Quantum mechanics is a fascinating field of study that delves into the behavior of particles on a microscopic scale. The principles of quantum mechanics govern everything from the behavior of subatomic particles to the structure of complex molecules. One of the fundamental concepts in quantum mechanics is the concept of orbitals, which are regions of space around an atom where electrons are likely to be found. The shape of an orbital is determined by a specific quantum number, which plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of electrons.
The quantum number that determines the shape of an orbital is known as the azimuthal quantum number, or l. This number describes the shape of the orbital and is defined by the quantum mechanics equation for angular momentum. The value of l can range from 0 to n-1, where n is the principal quantum number that describes the energy level of the electron. The value of l determines the shape of the orbital, with different values of l corresponding to different shapes. Understanding the role of the azimuthal quantum number is crucial in understanding the behavior of electrons and the structure of atoms.
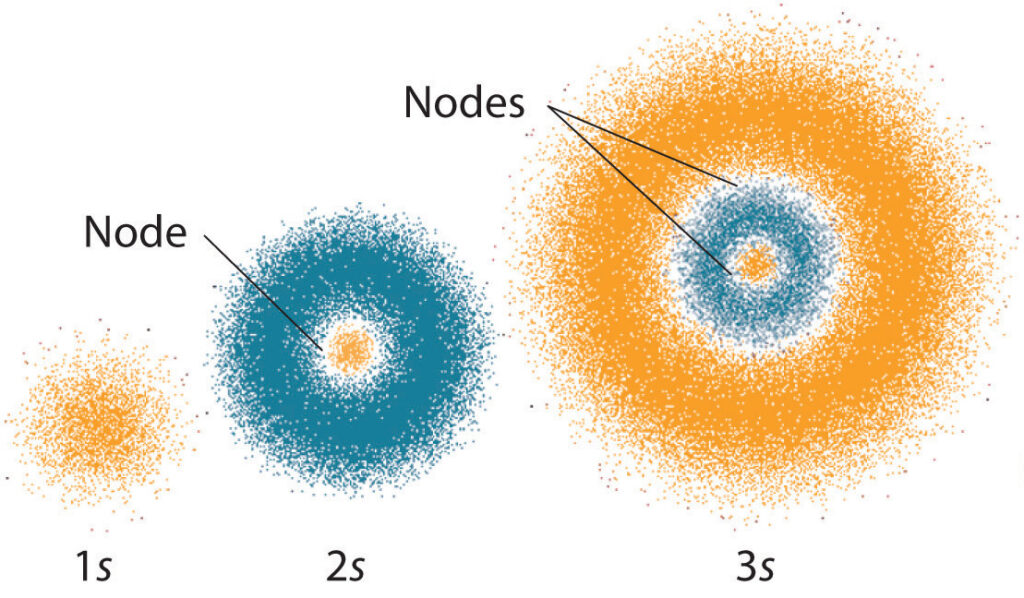
The quantum number n determines the shape of an orbital. The value of n indicates the energy level, or shell, of the orbital. The higher the value of n, the farther the orbital is from the nucleus of the atom. The shape of the orbital is determined by the value of the other three quantum numbers, ℓ, mℓ and ms. The angular momentum quantum number, ℓ, determines the shape of the orbital. The magnetic quantum number, mℓ, determines the orientation of the orbital, and the spin quantum number, ms, determines the spin of the electron.

Which Quantum Number Determines the Shape of an Orbital?
Quantum numbers, a set of four subscripts, are used to describe the unique characteristics of an electron’s orbit around the nucleus of an atom. The four quantum numbers are the principal quantum number (n), the angular momentum quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m), and the spin quantum number (s). The principal quantum number determines the energy level, while the angular momentum quantum number determines the shape of the orbital.
Principal Quantum Number (n)
The principal quantum number (n) is the most important of the four quantum numbers and is often referred to as the “shell” of the orbital. It defines the overall energy level of the electron, which is related to its distance from the nucleus. The principal quantum number is always a positive integer, and for any atom, the value can range from 1 to the number of electrons in the atom. The principal quantum number is not related to the shape of the orbital.
Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l)
The angular momentum quantum number (l) is the second most important of the four quantum numbers and is responsible for determining the shape of the orbital. This quantum number is represented by a letter ranging from s to f. The letter s corresponds to a spherical orbital, while the letters p, d, and f correspond to the shapes of the orbitals. The angular momentum quantum number is always an integer between 0 and n-1, where n is the value of the principal quantum number.
Magnetic Quantum Number (m)
The magnetic quantum number (m) is the third quantum number and is responsible for determining the orientation of the orbital within a given sub-shell. This quantum number can have any integer value ranging from -l to l, where l is the corresponding value of the angular momentum quantum number.
Spin Quantum Number (s)
The spin quantum number (s) is the fourth and final quantum number and is responsible for determining the spin of the electron. This quantum number has only two possible values, +1/2 and -1/2. The spin quantum number does not affect the shape of the orbital.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about what quantum number determines the shape of an orbital.
What is a Quantum Number?
A quantum number is a number that describes the state of a quantum mechanical system. In particular, it is used to determine the energy of an electron in an atom or molecule. Quantum numbers can also be used to describe the angular momentum of a particle, as well as the orientation and spin of its orbital.
What is an Orbital?
An orbital is a region of space in which an electron is likely to be found. The orbital is determined by the quantum numbers of the electron. The shape of the orbital is determined by the angular momentum quantum number, also known as the orbital angular momentum quantum number or l. This quantum number is related to the angular momentum of the electron, which is a measure of its “spin”.
What is the Angular Momentum Quantum Number?
The angular momentum quantum number, or l, is a quantum number associated with the angular momentum of an electron. This quantum number is related to the shape of the orbital of the electron. It is related to the magnetic quantum number, or m, which is a quantum number associated with the orientation of the orbital.
How Does the Angular Momentum Quantum Number Determine the Shape of an Orbital?
The angular momentum quantum number, or l, determines the shape of the orbital of an electron. This quantum number is related to the angular momentum of the electron, which is a measure of its “spin”. The angular momentum quantum number is related to the magnetic quantum number, or m, which is a quantum number associated with the orientation of the orbital. The shape of the orbital is determined by the angular momentum quantum number and the magnetic quantum number together.
What are the Different Shapes of Orbitals?
The shape of the orbital of an electron is determined by the angular momentum quantum number, or l. This quantum number is related to the angular momentum of the electron, which is a measure of its “spin”. The different shapes of orbitals are s, p, d and f. The s orbital is spherical, the p orbitals are dumbbell-shaped, the d orbitals are cloverleaf-shaped, and the f orbitals are complex, multi-lobed shapes.

Orbitals, Atomic Energy Levels, & Sublevels Explained – Basic Introduction to Quantum Numbers
In conclusion, the shape of an orbital is determined by the angular momentum quantum number, denoted as l. This quantum number serves as a crucial factor in determining the shape and energy of an electron in an atom. By providing information on the subshell and the number of orbitals present in it, the angular momentum quantum number helps to predict the distribution of electron density around the atomic nucleus.
In essence, understanding the concept of quantum numbers and their role in determining the properties of electrons in an atom is essential in the field of chemistry. It provides crucial information on the behavior of electrons and their interactions with other atoms, thereby helping to predict the chemical reactions and properties of different substances. Therefore, by delving deeper into the concept of quantum numbers, scientists can unlock new discoveries, broaden their understanding of the universe, and pave the way for new technological advancements.