Quantum cryptography is a fascinating field that has revolutionized the way we approach information security. This emerging technology is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which allow us to encrypt messages in a way that is theoretically impossible to break.
But when exactly did quantum cryptography first come into existence? The answer to this question is not as straightforward as one might think. While the idea of using quantum mechanics for secure communication was first proposed in the 1970s, it wasn’t until the 1980s that practical experiments began to take place. In this article, we will explore the history of quantum cryptography, from its earliest beginnings to the cutting-edge developments of today.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
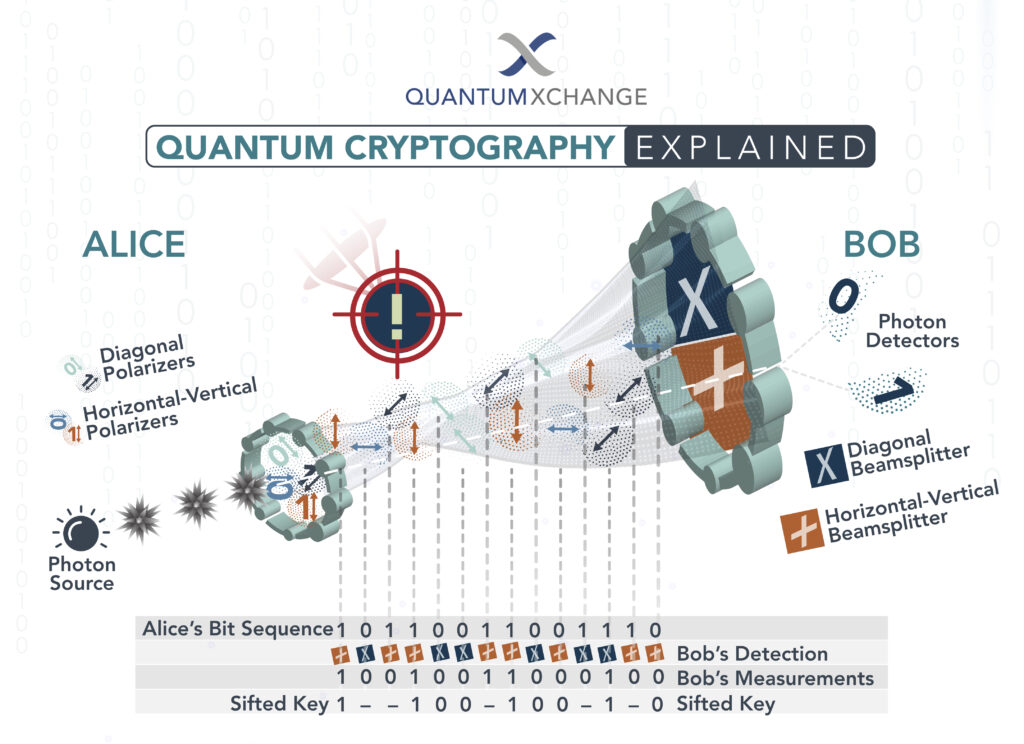
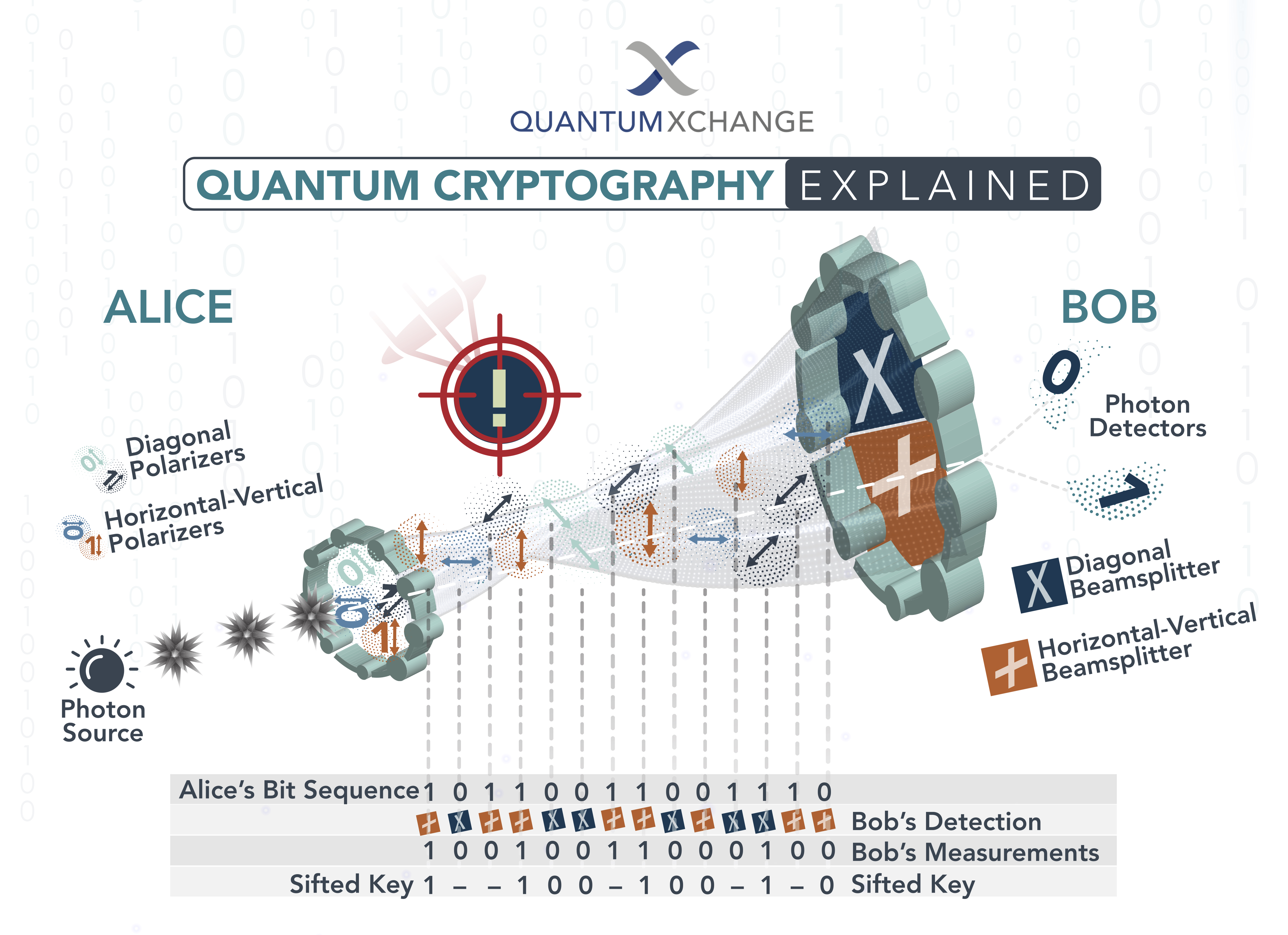
Quantum cryptography is an advanced encryption technique that uses individual particles of light, or photons, to secure communication between two parties. It is a secure and reliable way of communication that is impossible to decrypt without the right key. Quantum cryptography is a form of quantum computing that uses quantum mechanical systems to carry out calculations and encrypt data.
When Was Quantum Cryptography Invented?
Quantum cryptography was first developed in the early 1990s by physicist Charles Bennett and a team of researchers from IBM. The team developed a protocol called the Bennett-Brassard protocol, which is now widely used in quantum cryptography. This protocol is based on the principle of quantum entanglement, which is a phenomenon in quantum mechanics that occurs when two particles become linked together, regardless of their distance apart.
Quantum Cryptography in the 21st Century
Since its invention, quantum cryptography has become increasingly popular, and is now used by governments, banks, and corporations around the world. It is a secure and reliable form of communication that can’t be decrypted without the right key, making it an attractive option for protecting sensitive data. Quantum cryptography has been used to encrypt data in various applications, such as online banking and secure communications between military bases.
In recent years, the technology has evolved even further, with the development of quantum key distribution (QKD). QKD is a process that uses quantum mechanics to securely generate and distribute a cryptographic key, which can then be used to encrypt data. This technology has been used to create secure communications between two parties, as well as to encrypt data stored in the cloud.
The Future of Quantum Cryptography
As quantum computing continues to advance, so will quantum cryptography. This technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated, and researchers are now looking at ways to use it to create secure connections between multiple parties, as well as to encrypt data stored in distributed networks.
In addition, researchers are exploring ways to use quantum cryptography to create secure communication networks that are resistant to hacking and other cyberattacks. This could revolutionize the way we communicate, ensuring that our data is secure and protected from malicious actors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum cryptography is a method of secure communication that uses quantum mechanics to guarantee secure transmission of information over an insecure channel. It is the first protocol that provides information-theoretic security, meaning that an eavesdropper cannot gain any information about the transmitted data.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a method of secure communication that uses quantum mechanics to guarantee secure transmission of information over an insecure channel. It is the first protocol that provides information-theoretic security, meaning that an eavesdropper cannot gain any information about the transmitted data. This is achieved by using quantum entanglement, which is a physical phenomenon in which two particles are so strongly correlated that their wave-like behavior is linked, regardless of the distance between them. With quantum cryptography, the two communicating parties can detect any eavesdropping attempts and thereby prevent the transmission of any sensitive information.
When was Quantum Cryptography Invented?
Quantum cryptography was first proposed by physicist Charles Bennett in 1984, who was the first to realize the potential of quantum entanglement for secure communication. However, it was not until 1991 that the first quantum cryptography protocols were developed by researchers at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. Since then, quantum cryptography has become an active area of research and has been applied to various applications, such as secure communications, quantum key distribution, and quantum computing.
What are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography has several benefits over traditional cryptographic methods. It is the first protocol that provides information-theoretic security, meaning that an eavesdropper cannot gain any information about the transmitted data. It also offers unconditional security, meaning that the security of the system is not dependent on the computational power of an adversary. Additionally, quantum cryptography enables secure communication between two parties without the need for a trusted third party.
What are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
The main limitation of quantum cryptography is its limited range. This is due to the quantum nature of the signals used for communication, which are easily attenuated over long distances. Additionally, quantum cryptography systems require specialized hardware and expertise, which can be expensive and difficult to deploy. Furthermore, quantum cryptography systems are susceptible to various types of attacks, such as photon number splitting and entanglement swapping.
How is Quantum Cryptography Used?
Quantum cryptography is used in a variety of applications, including secure communication, quantum key distribution, and quantum computing. It is used in secure communication to ensure the privacy of data being transmitted over an insecure channel. Quantum key distribution is used to securely distribute encryption keys between two parties. Finally, quantum computing is used to solve problems that are intractable using traditional computing methods.

In conclusion, the invention of quantum cryptography marks a significant milestone in the world of cryptography. It has revolutionized the way we secure our communication channels by offering a level of protection that was previously thought impossible to achieve. The technology behind quantum cryptography is relatively new, having been invented in the early 1980s by Charles H. Bennett and Gilles Brassard.
Since its inception, quantum cryptography has undergone significant advancements, and we are now witnessing its implementation in various fields. It has been used to secure communication channels between banks, government agencies, and even military organizations. With the ever-increasing threat of cyber-attacks, the importance of quantum cryptography cannot be overstated. As technology continues to evolve, it is safe to say that quantum cryptography will remain an essential tool in securing our communication channels.