Quantum cryptography is a relatively new concept that has revolutionized the world of communication and data security. This technology is based on the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics, and it offers a level of security that is virtually unbreakable. But when was quantum cryptography first used? And how has it evolved over the years?
The concept of quantum cryptography was first proposed in the 1970s by physicists Stephen Wiesner and Charles Bennett. However, it wasn’t until the early 1990s that the first experimental demonstrations of quantum key distribution (QKD) were carried out. Since then, quantum cryptography has come a long way, and it is now being used in various applications, including secure communication, online banking, and military operations. In this article, we’ll explore the history of quantum cryptography, its applications, and the future of this exciting technology.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
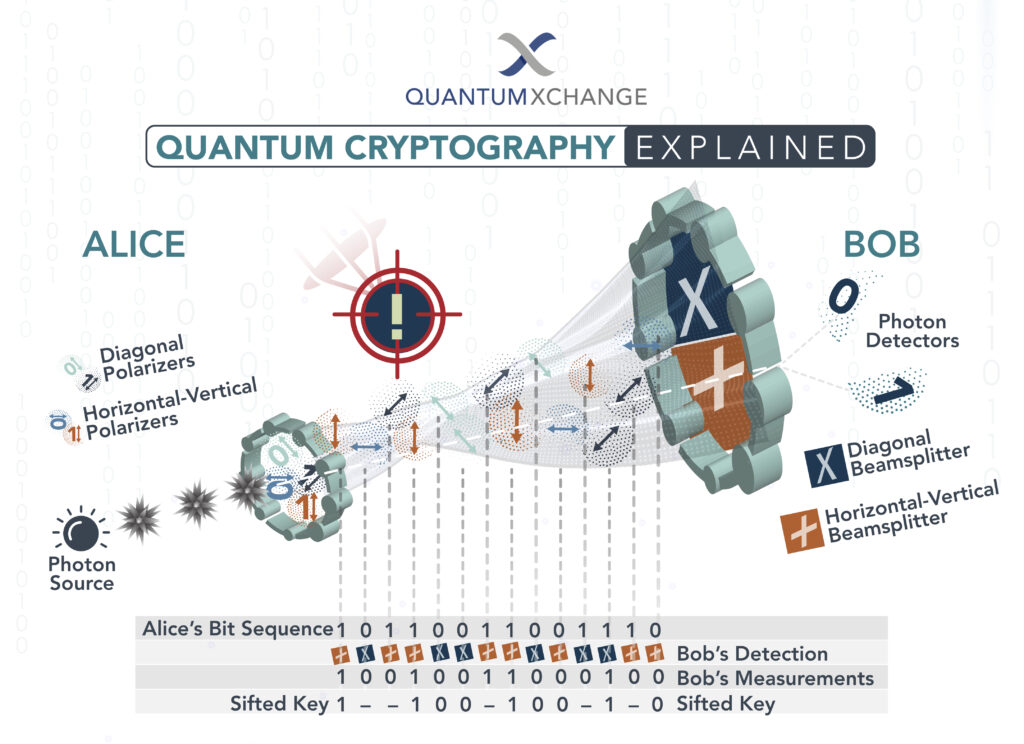
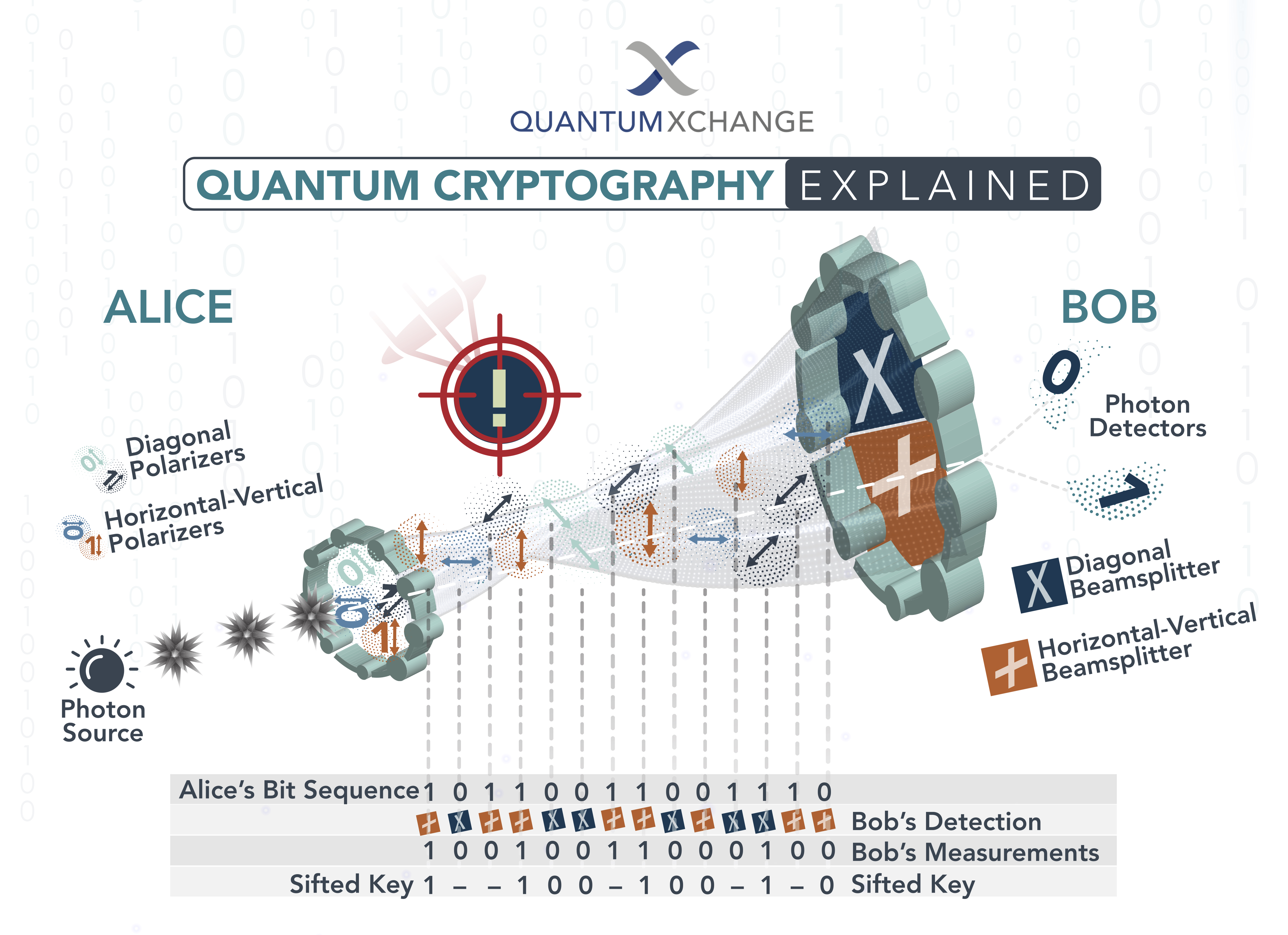
Quantum cryptography is an emerging field of cryptography that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to protect data. It is based on the fact that any attempt to measure or observe a quantum system changes its state. This makes it impossible for an eavesdropper to gain access to the data without being detected. Quantum cryptography is being used today to secure communications in banking, government and military applications.
When was Quantum Cryptography Used?
The first practical application of quantum cryptography was developed in the 1990s by researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Since then, quantum cryptography has been used in a variety of applications, including secure communication channels, secure storage of data, and authentication mechanisms. In addition, quantum cryptography is being used to protect the integrity of data in the cloud and to ensure the privacy of digital communications.
Secure Communication Channels
Quantum cryptography is used to secure communication channels, such as those used in banking and government applications. By using quantum cryptography, it is possible to ensure that the data sent over the channel remains secure from eavesdropping and other forms of tampering. This makes it ideal for applications where data needs to be kept confidential, such as those involving sensitive financial or government information.
Quantum cryptography can also be used to securely transmit data over long distances. By utilizing the principles of quantum mechanics, it is possible to send data securely through fiber optic cables or other mediums without the risk of interception. This makes it ideal for applications such as secure communication between military bases or between different countries.
Secure Storage of Data
Quantum cryptography can also be used to secure the storage of data. By using quantum cryptography, it is possible to ensure that data stored in the cloud remains secure from unauthorized access or tampering. This makes it ideal for applications where data needs to be kept confidential, such as those involving sensitive financial or government information.
In addition, quantum cryptography can be used to securely store data on computers and other devices. By using quantum cryptography, it is possible to ensure that data stored on a computer or other device remains secure from unauthorized access or tampering. This makes it ideal for applications such as the secure storage of digital currency and other sensitive data.
Authentication Mechanisms
Quantum cryptography can also be used to authenticate users and devices. By using quantum cryptography, it is possible to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access a given system or network. This makes it ideal for applications such as access control systems and authentication mechanisms.
In addition, quantum cryptography can be used to securely authenticate transactions. By using quantum cryptography, it is possible to ensure that only the intended parties involved in a transaction are able to access and complete the transaction. This makes it ideal for applications such as online banking, e-commerce, and other secure transactions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is an advanced form of cryptography that uses quantum mechanics to secure communication. It is based on principles of quantum mechanics which allow for secure communication and data transfer.
When was quantum cryptography first used?
Quantum cryptography was first developed in the 1980s by scientists working at IBM and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The first quantum cryptography system was developed in 1984 and was used to securely transmit data over a fiber-optic link. In the 1990s, the first commercial quantum cryptography systems were developed and deployed in the banking and finance industries.
Since then, quantum cryptography has been used in a variety of applications, ranging from secure government communications to protecting data in the healthcare industry. Quantum cryptography is also becoming increasingly popular in consumer applications, such as the use of quantum key distribution (QKD) to protect Wi-Fi networks and other online services.
What are the advantages of quantum cryptography?
The primary advantage of quantum cryptography is its ability to provide secure communication without requiring any prior knowledge between the sender and receiver. This makes it ideal for applications such as secure government communications and military operations, where the participants may not have any prior knowledge of each other.
Another advantage of quantum cryptography is its high level of security. Unlike classical cryptography, quantum cryptography is impossible to break, as any attempt to intercept the data will result in the data being destroyed. This makes it ideal for applications where data must remain secure, such as financial transactions and sensitive data transfers.
How does quantum cryptography work?
Quantum cryptography works by using the principles of quantum mechanics to encrypt data. In a quantum cryptography system, the sender and receiver both generate a random string of numbers, called a quantum key. This key is then used to encrypt and decrypt the data that is sent between the two parties.
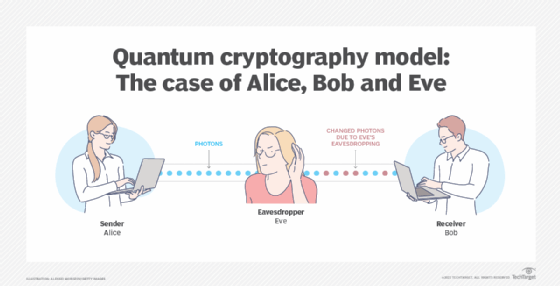
The key is generated by using a process known as quantum key distribution (QKD). In QKD, the sender and receiver generate a random key using a stream of photons (particles of light). The photons are sent through a quantum channel, and any attempt to intercept them will result in the photons being destroyed, thus preventing the key from being intercepted.
What are the limitations of quantum cryptography?
While quantum cryptography offers many advantages, it also has some limitations. One limitation is that it is only effective when the participants have a direct line of sight between them. This makes it impractical for applications such as long-distance communication. Additionally, quantum cryptography systems require specialized hardware and are expensive to implement.
Another limitation is that quantum cryptography is only effective if the participants trust each other. If either party is suspected of tampering with the data, the system will not be secure. Finally, quantum cryptography is not effective against certain types of attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks.
What are some applications of quantum cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is used in a variety of applications, ranging from secure government communication to protecting data in the healthcare industry. It is also becoming increasingly popular in consumer applications, such as the use of quantum key distribution (QKD) to protect Wi-Fi networks and other online services. Additionally, quantum cryptography is being used in the banking and finance industry to securely transmit data. Finally, quantum cryptography is being used to protect data stored in the cloud.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a relatively new and exciting field that has already seen practical applications in modern technology. While it was first proposed in the 1970s, it wasn’t until the 1990s that experimental demonstrations of quantum key distribution were reported. Today, quantum cryptography is used in various applications, including secure communication networks, financial transactions, and even elections.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more widespread use of quantum cryptography in various industries. With its ability to provide unbreakable security, it’s no wonder that many companies and government agencies are investing in this technology. So, when was quantum cryptography used? It’s being used right now, and its future is looking brighter than ever.