As networks continue to grow in complexity, so does the need for efficient communication between different devices. Switch virtual interfaces (SVIs) play a crucial role in enabling this communication by bridging the gap between different network segments. A characteristic of an SVI is a critical aspect that network engineers need to understand to ensure that their networks operate optimally.
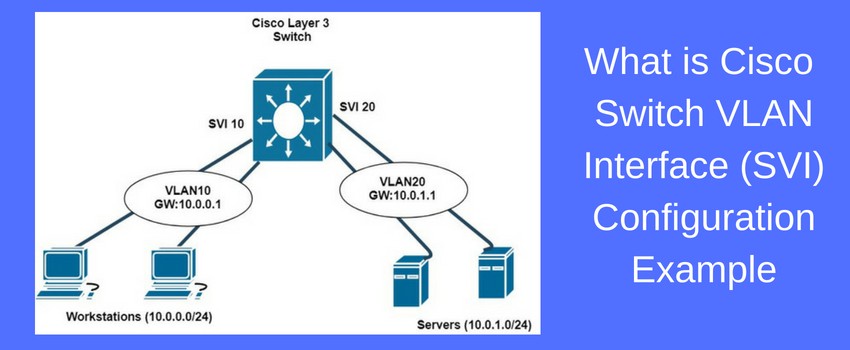
In essence, an SVI is a virtual interface created on a switch that allows communication between different VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) or subnets. It acts as a gateway between the devices on the network and the outside world, allowing the devices to communicate with each other and access resources outside their network segment. A characteristic of an SVI is that it is configured with an IP address, which enables it to act as a router interface for the VLAN or subnet it is assigned to. This characteristic is important because it allows the SVI to perform critical routing functions, such as forwarding packets between different network segments and managing traffic flow.
- It is configured in software on the switch instead of hardware.
- It provides a single point of configuration for all the switch ports.
- It allows the switch to be managed remotely.
- It can be configured with VLANs and Quality of Service (QoS) policies.
- It allows for the creation of routed connections between different VLANs.
What is a Switch Virtual Interface SVI?
A Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a virtual routing interface in a Layer 3 switch. It is used to provide inter-VLAN communication. An SVI is a logical interface in the network core that is created for each VLAN. It allows traffic to be routed between different VLANs, and provides a default gateway for each VLAN.
Characteristics of a Switch Virtual Interface SVI
Routing Protocols
A Switch Virtual Interface SVI supports various routing protocols, such as OSPF, RIP, EIGRP, and BGP. It also supports static routing, which allows for manually entered routes. The routing protocols used can be configured on the SVI to provide the most efficient path for traffic between different VLANs.
VLAN Access
A Switch Virtual Interface SVI allows for VLAN access. This means that the SVI can be used to provide access to different VLANs. Each SVI can be configured with a different VLAN ID, allowing for traffic to be routed to different VLANs. This allows for greater flexibility in the network, as it allows for different VLANs to be connected to different devices.
Security
A Switch Virtual Interface SVI provides improved security for the network. It allows for traffic to be routed to different VLANs, which can be configured with different security settings. This allows for greater control over who can access different areas of the network. Additionally, the SVI can be configured with access control lists (ACLs) to provide further security.
Management
A Switch Virtual Interface SVI can be managed through various management tools. These include the Cisco IOS command line interface, as well as various third-party management tools. This allows for greater flexibility in managing the network, and provides a centralized point for managing the SVI.
Performance
A Switch Virtual Interface SVI provides improved performance for the network. It allows for traffic to be routed more efficiently, as well as providing better control over the traffic. Additionally, the SVI can be configured to prioritize certain types of traffic, allowing for greater control over the network.
Frequently Asked Questions
Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a virtual Layer 3 interface on a switch that provides inter-VLAN routing in a multi-layer switch. It is an important feature of a switch that provides inter-VLAN routing in a multi-layer switch.
What is a switch virtual interface (SVI)?
A Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) is a virtual Layer 3 interface on a switch that provides inter-VLAN routing in a multi-layer switch. SVIs are created on a switch and are used to provide layer 3 connectivity between different VLANs. It is an important feature of a switch that provides inter-VLAN routing in a multi-layer switch.
An SVI is a Layer 3 interface that is configured on a switch and is used to provide Layer 3 connectivity between different VLANs. It is used to provide routing between VLANs within the same switch, as well as to external networks. SVIs are configured using the IP address assigned to each VLAN and are used for routing packets between VLANs.
What is the purpose of a switch virtual interface (SVI)?
The purpose of a switch virtual interface (SVI) is to provide layer 3 connectivity between different VLANs. It is used to provide routing between VLANs within the same switch, as well as to external networks. SVIs are configured using the IP address assigned to each VLAN and are used for routing packets between VLANs.
SVIs can also be used for other purposes such as providing virtual interfaces for spanning tree protocol, configuring port security, and configuring IP access lists. SVIs are also useful for providing connectivity between different VLANs, which is important for traffic control, security, and network management.
What are the benefits of using a switch virtual interface (SVI)?
One of the main benefits of using a switch virtual interface (SVI) is that it allows for inter-VLAN routing, allowing for better traffic control, security, and network management. It also allows for more efficient use of the available bandwidth and resources, as it eliminates the need for multiple physical interfaces. Additionally, it simplifies the configuration process, as all the necessary settings for VLANs can be configured in one place.
Another benefit of using an SVI is that it provides a layer of security as it isolates traffic from other VLANs. This is especially important in enterprise networks, where different departments or divisions are using different VLANs. Furthermore, SVIs can also be used to provide a virtual interface for spanning tree protocol, configuring port security, and configuring IP access lists.
What are the drawbacks of using a switch virtual interface (SVI)?
One of the main drawbacks of using a switch virtual interface (SVI) is that it can result in decreased performance as it requires more processing power to route traffic between VLANs. Additionally, it is not suitable for applications that require high throughput, as the interface cannot be configured to use multiple physical interfaces.
Another drawback is that SVIs are not compatible with all switch models, and some switches may require the installation of additional software or hardware in order to support this feature. Furthermore, SVIs can be vulnerable to security threats, as they must be configured correctly in order to ensure that traffic is properly routed between VLANs.
What is the difference between a switch virtual interface (SVI) and a physical interface?
The primary difference between a switch virtual interface (SVI) and a physical interface is that an SVI is a virtual interface that is configured on a switch, while a physical interface is a physical port on the switch. An SVI is used to provide layer 3 connectivity between different VLANs, while a physical interface is used to provide layer 2 connectivity between different devices.
Another key difference between an SVI and a physical interface is that an SVI can be used for other purposes such as providing virtual interfaces for spanning tree protocol, configuring port security, and configuring IP access lists. On the other hand, a physical interface can only be used to connect physical devices, such as computers, printers, or other network devices.
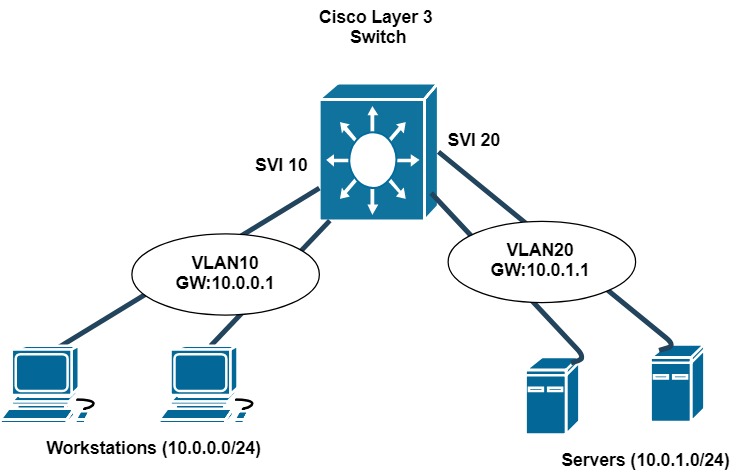
166 SVI and Routed Port Concepts
In conclusion, a switch virtual interface (SVI) is an essential component of a network switch that provides a logical interface for VLANs. It enables communication between VLANs by routing traffic between them and enables the creation of Layer 3 interfaces on a Layer 2 switch. One of the most critical characteristics of an SVI is its ability to assign a virtual IP address to a VLAN, allowing for network communication between different devices.
Without an SVI, VLANs would not be able to communicate with each other, and network performance would suffer. Therefore, it is essential to understand the characteristics of an SVI when designing a network infrastructure. As technology continues to evolve, the role of the SVI in network design will continue to be critical, making it an essential component for any network administrator to understand. By mastering this concept, network administrators can ensure that their networks are efficient, secure, and scalable, meeting the needs of today’s businesses and organizations.