In today’s world where the internet plays a significant role in our daily activities, the need for secure communication has become more crucial than ever. Cyberattacks have become a common occurrence, and traditional encryption methods are no longer enough to protect sensitive data. This is where quantum cryptography comes into play. But the question remains, is quantum cryptography required?
Quantum cryptography is a new technology that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to provide a highly secure method of communication. Unlike traditional encryption methods, quantum cryptography uses the laws of physics to ensure that data is transmitted securely. However, the implementation of quantum cryptography is still in its early stages, and it is not yet clear whether it is required for all types of communication or just for highly sensitive data. In this article, we will explore the benefits and limitations of quantum cryptography to help you understand whether it is necessary for your organization.
Is Quantum Cryptography Required?
Quantum cryptography is a rapidly evolving field of technology that has wide-reaching implications for the security of data and communication. Quantum cryptography is a mathematical and physical process that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure secure communication between two or more parties. Quantum cryptography is widely regarded as the most secure form of data encryption available today, and is increasingly being adopted by organizations and individuals to protect their sensitive information.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
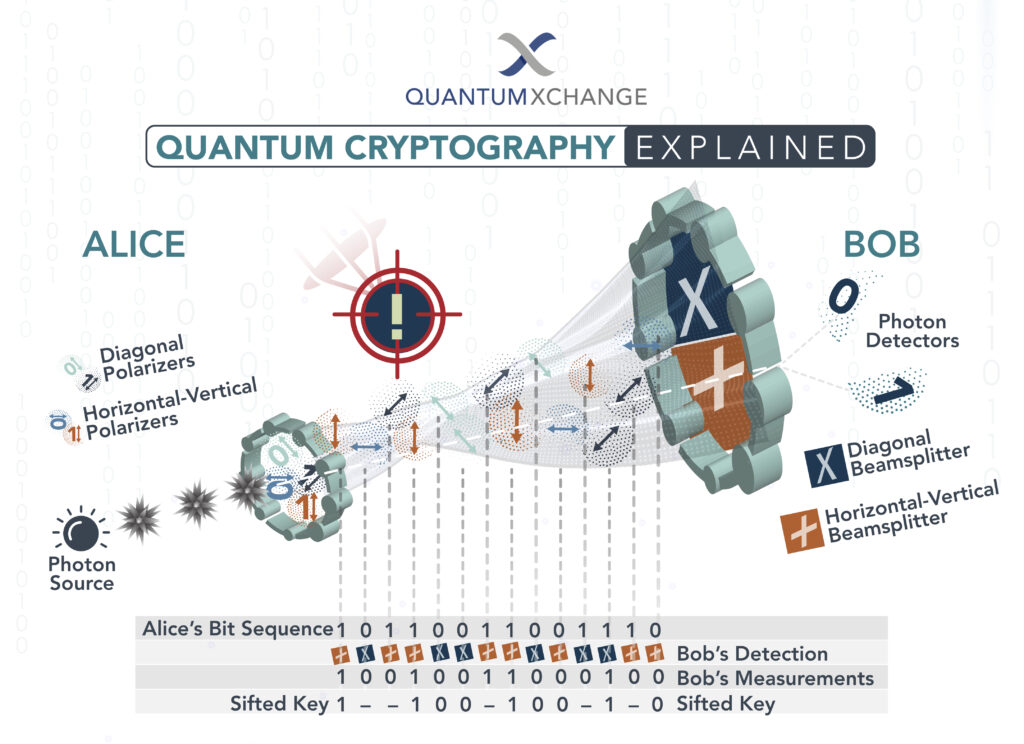
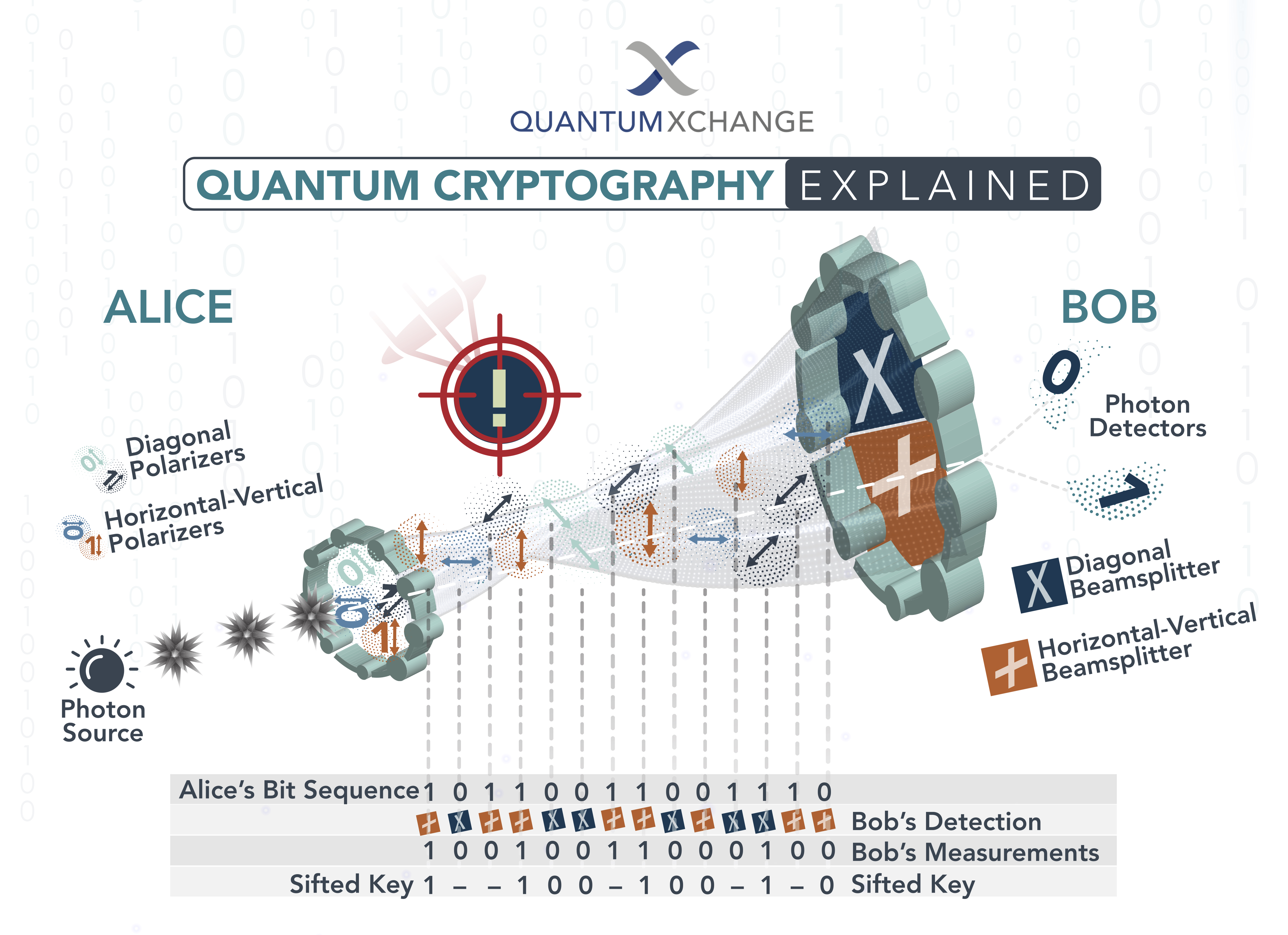
Quantum cryptography is a technique that uses quantum mechanical properties such as entanglement and non-locality to create secure communication links between two or more parties. It is based on principles of quantum mechanics and is designed to provide a secure form of data encryption. The main advantage of quantum cryptography is that it is virtually unbreakable, as the encryption keys cannot be intercepted or decrypted. This makes it an ideal solution for data security in industries such as banking and finance, where sensitive data needs to be protected from unauthorized access.
Quantum cryptography is based on a number of principles, including the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, which states that it is impossible to know the exact position and momentum of a particle at the same time. This uncertainty makes it impossible to decrypt the data encrypted using quantum cryptography, as the encryption key is constantly changing. This means that data encrypted using quantum cryptography is virtually impossible to hack or intercept.
Advantages of Quantum Cryptography
The main advantage of quantum cryptography is its unbreakable security. This makes it the ideal choice for organizations and individuals who need to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Additionally, quantum cryptography is highly scalable, meaning that it can be used to protect data over long distances. This makes it an ideal solution for communication networks and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Another advantage of quantum cryptography is its speed. Quantum cryptography can be significantly faster than traditional encryption methods, meaning that data can be transferred more quickly and securely. This can be especially beneficial for organizations that need to transfer large amounts of data over secure networks. Additionally, quantum cryptography is a relatively inexpensive solution, making it an ideal choice for organizations with limited budgets.
Finally, quantum cryptography is also highly reliable. It is designed to be resilient against attack and can be used in a variety of different environments. This makes it a reliable solution for data protection and secure communication.
Frequently Asked Questions About Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a relatively new technology that uses quantum mechanical principles to secure data transmission. It is considered to be the most secure form of cryptography available and is being increasingly adopted in various applications.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a form of cryptography that makes use of quantum mechanical principles to secure the transmission of data. It is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which are the laws of physics that govern the behavior of particles on an atomic scale. Quantum cryptography works by encoding data in a form that is resistant to interception, tampering, and other forms of attack. Unlike traditional cryptography, which relies on mathematical algorithms, quantum cryptography relies on the uncertainty principle and the no-cloning theorem to ensure the security of the data.
What are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography offers a number of advantages over traditional cryptography. Firstly, it provides a much higher level of security than traditional methods. This is because the principles of quantum mechanics make it impossible for an attacker to intercept, tamper with, or otherwise manipulate the data being transmitted. Secondly, quantum cryptography is much faster than traditional cryptography, allowing for faster data transmission. Finally, quantum cryptography is much more resistant to quantum computing attacks, which makes it a much more secure form of cryptography.
Is Quantum Cryptography Required?
Whether or not quantum cryptography is required depends on the level of security that is needed for the data being transmitted. In general, quantum cryptography is recommended for any data transmission that requires a high level of security, such as financial information or confidential documents. For less sensitive data, traditional cryptography may be sufficient. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to use quantum cryptography should be based on the specific requirements of the situation.
What is Quantum Key Distribution?
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a type of quantum cryptography that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to securely exchange cryptographic keys. This process works by exploiting the uncertainty principle and the no-cloning theorem to ensure that the keys cannot be intercepted or tampered with during transmission. QKD has been used in a number of high-security applications, such as military and government communications, and is becoming increasingly adopted in other areas as well.
What is Post-Quantum Cryptography?
Post-quantum cryptography is a type of cryptography that is designed to be resistant to attacks from quantum computers. While traditional cryptography relies on mathematical algorithms, post-quantum cryptography uses a different set of algorithms that are designed to be resistant to attacks from quantum computers. This type of cryptography is still in development, but it is expected to become increasingly important as quantum computers become more powerful and capable of breaking traditional cryptography.
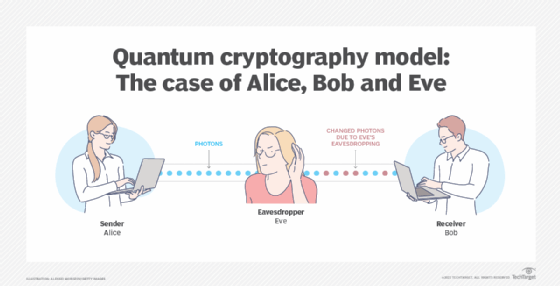
In conclusion, the question of whether quantum cryptography is required is a complex one that requires careful consideration of many factors. While quantum cryptography offers many advantages over traditional cryptographic methods, such as increased security and the ability to detect eavesdropping attempts, it also comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. Ultimately, the decision of whether to adopt quantum cryptography will depend on a variety of factors, including the level of security required, the resources available to implement and maintain the technology, and the potential risks and benefits associated with its use.
Regardless of whether or not quantum cryptography is deemed necessary, the importance of strong cryptographic methods in protecting sensitive data cannot be overstated. As technology continues to advance, so too must our methods of securing information. With the potential for cyber attacks and data breaches increasing every day, it is essential that individuals and organizations take proactive steps to protect themselves and their data. Whether through the adoption of quantum cryptography or other advanced cryptographic methods, the need for strong security measures has never been more critical.