Quantum mechanics is a fascinating and complex field of study that has challenged scientists for decades. One of the most intriguing aspects of this branch of physics is the concept of quantum numbers, which are used to describe the properties of subatomic particles. These numbers provide a way to understand the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules, and they play a crucial role in determining the arrangement of electrons in different energy levels.
In this article, we will explore the topic of quantum numbers and how they relate to subshells in the 6s energy level. We will delve into the specifics of these subshells, examining their unique properties and the factors that contribute to their behavior. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of quantum mechanics and the role that quantum numbers play in shaping our understanding of it. So, let’s dive in and explore the mysteries of the 6s subshells!
The 6s subshells are identified by the four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms.
The principal quantum number (n) determines the size of the orbital and the energy of the electron. It can take on any integer values from 1 to infinity. For the 6s subshell, n = 6.
The azimuthal quantum number (l) determines the shape of the orbital. It can have integer values ranging from 0 to n-1. For the 6s subshell, l = 0.
The magnetic quantum number (ml) determines the orientation of the orbital in space. It can take on integer values from -l to +l. For the 6s subshell, ml = 0.
The spin quantum number (ms) determines the orientation of the electron relative to its orbit. It can take on values of +1/2 or -1/2. For the 6s subshell, ms = +1/2 or -1/2.
What Are Quantum Numbers?
Quantum numbers are a set of four numbers that describe the state of a particular electron in an atom. Each quantum number has a specific meaning, and they are used to describe the energy levels, orientation, spin, and orbital shape of an electron.
What Does 6s Specify?
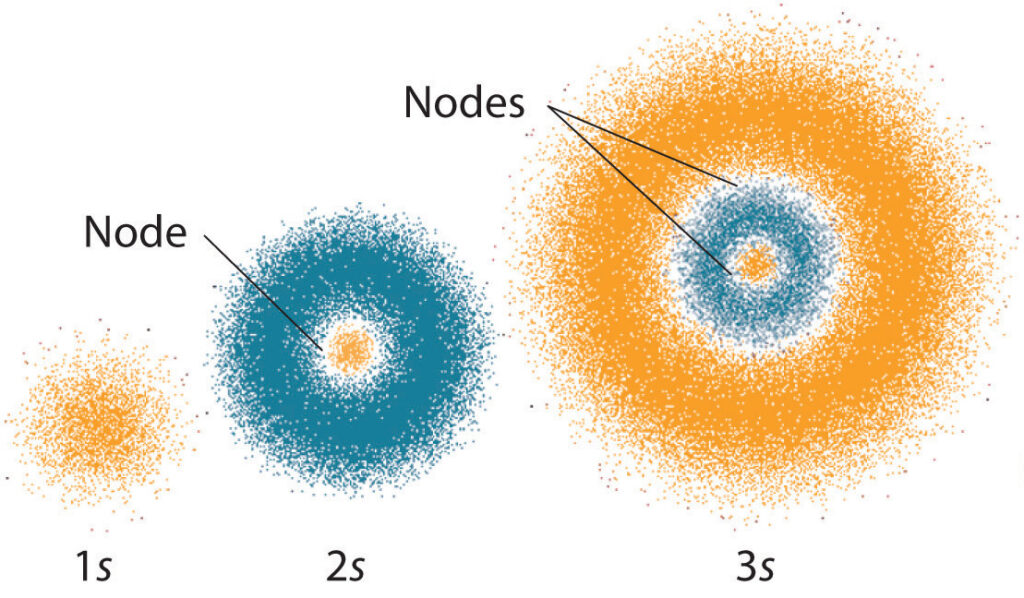
The 6s quantum number specifically identifies the subshells of an atom. A subshell is the set of orbitals that hold electrons with the same energy level. The 6s quantum number indicates that the subshell is of s type, which means that it is spherical in shape and has a single orbital. The number 6 indicates that the energy level is the sixth energy level from the nucleus.
Subshells and Orbitals
A subshell is a set of orbitals that hold electrons with the same energy level. Each orbital within the subshell can hold up to two electrons and has a different shape. The s-type subshell has one orbital, which is spherical in shape. The other types of subshells, such as p, d, and f, have multiple orbitals with different shapes.
The 6s quantum number can be used to identify the subshells of an atom. It indicates that the subshell is of s type and that the energy level is the sixth energy level from the nucleus. Knowing this information can help scientists understand the structure of an atom and how it interacts with other atoms.
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations
The quantum numbers of an electron can be used to determine its electron configuration. An electron configuration is a description of the arrangement of electrons within an atom. It is important for understanding the chemical behavior of an element.
The 4 quantum numbers – n, l, mℓ, and s – are used to describe the state of an electron. The quantum numbers indicate the energy level, orbital shape, orientation, and spin of the electron. By combining the quantum numbers, scientists can determine the electron configuration of an atom.
The 6s quantum number specifically indicates the subshells of an atom. It indicates that the subshell is of s type and that the energy level is the sixth energy level from the nucleus. Knowing this information is useful for understanding the structure of an atom and its electron configuration.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section covers questions about quantum numbers that are used to describe the subshells of 6s.
What are quantum numbers?
Quantum numbers are a set of numbers used to describe the energy states of particles, such as electrons. They are related to the values of energy, angular momentum, and other physical properties of a particle. In particular, the quantum numbers are used to identify the subshells of electrons in an atom. Each subshell is characterized by a set of four quantum numbers, which include the principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m_l), and the spin quantum number (m_s).
How do quantum numbers specify the subshells of 6s?
The quantum numbers are used to identify the subshells of an atom. For example, the 6s subshell of an atom is characterized by a principal quantum number of 6, an angular momentum quantum number of 0, a magnetic quantum number of 0, and a spin quantum number of +1/2. This means that the 6s subshell is composed of electrons with a total energy of 6 and an angular momentum of 0. The magnetic quantum number of 0 indicates that the electrons in the 6s subshell have no magnetic moment, while the spin quantum number of +1/2 indicates that the electrons have a spin of one-half.
What are the energy levels of the 6s subshell?
The energy levels of the 6s subshell are determined by the principal quantum number (n). The 6s subshell has a total energy of 6 and consists of electrons with an angular momentum of 0. The energy levels of the 6s subshell are the same as those of the 5s subshell and the 4s subshell. The energy of the 6s subshell is greater than that of the 5s subshell, and lower than that of the 4s subshell.
What is the maximum number of electrons in the 6s subshell?
The maximum number of electrons in the 6s subshell is 2. This is due to the fact that the angular momentum quantum number (l) for the 6s subshell is 0. This means that the electrons in the 6s subshell can only have two possible spin orientations: up or down. Each spin orientation can accommodate one electron, for a total of two electrons.
What are the properties of the 6s subshell?
The 6s subshell has a principal quantum number of 6, an angular momentum quantum number of 0, a magnetic quantum number of 0, and a spin quantum number of +1/2. This indicates that the 6s subshell consists of electrons with a total energy of 6 and an angular momentum of 0. The magnetic quantum number of 0 indicates that the electrons in the 6s subshell have no magnetic moment, while the spin quantum number of +1/2 indicates that the electrons have a spin of one-half. The 6s subshell is capable of accommodating up to two electrons, and is higher in energy than the 5s subshell, but lower in energy than the 4s subshell.
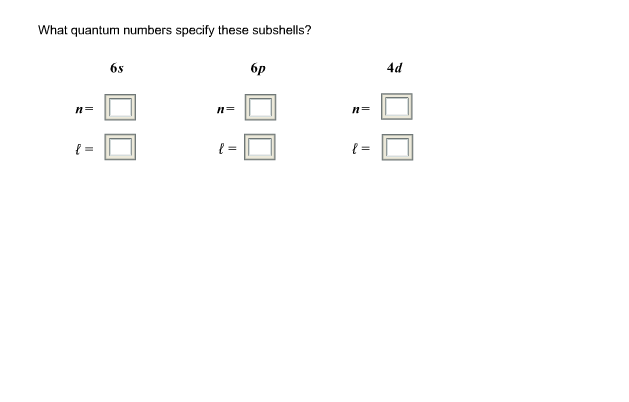
In conclusion, the quantum numbers play an essential role in describing the arrangement of subshells within an atom. By specifying the values of n, l, m, and s, we can determine the energy levels and orientation of electrons in the subshells. For the subshell 6s, the quantum numbers are n=6, l=0, m=0, and s=+1/2. This means that the 6s subshell has six energy levels and no angular momentum, but it does have a spin of +1/2.
Understanding the quantum numbers is crucial in explaining the behavior of atoms, including their chemical properties and reactivity. As scientists continue to explore the mysteries of quantum mechanics, we gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental building blocks of our universe. The subshell 6s may seem like a small piece of the puzzle, but it is a crucial component in unlocking the secrets of the quantum world.