Quantum cryptography is a cutting-edge technology that has revolutionized the field of information security. In today’s interconnected world, security breaches and data thefts have become a major concern for individuals and organizations alike. Traditional methods of cryptography, such as encryption and decryption, have proven to be vulnerable to attacks by hackers and cybercriminals. This has led to a growing need for more advanced and secure methods of communication, which is where quantum cryptography comes in.
Unlike traditional cryptography, which relies on mathematical algorithms to secure data, quantum cryptography uses the principles of quantum mechanics to create an unbreakable code. By harnessing the properties of subatomic particles such as photons, quantum cryptography ensures that any attempt to intercept or tamper with the data being transmitted will be immediately detected. This has made it an ideal solution for securing sensitive information such as financial transactions, military communications, and medical records. In this article, we will explore in detail the various applications of quantum cryptography and how it is solving some of the most pressing security challenges of our time.

Introduction to Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a form of cryptography that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to protect information. It is used to secure data transfers and communications, and to prevent the interception of sensitive information. Quantum cryptography has become increasingly important in recent years, due to the increasing need for secure communication systems.
What Problem is Quantum Cryptography Solving?
Quantum cryptography is used to protect information from being intercepted or compromised. It is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which allow particles of light (photons) to interact with each other without being observed. This makes it impossible for an eavesdropper to gain access to the information without being detected.
Quantum Key Distribution
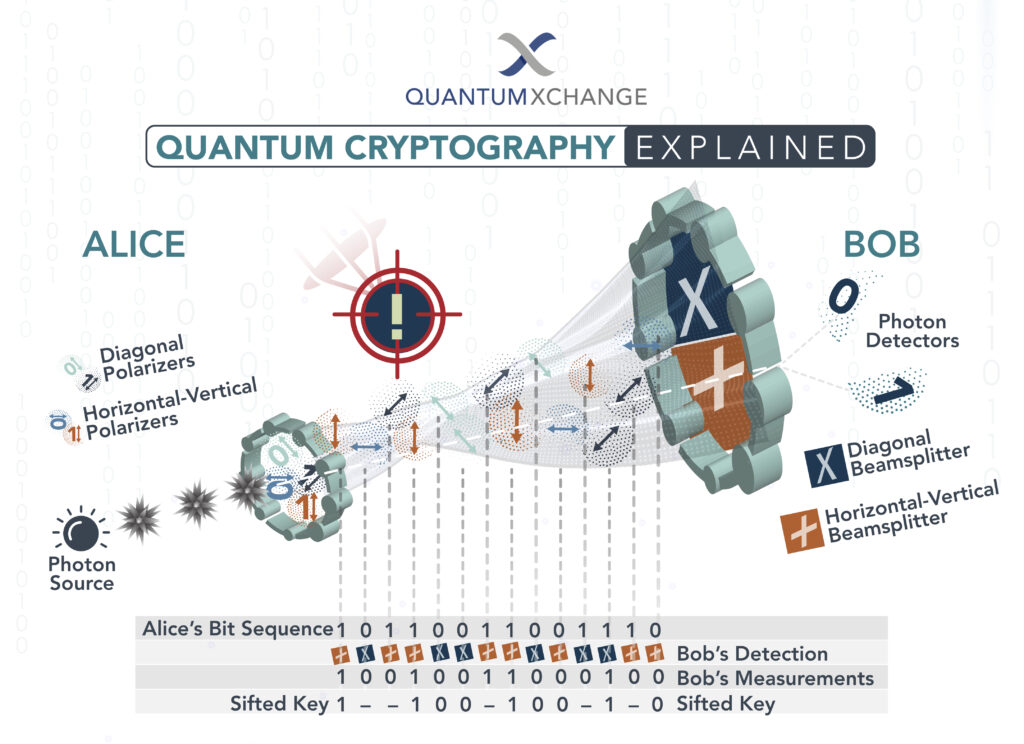
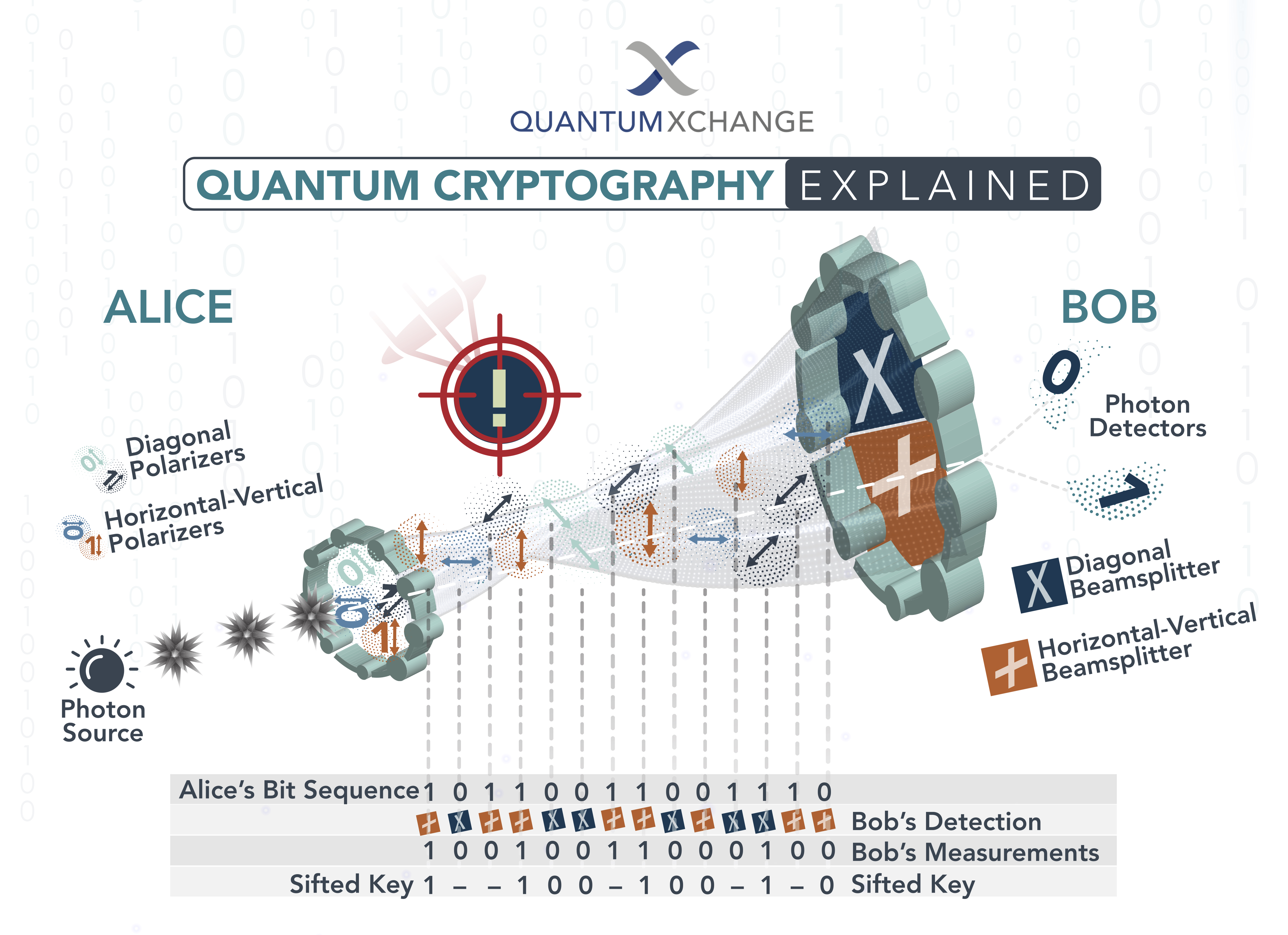
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a method of securely transferring a secret key between two parties, using the principles of quantum mechanics. In a QKD system, two parties generate a random string of numbers, which is used to encrypt the data they wish to send. This key is then securely sent over a quantum channel, making it impossible for an eavesdropper to gain access to the information.
QKD is an important part of quantum cryptography, as it prevents an eavesdropper from gaining access to the information without being detected. By using quantum mechanics, the two parties can be sure that their data is secure and that the key is not being intercepted.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a form of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. In a quantum computer, the data is stored in qubits, which are quantum particles that can exist in multiple states at the same time. This allows quantum computers to perform calculations that would be impossible for traditional computers.
Quantum computing has many potential applications, including cryptography. By using quantum computing, it is possible to create secure communication systems that are resistant to eavesdropping and data tampering. This makes quantum cryptography an important tool for protecting sensitive information.
Quantum Encryption
Quantum encryption is a form of cryptography that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to protect data. It is a type of encryption that is designed to be resistant to attacks from quantum computers. By using quantum encryption, it is possible to protect data from being accessed by an attacker, even if they have access to a quantum computer.
Quantum encryption is an important part of quantum cryptography, as it allows data to be securely transmitted without the risk of being intercepted or tampered with. This makes it an invaluable tool for protecting sensitive information.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum cryptography is a revolutionary technology, which is revolutionizing the way we secure data. It is a form of encryption, which uses quantum mechanics to ensure the secure transmission of data.
What problem is quantum cryptography solving?
Quantum cryptography is solving the problem of secure data transmission. Traditional cryptography relies on mathematical algorithms to secure data, which can be broken by powerful computers. Quantum cryptography, on the other hand, uses the laws of quantum mechanics to secure data. This is because quantum mechanics is inherently unpredictable, making it nearly impossible for an attacker to decode the data. Quantum cryptography also offers improved security, as it makes it almost impossible for an attacker to eavesdrop on the communication channel.
Quantum cryptography also offers a way to detect if a third party is attempting to intercept the data. This is because quantum cryptography relies on the exchange of particles, which can be detected if someone is attempting to interfere with the transmission. This makes it much harder for an attacker to intercept the data, and it also helps to ensure that the data is not tampered with during transmission.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a ground-breaking technology that is revolutionizing the way we approach data security. By harnessing the power of quantum mechanics, this technology can address many of the weaknesses that plague traditional cryptographic systems. With the increasing prevalence of cyber attacks and the growing importance of data protection, quantum cryptography is becoming an increasingly important tool in safeguarding sensitive information.
In order to fully realize the potential of quantum cryptography, it is essential that we continue to invest in research and development. While this technology is still in its infancy, the benefits it can provide are enormous. As we continue to explore the possibilities of quantum cryptography, it is clear that this technology has the potential to transform the way we approach data security and protect our most valuable assets.