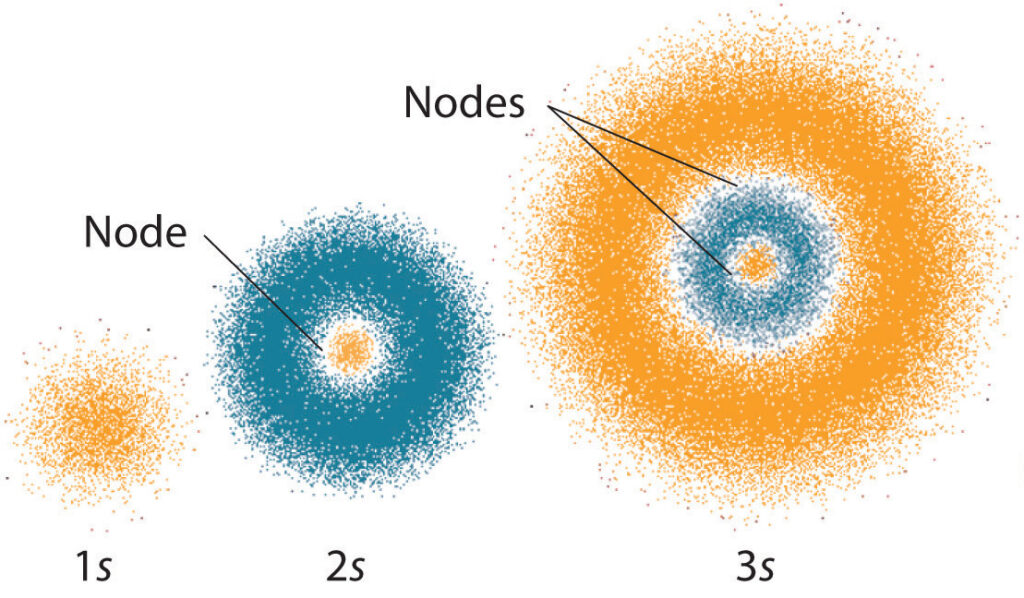
Quantum mechanics is a complex and fascinating branch of physics that has revolutionized our understanding of the universe. One of the fundamental concepts in this field is the idea of electron subshells, which are regions of space where electrons are likely to be found. Each subshell is characterized by a set of quantum numbers that provide information about the energy, angular momentum, and magnetic properties of the electrons within it. In this article, we will explore the question of what quantum numbers specify these subshells, and delve into the implications of this for our understanding of the behavior of atoms.
To begin with, it is important to understand the basic structure of an atom. At its core is a nucleus made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of electrons that orbit the nucleus. The electrons occupy different energy levels, or shells, which are further divided into subshells. These subshells are labeled using a four-part notation that indicates the values of four quantum numbers: n, l, m, and s. The values of these numbers determine the shape, orientation, and energy of the subshell, and provide important clues about the behavior of electrons within it.
Quantum numbers are used to specify the subshells in an atom. The four quantum numbers that specify a subshell are the principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (ml), and the spin quantum number (ms). The principal quantum number (n) describes the energy level of the electron, the angular momentum quantum number (l) describes the shape of the orbital, the magnetic quantum number (ml) describes the orientation of the orbital in space, and the spin quantum number (ms) describes the electron spin.
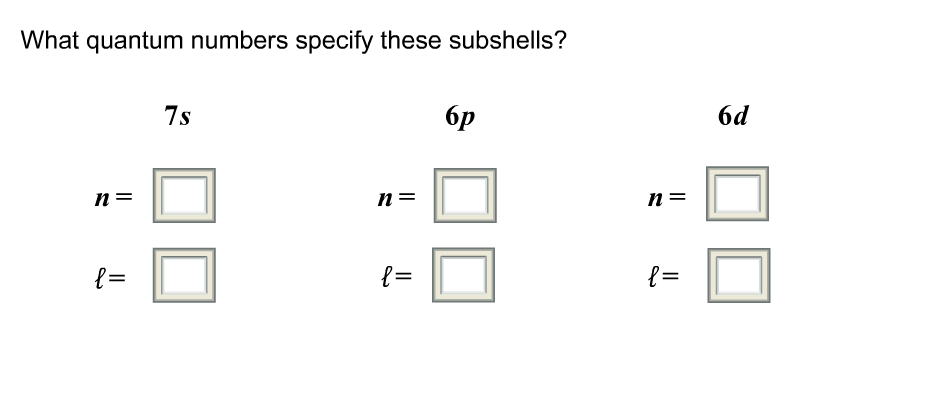
What is a Quantum Number?
Quantum numbers are used to describe the properties of an electron in an atom. They are used to describe the energy, angular momentum, and magnetic moment of the electron. In addition, quantum numbers also specify the size and shape of the electron’s orbit.
Quantum numbers are an important part of understanding the behavior of electrons in an atom. They are a tool used by scientists to study the structure of atoms and molecules.
What Quantum Numbers Specify Subshells?
Quantum numbers are used to identify the subshells of an atom. Subshells are regions of the atom where electrons are found. Each subshell contains a specific number of electrons and is identified by a unique combination of quantum numbers.
The first quantum number, known as the principal quantum number (n), is used to identify the subshell. The principal quantum number is equal to the number of electrons in the subshell. For example, the subshell with n = 1 contains one electron, while the subshell with n = 2 contains two electrons.
The second quantum number, known as the angular momentum quantum number (l), specifies the shape of the subshell. This quantum number can have values of 0, 1, 2, or 3. For example, a subshell with l = 0 is a s-subshell, a subshell with l = 1 is a p-subshell, and a subshell with l = 2 is a d-subshell.
The third quantum number, known as the magnetic quantum number (ml), specifies the orientation of the subshell. This quantum number can have values ranging from -l to +l. For example, a subshell with ml = -1 is an ml-subshell, a subshell with ml = 0 is an ms-subshell, and a subshell with ml = +1 is an mp-subshell.
The fourth quantum number, known as the spin quantum number (ms), specifies the spin of the electron. This quantum number can have values of +1/2 or -1/2. For example, an electron with ms = +1/2 has a clockwise spin, while an electron with ms = -1/2 has a counter-clockwise spin.
Together, these four quantum numbers specify the subshell of an atom. They provide a detailed description of the electron’s energy, angular momentum, and magnetic moment. By understanding the behavior of electrons in an atom, scientists are able to study the structure of atoms and molecules.
Frequently Asked Questions
A quantum number is a number that describes some physical property of an object, such as the energy state of an electron in an atom. Quantum numbers are used to describe the subshells, or orbitals, in an atom. In this article, we will answer questions about how quantum numbers specify subshells.
What are quantum numbers?
Quantum numbers are numerical values that describe the physical properties of particles, such as electrons. Specifically, they are used to describe the energy state of electrons in an atom. Each electron in an atom is designated by four quantum numbers, which describe its orbital and spin. These four quantum numbers are called the principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m_l), and the spin quantum number (m_s).
What does each quantum number represent?
The principal quantum number (n) represents the energy level of the electron. The larger the number, the higher the energy level. The angular momentum quantum number (l) represents the shape of the orbital, and can range from 0 to n-1. The magnetic quantum number (m_l) represents the orientation of the orbital in space, and can range from -l to l. Finally, the spin quantum number (m_s) represents the spin of the electron, and can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
How do the quantum numbers specify a subshell?
The quantum numbers specify the subshell of an electron by determining the energy level, shape, orientation, and spin of the electron’s orbital. The principal quantum number (n) determines the energy level, the angular momentum quantum number (l) determines the shape, the magnetic quantum number (m_l) determines the orientation, and the spin quantum number (m_s) determines the spin.
What is the significance of the subshells?
The subshells are important because they determine how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom. This arrangement of electrons determines the chemical properties of the atom, such as its reactivity and stability.
Is there a pattern to the quantum numbers?
Yes, there is a pattern to the quantum numbers. The principal quantum number (n) can range from 1 to infinity, while the angular momentum quantum number (l) can range from 0 to n-1. The magnetic quantum number (m_l) can range from -l to l, and the spin quantum number (m_s) can either be +1/2 or -1/2.

In conclusion, the concept of quantum numbers can be quite complex and intimidating for those who are not well-versed in the field of physics. However, understanding the quantum numbers that specify subshells is essential for comprehending the behavior of electrons in atoms. The four quantum numbers – principal, orbital, magnetic, and spin – all work together to define the unique properties of each subshell.
It is fascinating to consider how these quantum numbers play a crucial role in the behavior of electrons in atoms. The arrangement of electrons within subshells determines the properties of elements and their behavior in chemical reactions. As such, the study of quantum numbers and subshells is essential for those seeking to understand the fundamental nature of matter and the universe as a whole. By delving deeper into this subject, we can unlock the secrets of the physical world and gain a greater appreciation for the wonders of science.