Quantum cryptography is a revolutionary technology that promises to revolutionize the way we communicate and secure sensitive information. It is often touted as the ultimate solution to the problem of secure communication, with advocates claiming that it is unbreakable and impervious to hacking. But is quantum cryptography really unbreakable, or is it just another hype in the world of technology?
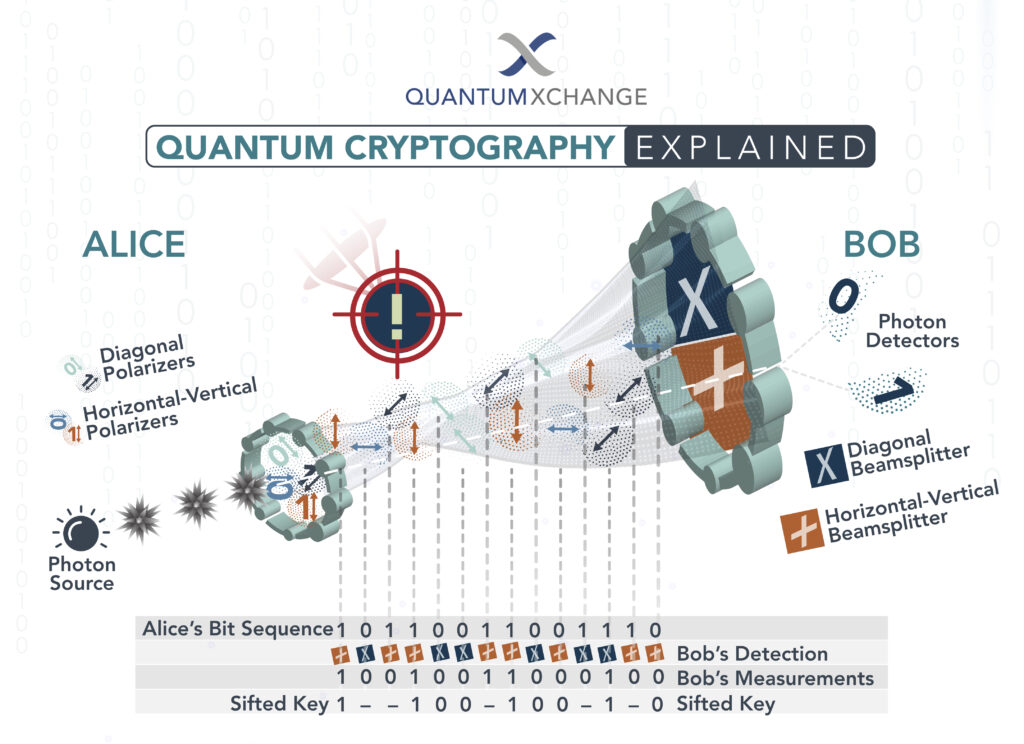
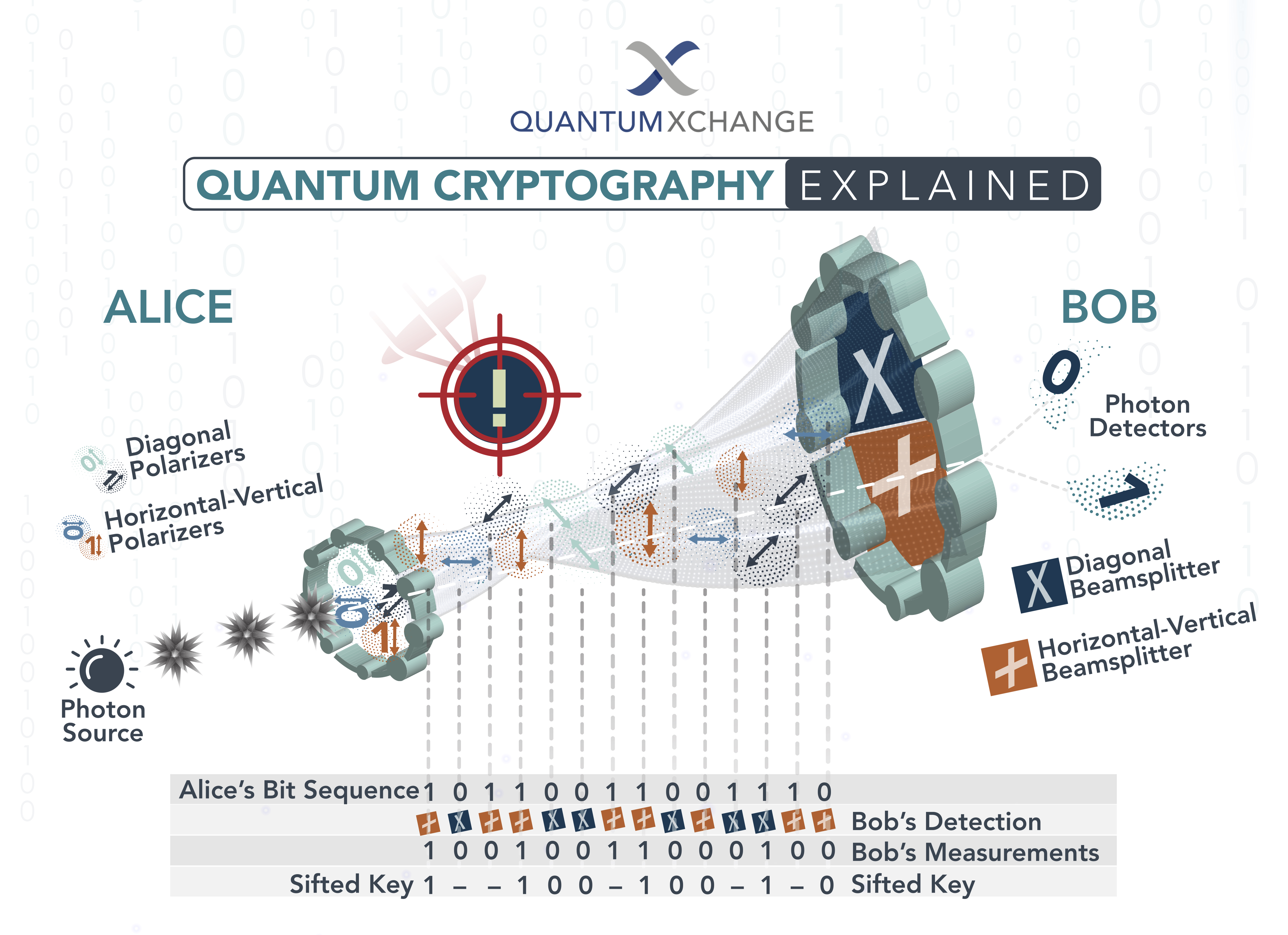
To answer this question, we need to understand what quantum cryptography is and how it works. At its core, quantum cryptography is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which govern the behavior of particles at the subatomic level. The idea behind quantum cryptography is to use the unique properties of quantum particles to create a secure communication channel between two parties. This channel is secure because any attempt to intercept or eavesdrop on the communication will disturb the quantum particles, making it impossible for the attacker to obtain any useful information.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a method of secure communication that uses quantum mechanics to guarantee secure communication. It relies on the properties of quantum mechanics to ensure that any eavesdropping will be detected. By using quantum mechanics, it is possible to create a secure communication channel that is unbreakable. This makes it the ideal choice for sensitive transmissions, such as military and financial applications.
Is Quantum Cryptography Unbreakable?
Theoretical Unbreakability
Theoretically, quantum cryptography is unbreakable. This is because quantum mechanics ensures that any information sent through a quantum channel is secure, as it is impossible to eavesdrop without being detected. This means that the only way to break a quantum channel is to break the laws of physics, which is impossible.
However, there are still ways in which a quantum channel can be compromised. For example, if an eavesdropper is able to intercept the transmission, they may be able to modify the information before it is sent. This means that the data is no longer secure, as the eavesdropper can access the information.
Practical Challenges
In practice, there are a number of challenges that make it difficult to use quantum cryptography. Firstly, quantum cryptography requires expensive and complex equipment to implement. This makes it difficult to use in many situations, such as in large networks or over long distances.
Another challenge is that quantum cryptography is vulnerable to attacks that do not rely on eavesdropping. For example, an attacker can use a ‘denial of service’ attack to prevent the quantum channel from being used. This means that the data is not secure, as the attacker can prevent the transmission from taking place.
Finally, quantum cryptography is vulnerable to other forms of attack, such as ‘man-in-the-middle’ attacks. This type of attack involves an attacker intercepting the transmission and substituting their own data for the original transmission. Again, this means that the data is not secure, as the attacker can access the information.
Overall, quantum cryptography is theoretically unbreakable, but there are still a number of practical challenges that make it difficult to use in practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum cryptography is an emerging technology that uses quantum mechanics to secure data. While it is generally considered unbreakable, there are still some security concerns that must be addressed. Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about quantum cryptography.
Is quantum cryptography unbreakable?
Yes, quantum cryptography is generally considered unbreakable. This is because it uses the principles of quantum mechanics to encrypt data, making it impossible to decrypt without the correct keys. The only way to break the encryption is by exploiting a flaw in the system, which is extremely difficult to do. As such, quantum cryptography is considered to be one of the most secure forms of encryption available today.
However, it is important to note that quantum cryptography is not without its weaknesses. For instance, it is possible for an attacker to intercept the data being sent, which could potentially be used to gain access to the encrypted data. Additionally, quantum cryptography relies on the use of specialized hardware, which could be vulnerable to attack. As such, it is important to ensure that all security measures are in place in order to protect the data being sent.
How does quantum cryptography work?
Quantum cryptography works by using a process called quantum entanglement. This process involves two particles that are entangled, meaning that they are linked together in a way that is impossible to undo. Once these particles are entangled, they can be used to send encrypted data over a secure channel. The data transmitted is encoded using quantum keys, which are virtually impossible to decrypt without the correct keys.
The process of quantum cryptography is incredibly secure, as it is virtually impossible for an attacker to intercept the data being sent. Additionally, quantum cryptography is also resistant to quantum computing, meaning that it is unlikely that an attacker will be able to decode the data even if they have access to powerful quantum computers.
What are the benefits of quantum cryptography?
The main benefit of quantum cryptography is its unparalleled security. As mentioned previously, it is virtually impossible to break the encryption without the correct keys. This makes it ideal for sending sensitive information, such as financial data or medical records. Additionally, quantum cryptography is also resistant to quantum computing, meaning that it is unlikely that an attacker will be able to decode the data even if they have access to powerful quantum computers.
Another benefit of quantum cryptography is its scalability. As the technology advances, it is likely that quantum cryptography will become more widely available and easier to implement. This means that organizations of all sizes will be able to take advantage of its security benefits without having to invest in expensive hardware or software.
What are the limitations of quantum cryptography?
While quantum cryptography is generally considered to be unbreakable, there are still some limitations that must be taken into account. For instance, quantum cryptography relies on the use of specialized hardware, which could be vulnerable to attack. Additionally, quantum cryptography is vulnerable to interception, meaning that an attacker could potentially gain access to the encrypted data. As such, it is important to ensure that all security measures are in place in order to protect the data being sent.
Another limitation of quantum cryptography is that it is not yet widely available. This means that organizations may have difficulty finding the hardware and software needed to implement the technology. Additionally, quantum cryptography requires a secure channel in order to send the encrypted data, which may add to the cost of implementation.
Is quantum cryptography the future of encryption?
While quantum cryptography is generally considered to be the most secure form of encryption available today, it is unlikely to become the standard in the near future. This is because quantum cryptography requires specialized hardware and is not yet widely available. Additionally, quantum computing is still in its infancy and is not yet powerful enough to break quantum cryptography.
However, it is likely that quantum cryptography will become more widely adopted as the technology advances. As the technology becomes more advanced and easier to implement, it is likely that it will become more popular and become the standard for encryption in the future.

In conclusion, quantum cryptography holds great promise in providing secure communication channels as it leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to secure data transmission. However, as with any security technology, it is not completely foolproof, and there are limitations to its use. While quantum cryptography is currently considered unbreakable due to the laws of physics, there is always the possibility of new attacks being developed in the future.
Despite these limitations, quantum cryptography remains a promising technology that continues to be researched and developed. As the world becomes increasingly dependent on secure communication channels, quantum cryptography is poised to become an essential tool in protecting sensitive information. While it may not be completely unbreakable, it is undoubtedly one of the most secure methods available today, and its impact on the field of cryptography will undoubtedly be felt for years to come.