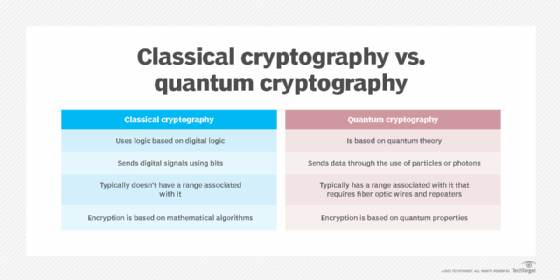
Quantum cryptography is a new field that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize the way we secure our data. Unlike classical cryptography, which relies on mathematical algorithms to secure information, quantum cryptography leverages the properties of quantum mechanics to provide unparalleled security. However, despite its promise, quantum cryptography is not without its limitations and problems. In this article, we will explore some of the key challenges associated with quantum cryptography and discuss how they may impact the future of data security.
One of the most significant limitations of quantum cryptography is its dependence on complex technology. Quantum key distribution, the most common application of quantum cryptography, requires the use of expensive and highly specialized equipment, such as single-photon detectors and high-speed lasers. This equipment must be carefully calibrated and maintained to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the cryptography, which can be a significant challenge for organizations with limited resources. Additionally, the technology is still in its early stages of development, and there is a lack of standardization across different implementations, making it difficult to compare and evaluate different systems.
Quantum cryptography has some limitations, primarily related to practical implementation. For example, it is difficult to maintain a secure connection over a long distance, and the cost of setting up a secure network is expensive. Additionally, the technology is limited to the exchange of data between two parties, and there is no secure way to transfer data to multiple parties simultaneously.
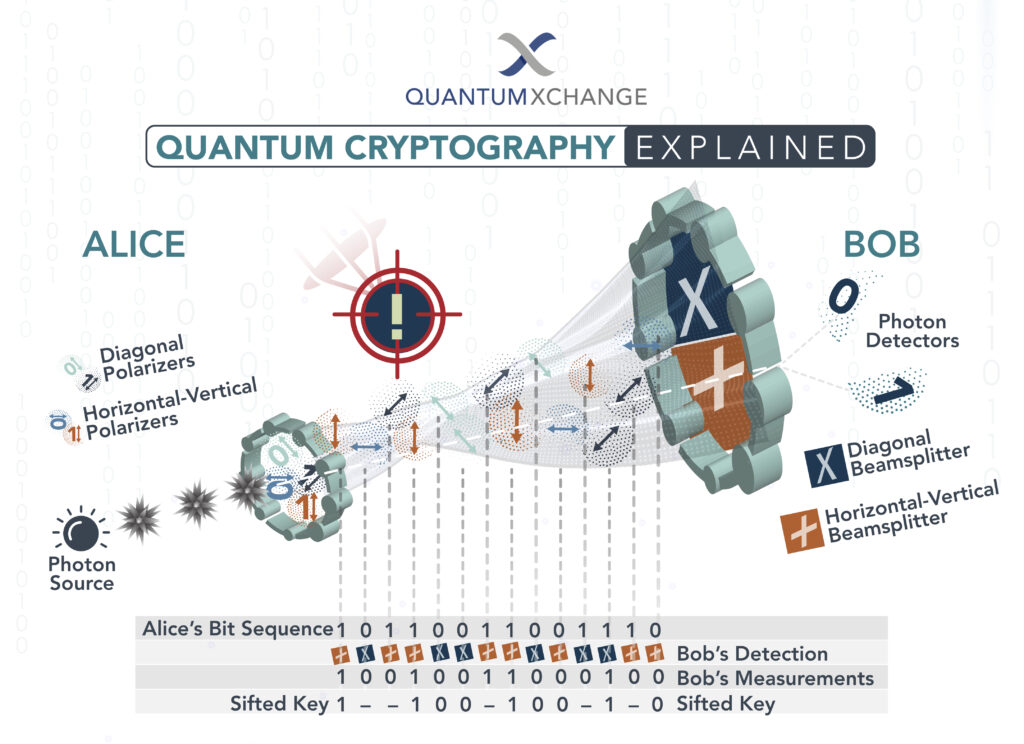
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is the science of using quantum mechanics to transfer and store data securely. It is a powerful and secure form of cryptography that relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure the security of data. Quantum cryptography works by using the laws of physics to make it virtually impossible for someone to intercept or alter the data being transferred. The data is encoded and transmitted using photons, the smallest particles of light, and the laws of physics ensure that any attempt to intercept or alter the data will be detected.
Limitations or Problems Associated with Quantum Cryptography
Complexity
Quantum cryptography is a complex technology and requires a great deal of knowledge to understand and implement. It is not suitable for most applications as the complexity of the technology makes it difficult and time-consuming to set up and maintain. In addition, the quantum cryptography system requires a lot of power and is expensive to operate.
Distance Limitations
The distance between the sender and the receiver is a major limitation of quantum cryptography. The photons used to transmit the data are easily absorbed or scattered by air molecules, and the farther away the receiver is, the greater the chances of this happening. This means that quantum cryptography is only suitable for short-range communication, such as between two computers in the same room.
Atmospheric Conditions
The performance of quantum cryptography systems is greatly affected by atmospheric conditions. The photons used to transmit the data are easily absorbed by water vapor, dust, and other particles in the air. This means that the performance of the system can be adversely affected if the atmospheric conditions are not ideal.
Cost
Quantum cryptography systems are expensive to purchase and operate. In addition, the hardware and software required to use the system are costly and difficult to obtain. This makes quantum cryptography an expensive and impractical solution for most applications.
Security
Although quantum cryptography is an incredibly secure form of encryption, it is not completely foolproof. There is still a chance that someone could intercept or alter the data, and the encryption algorithms used by quantum cryptography systems can be cracked with enough time and effort.
Speed
The speed of quantum cryptography systems is relatively slow. This is due to the fact that the photons used to transmit the data take a finite amount of time to travel from the sender to the receiver. This can make quantum cryptography impractical for applications that require real-time communication.
Frequently Asked Questions About Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a form of cryptography that uses quantum mechanics to make it secure. This technology has the potential to revolutionize data security and encryption methods, but there are also some limitations and problems associated with it. Here are some frequently asked questions about quantum cryptography and the limitations and problems associated with it.
What are the Limitations or Problems Associated with Quantum Cryptography?
One of the main limitations of quantum cryptography is the cost of implementation. The technology is still in its infancy and the equipment required is expensive and not widely available. Furthermore, the range of the communication is limited due to the speed of light and the nature of the quantum particles used. Additionally, the complexity of the technology means that it is difficult to maintain and manage.
Another limitation of quantum cryptography is that it can only be used for point-to-point communication. This means that it is not suitable for large-scale networks, such as those used for the internet. Furthermore, the process is vulnerable to attacks from even the most advanced quantum computers, which could potentially crack the code. Finally, the cryptography is still unproven, so there is no guarantee that it is secure.

In conclusion, while quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize the field of information security, there are several limitations and problems that must be taken into consideration. These limitations include the need for specialized equipment, the vulnerability to side-channel attacks, and the difficulty in implementing large-scale quantum networks. Additionally, quantum cryptography is still a relatively new technology, which means that there is much that is still unknown about its potential risks and limitations.
Despite these limitations, quantum cryptography remains a promising area of research, with many experts working to address these challenges and improve the technology. As our reliance on digital communication continues to grow, it is becoming increasingly important to explore new and innovative approaches to information security. By continuing to invest in research and development of quantum cryptography, we can ensure that our digital systems remain secure and protected against even the most sophisticated cyber threats.