As the world becomes increasingly reliant on the internet, the need for secure communication has never been more important. Cryptography, the science of encoding and decoding messages, has been a cornerstone of secure communication for centuries. However, with the advent of quantum computing, there are growing concerns that cryptography as we know it may be vulnerable to attack.
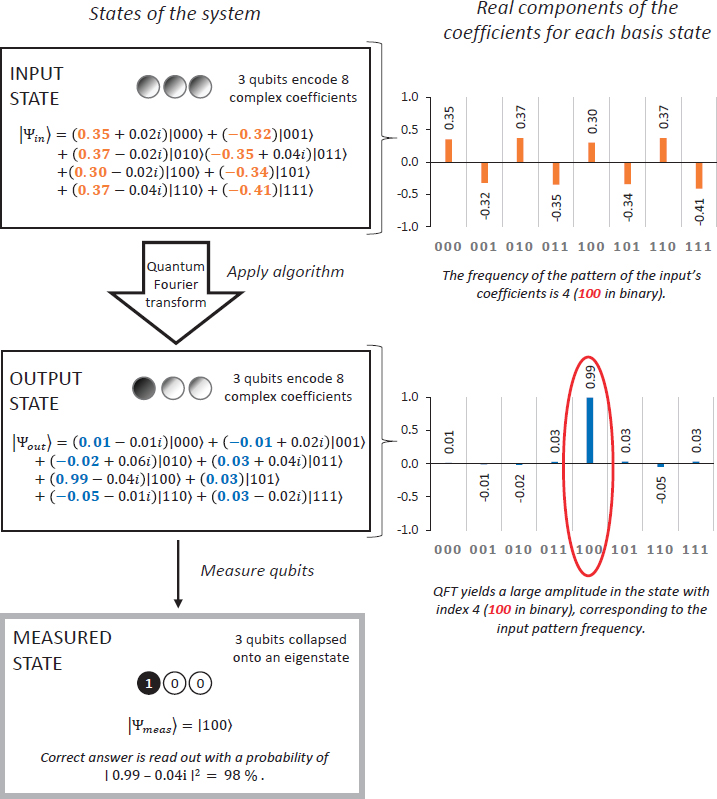
Quantum computing is a rapidly advancing field of study that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. Unlike classical computers, which use bits to represent information as either 0 or 1, quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical computers. While this has the potential to revolutionize computing and solve some of the world’s most complex problems, it also poses a significant threat to cryptography. In this article, we will explore how quantum computing could break cryptography and what steps are being taken to mitigate this risk.
How Would Quantum Computing Break Cryptography?
Cryptography is a method used to secure and protect data, and it has been used since ancient times. Quantum computing is a new and promising technology that could potentially break existing cryptography. In this article, we will discuss how quantum computing could break cryptography and the potential implications of this advancement.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a method of protecting and storing data using mathematical algorithms and secret codes. These algorithms are designed to make it difficult for unauthorized parties to access the data. This method of data protection has been used for centuries, and is often used in secure communication systems, electronic banking, and for protecting sensitive information.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a relatively new technology that uses quantum bits (qubits) instead of traditional bits to store and process information. Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, which allows them to process and store much more information than traditional bits. This makes quantum computers much faster and more powerful than traditional computers.
How Could Quantum Computing Break Cryptography?
Because quantum computers are so powerful, they could potentially be used to break existing cryptography. This is because quantum computers are able to process large amounts of data much faster than traditional computers. This means that they could potentially be used to decipher codes and algorithms that have been designed to protect data.
What Are the Implications of Quantum Computing Breaking Cryptography?
If quantum computing is able to break existing cryptography, it could have serious implications for the security of data. This could mean that confidential information, such as banking records and medical records, could be accessed by unauthorized parties. This could lead to a wide range of issues, including identity theft, financial loss, and even cyber-attacks.
What Can Be Done to Prevent Quantum Computing from Breaking Cryptography?
To prevent quantum computing from breaking existing cryptography, it is important to develop better algorithms and encryption methods that are more resistant to quantum computing. Additionally, governments and organizations should invest in research and development into quantum-resistant cryptography. This will help to ensure that data remains secure even in the face of quantum computing.
What Does the Future Hold for Quantum Computing and Cryptography?
Although quantum computing could potentially break existing cryptography, research and development into quantum computing and cryptography is ongoing. This means that new and improved algorithms and encryption methods could be developed that make data more secure. Additionally, there is potential for quantum computing to be used to develop new forms of encryption and cryptography that are even more secure than existing methods.
Frequently Asked Questions about Quantum Computing and Cryptography
Quantum computing is a new and rapidly advancing area of computer science. It has the potential to revolutionize the way we process and store data, but it also poses a potential threat to existing encryption methods. In this article, we will look at the basics of quantum computing and how it could break cryptography.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a form of computing that uses quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. Unlike classical computers, which use bits represented by either 0s or 1s, quantum computers use qubits, which can represent both 0s and 1s simultaneously. This allows them to process and store data much more quickly and efficiently than traditional computers.
How Could Quantum Computing Break Cryptography?
Cryptography is a system of encoding data to protect it from unauthorized access or manipulation. It relies on complex mathematical algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data, and these algorithms are usually too complex for traditional computers to break in a reasonable amount of time. However, quantum computers have the potential to break these algorithms much faster, due to their increased processing power. This could potentially put sensitive data at risk, as it could be decrypted in a fraction of the time it would take with a traditional computer.
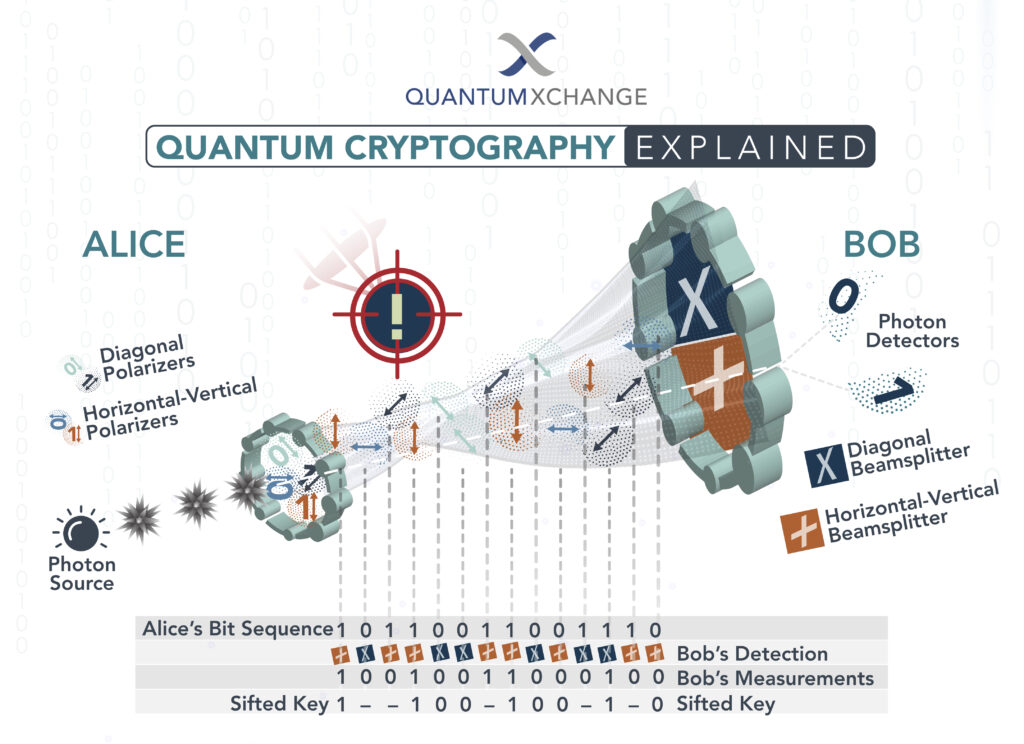
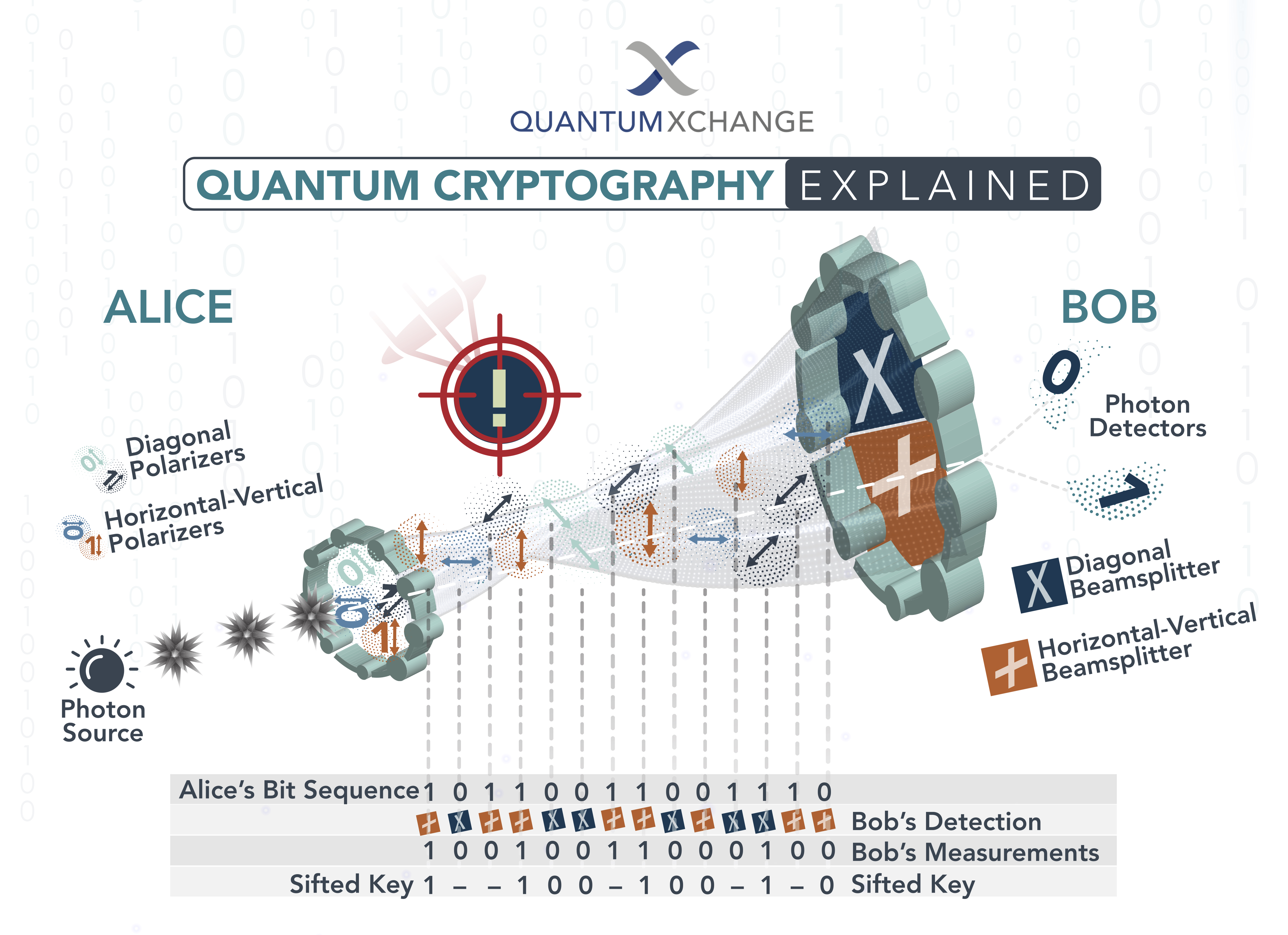
What is Quantum Key Distribution?
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a technology that uses quantum mechanics to securely transmit cryptographic keys over a network. It uses the principles of quantum entanglement to ensure that the keys cannot be intercepted or modified by a third party. By using QKD, it is possible to securely transmit data over a network without the risk of it being intercepted or decrypted.
What is Quantum-Safe Cryptography?
Quantum-safe cryptography is a system of encrypting data that is designed to be resistant to attacks from quantum computers. It uses quantum-resistant algorithms, such as lattice-based cryptography, to ensure that data is encrypted in a way that is secure even if a quantum computer were to attempt to break it. This is important as it helps to protect sensitive data from being accessed by unauthorized parties.
What is Post-Quantum Cryptography?
Post-quantum cryptography is a form of cryptography that is designed to be resistant to attacks from quantum computers. It uses algorithms that are designed to be resistant to quantum computing attacks, such as hash-based cryptography or code-based cryptography. This ensures that data is encrypted in a way that is secure even if a quantum computer were to attempt to break it.

In conclusion, the development of quantum computing has the potential to break cryptography as we know it. The ability of quantum computers to perform calculations at an exponentially faster rate than classical computers means that the encryption methods currently used to secure data could be easily cracked. This would have far-reaching implications for the security of personal and sensitive information, as well as for businesses and governments that rely on secure communication and data storage.
As we move towards a world where quantum computing becomes more prevalent, it is important that we invest in developing new encryption methods that are resistant to quantum attacks. This requires collaboration between industry experts, academics, and government agencies to stay ahead of the curve and ensure that our data remains secure. While the potential for quantum computing to break cryptography is a cause for concern, it also presents an opportunity to innovate and create new, more robust encryption methods that can withstand the power of quantum computers.