by establishing a shared secret key. This key is generated by exploiting the properties of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, to create a secure communication channel. The parties can then use this key to encrypt and decrypt messages, ensuring that they can only be read by the intended recipient.
How Does it Work?
Quantum cryptography works by using photons to generate a shared secret key between two parties. The photons are sent through a quantum channel and then measured by a receiver. The properties of the photons are then used to generate a secret key that is known only to the two parties. Once the key is generated, it can be used to encrypt and decrypt messages sent over the channel, ensuring that only the intended recipient can access the message.
What are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
The main benefit of quantum cryptography is that it is unbreakable. Since the key is generated using the properties of quantum mechanics, it is impossible to crack or copy. This provides a secure communication channel that is not vulnerable to eavesdropping or interception.
What are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
The main limitation of quantum cryptography is that it is limited in range. The photons used to generate the secret key must remain within a certain range in order to be accurately measured. This means that the communication channel must be kept relatively short, limiting the practical applications of quantum cryptography.
What is the Future of Quantum Cryptography?
The future of quantum cryptography is promising. As the technology continues to develop, it is expected that quantum cryptography will become more widely used as a secure communication solution. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to extend the range of quantum cryptography, allowing it to be used for longer-distance communication.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a cutting-edge technology that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to provide secure communication channels. By harnessing the unique properties of quantum particles, quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize the way we transmit sensitive information. It offers an unparalleled level of security that is impossible to achieve with traditional cryptographic techniques.
Despite the many challenges that still need to be addressed before quantum cryptography becomes widely adopted, the potential benefits are clear. As we continue to rely more and more on digital communication, the need for secure channels becomes increasingly important. Quantum cryptography offers a promising solution to these security concerns, and it is an exciting field that will undoubtedly continue to evolve and grow in the years to come.