Quantum cryptography is one of the most revolutionary technologies of the modern era. Its ability to transmit data in a way that is seemingly unbreakable has made it a popular choice for governments, businesses, and individuals who want to protect their sensitive information. However, as with any technology, there are always questions about its security. One of the most pressing questions is whether quantum cryptography is truly unbackable.
At its core, quantum cryptography is based on the principles of quantum physics. It uses photons to transmit information in a way that is impossible to intercept without disrupting the transmission. This means that any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication would be immediately detected, making it a highly secure method of communication. However, there are still concerns about the technology’s vulnerability to attacks, and experts are constantly working to improve its security to ensure that it remains unbreakable.
Is Quantum Cryptography Truly Unbackable?
Quantum cryptography, also known as quantum key distribution (QKD), is a form of encrypting data using quantum mechanics. Unlike traditional methods of cryptography, which are vulnerable to hacking, quantum cryptography is said to be unbreakable. This article will discuss the technology behind quantum cryptography and how secure it really is.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
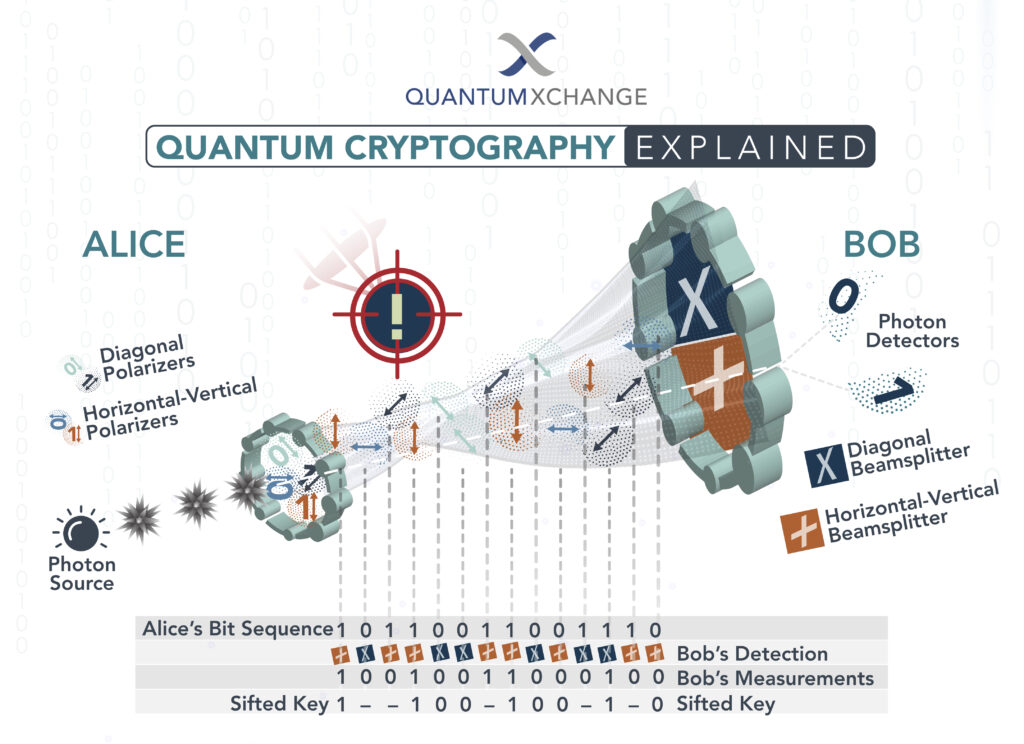
Quantum cryptography is a method of encrypting data using the principles of quantum mechanics. It is based on the idea that a sender and a receiver can share a secure key, known as a quantum key, which is impossible to duplicate, intercept, or decode. In essence, it allows for communication that is theoretically secure from intrusion. Quantum cryptography is different from traditional cryptography in that it relies on the properties of quantum mechanics rather than mathematical algorithms.
Quantum cryptography works by taking advantage of the fact that quantum particles, such as photons, behave differently when observed. If an eavesdropper attempts to intercept a quantum key, the particles will change in such a way that the sender and receiver can detect that interference. This allows them to detect any attempts to breach the security of their communication and take the necessary steps to protect it.
How Secure is Quantum Cryptography?
Theoretically, quantum cryptography is unbreakable. This is because it relies on the laws of physics instead of mathematical algorithms, which can be cracked with enough computing power. As a result, it is believed to be the only form of cryptography that can truly be considered secure.
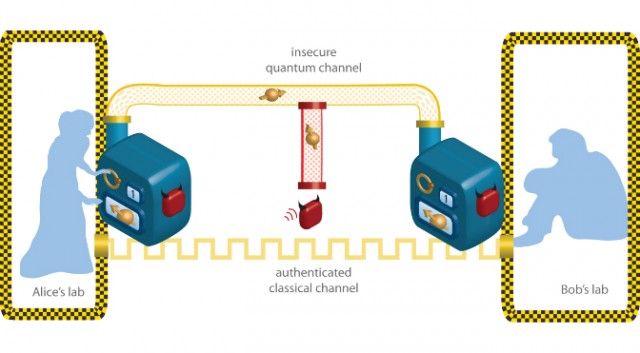
However, there are some potential weaknesses in quantum cryptography. For example, the quantum key must be transmitted over a secure channel, and if it is intercepted, the eavesdropper can potentially gain access to the encrypted data. Additionally, there are some quantum algorithms that are not yet fully understood, and there is a possibility that they could be cracked with enough computing power. Finally, quantum cryptography is still a relatively new technology, and there is still much research to be done in order to understand its full capabilities.
Conclusion
Quantum cryptography is a promising technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate. It is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which make it theoretically unbreakable. However, there are still some potential weaknesses that must be addressed before it can be considered truly secure. Nonetheless, quantum cryptography is an exciting development in the field of cryptography, and it is likely to be an integral part of our future communication systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is an emerging form of secure communication that uses quantum-mechanical properties to encrypt data. It is seen as a revolutionary way to protect sensitive information from hackers and other malicious actors.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a form of encryption based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It uses the properties of quantum particles, such as their entanglement, to create secure keys for encrypting data. The encryption keys are generated by measuring the states of entangled particles. These measurements are done randomly, ensuring that the keys are unique and unguessable. This makes it impossible for an outside party to decrypt the data without access to the key.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by using the principles of quantum mechanics to generate random encryption keys. These keys are then used to encrypt and decrypt data. The encryption keys are created by measuring the states of entangled particles. These measurements are done randomly, ensuring that the keys are unique and unguessable. This makes it impossible for an outside party to decrypt the data without access to the key.
Is Quantum Cryptography Truly Unhackable?
Quantum cryptography is seen as one of the most secure forms of encryption available. The encryption keys used in quantum cryptography are generated by measuring the states of entangled particles. These measurements are done randomly, ensuring that the keys are unique and unguessable. This makes it impossible for an outside party to decrypt the data without access to the key. However, it is important to note that quantum cryptography is still a relatively new technology and is not yet widely used.
What Are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
The primary benefit of quantum cryptography is its improved security. The encryption keys are generated by measuring the states of entangled particles. These measurements are done randomly, ensuring that the keys are unique and unguessable. This makes it impossible for an outside party to decrypt the data without access to the key. Additionally, quantum cryptography is difficult to intercept, as it is transmitted over a quantum channel.
What Are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
One of the main limitations of quantum cryptography is its complexity. The encryption keys used in quantum cryptography are generated by measuring the states of entangled particles. This means that special equipment is needed to generate the encryption keys, making it difficult to implement on a large scale. Additionally, quantum cryptography is only as secure as the quantum channel over which it is transmitted. If the quantum channel is compromised, the data can be intercepted.

In conclusion, quantum cryptography has been hailed as the ultimate solution to secure communications. The technology promises a level of security that is unbreakable even by the most advanced computing systems. However, as with any technology, there are still concerns regarding its vulnerability to attacks. Despite the challenges, quantum cryptography remains a promising solution that could revolutionize the way we communicate and exchange information.
As the field of quantum computing continues to evolve, it is likely that quantum cryptography will become even more robust and secure. While there may be some vulnerabilities that are yet to be discovered and addressed, the technology is still considered to be one of the most secure methods of communication available today. With ongoing research and development, we can only expect to see more advancements in this field, making quantum cryptography an even more reliable solution for secure communication in the future.