As we delve deeper into the world of chemistry and physics, we come across the fascinating topic of atomic structure. The atomic model has undergone numerous changes since its inception, and one of the most significant contributions to this field was the development of the quantum mechanical model of the atom. But the question remains: who was the scientist behind this groundbreaking theory?
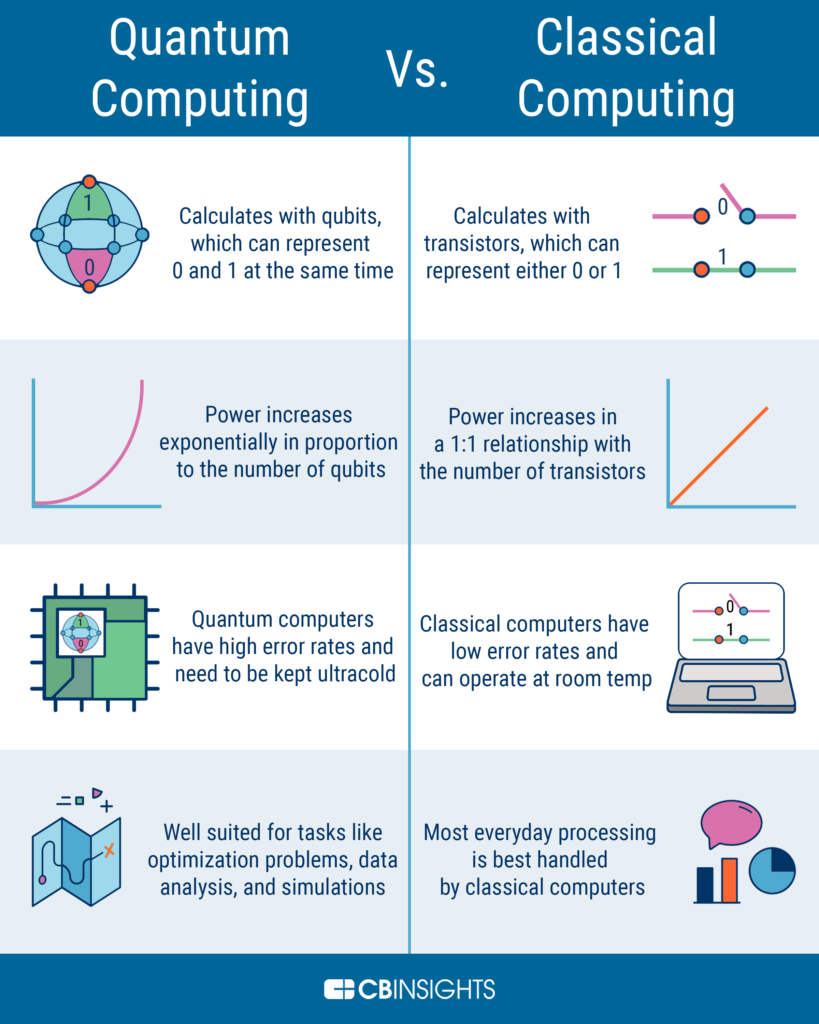
The quantum mechanical model of the atom was developed by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger in 1926. This model revolutionized the way we understand the structure of atoms and their behavior. Schrödinger’s model is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which describe the behavior of subatomic particles such as electrons. This model allows us to predict the probability of finding an electron in a particular region around the nucleus, rather than pinpointing its exact location. In this way, Schrödinger’s model provides a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the atom’s behavior than any previous model.
The quantum mechanical model of the atom was developed by the theoretical physicist, Erwin Schrödinger in 1926. Schrödinger’s model of the atom is based on a mathematical equation known as the Schrödinger equation. This equation is used to calculate the probability of particles being in certain positions and states within the atom. The model was groundbreaking at the time and is still used today to explain the behavior of atoms, molecules, and subatomic particles.

Introduction to the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
The quantum mechanical model of the atom is a theory that explains the behavior of atoms and their components. It was developed by a number of scientists in the early 20th century, including Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg, and Erwin Schrödinger. This model has been used to describe the structure, motion, and interactions of atoms, as well as the nature of the atomic nucleus.
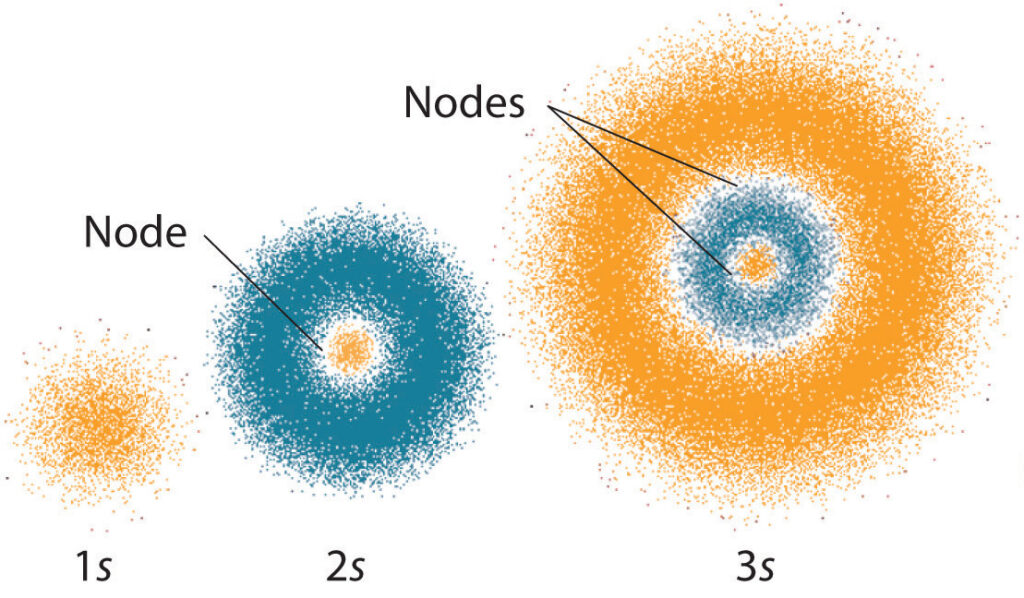
The quantum mechanical model of the atom is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which states that particles can exist in multiple states at the same time. This means that particles, such as electrons, can have different energies and positions, depending on the situation. This model is used to explain not only the behavior of atoms, but also the behavior of molecules, and even larger systems.
Niels Bohr and the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Niels Bohr and the Bohr Model
Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who is best known for his work on the quantum mechanical model of the atom. His work began in 1913 and he developed the Bohr Model of the atom, which proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in discrete energy levels. This model was able to explain the nature of the atom and its components, as well as the nature of the chemical bond.
The Bohr Model was the basis of the quantum mechanical model of the atom and it was later developed and refined by other scientists, such as Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger. The Bohr Model is still used today to describe the structure and behavior of atoms.
Heisenberg and Schrödinger’s Contributions to the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger both made significant contributions to the development of the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Heisenberg proposed the uncertainty principle, which states that the position and momentum of a particle cannot be known simultaneously. This principle was an important part of the quantum mechanical model of the atom and has been used to explain the behavior of atoms and their components.
Schrödinger proposed the wave equation, which is used to describe the behavior of particles. This equation is used to calculate the probability of a particle being in a certain state, as well as the energy of the system. This equation has been used to calculate the behavior of electrons, as well as the behavior of the nucleus.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section provides answers to questions about the scientist who developed the quantum mechanical model of the atom.
Who Developed the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom?
The quantum mechanical model of the atom was developed by the physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. A native of Denmark, Bohr was a student of Ernest Rutherford, the scientist who first proposed the nuclear model of the atom. Bohr’s quantum mechanical model was a refinement of Rutherford’s model, and it incorporated the principles of quantum theory to explain the behavior of electrons in atoms.
In his model, Bohr proposed that electrons existed in specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus of the atom. Electrons could only exist in these energy levels, and they could move between them by absorbing or emitting certain amounts of energy. This model helped to explain the behavior of electrons in atoms and was an important contribution to the development of atomic theory.
What is the Difference Between the Quantum Mechanical Model and the Nuclear Model?
The nuclear model of the atom was proposed by Ernest Rutherford in 1911 and proposed that the atom was composed of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of electrons. This model helped to explain the structure of the atom, but it did not explain the behavior of the electrons in the atom.
The quantum mechanical model was proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913 and incorporated the principles of quantum theory to explain the behavior of the electrons in the atom. In this model, Bohr proposed that electrons existed in specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus of the atom and that they could move between these energy levels by absorbing or emitting certain amounts of energy. This model provided a more accurate explanation of the behavior of electrons in atoms and was an important advancement in the development of atomic theory.
What is the Significance of Niels Bohr’s Quantum Mechanical Model?
Niels Bohr’s quantum mechanical model of the atom was an important advancement in the development of atomic theory. This model provided a more accurate explanation of the behavior of electrons in atoms and helped to explain phenomena such as the emission and absorption of light by atoms. This model also laid the foundation for the development of quantum mechanics and helped to explain the structure and behavior of atoms at the subatomic level.
Bohr’s model was also an important contribution to the development of modern chemistry and provided the basis for understanding how atoms interact with one another. This understanding has allowed scientists to develop a better understanding of how chemical reactions occur and has enabled the development of new materials and technologies.
What is Quantum Mechanics?
Quantum mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic levels. This branch of physics was developed in the early 20th century and was based on the principles outlined in Niels Bohr’s quantum mechanical model of the atom. Quantum mechanics explains the behavior of particles at the subatomic level and it is used in areas such as quantum computing, quantum cryptography, and nanotechnology.
Quantum mechanics is an incredibly complex field of study and it is not fully understood. It has been used to explain phenomena such as the behavior of electrons in atoms, the structure of molecules, and the behavior of light. It has also been used to develop new technologies, such as quantum computing, which have the potential to revolutionize the world of computing.
What is the Relationship Between Quantum Mechanics and Chemistry?
The quantum mechanical model of the atom proposed by Niels Bohr helped to explain the behavior of electrons in atoms and laid the foundation for the development of quantum mechanics. This model also provided the basis for understanding how atoms interact with one another and how chemical reactions occur.
Quantum mechanics has been used to explain the behavior of molecules and atoms and has enabled scientists to develop a better understanding of how chemical reactions occur. This understanding has allowed scientists to develop new materials and technologies, such as drugs and semiconductors, which have revolutionized the world of chemistry.

In conclusion, the development of the quantum mechanical model of the atom was a groundbreaking achievement in the field of physics. The model revolutionized our understanding of the behavior of atoms and their constituent particles, providing a more accurate and comprehensive picture of the subatomic world. While several scientists contributed to the development of the model, it was ultimately crafted by the brilliant mind of Erwin Schrödinger. His work on quantum mechanics not only earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics, but also paved the way for future generations of scientists to explore the fascinating and mysterious realm of quantum physics.
As we continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, it is essential to recognize the immense contributions of scientists like Schrödinger. Their tireless efforts and groundbreaking discoveries have brought us closer to unlocking the secrets of the universe and understanding the fundamental forces that govern our world. The quantum mechanical model of the atom is a testament to the power of human curiosity and ingenuity, and it will undoubtedly continue to inspire and inform generations of scientists for years to come.


Hello, I wish for to sbscribe for thhis web site to gett most recent updates,
sso whgere can i doo it please assist.
Have a look at my homepage https://team3connect.com/