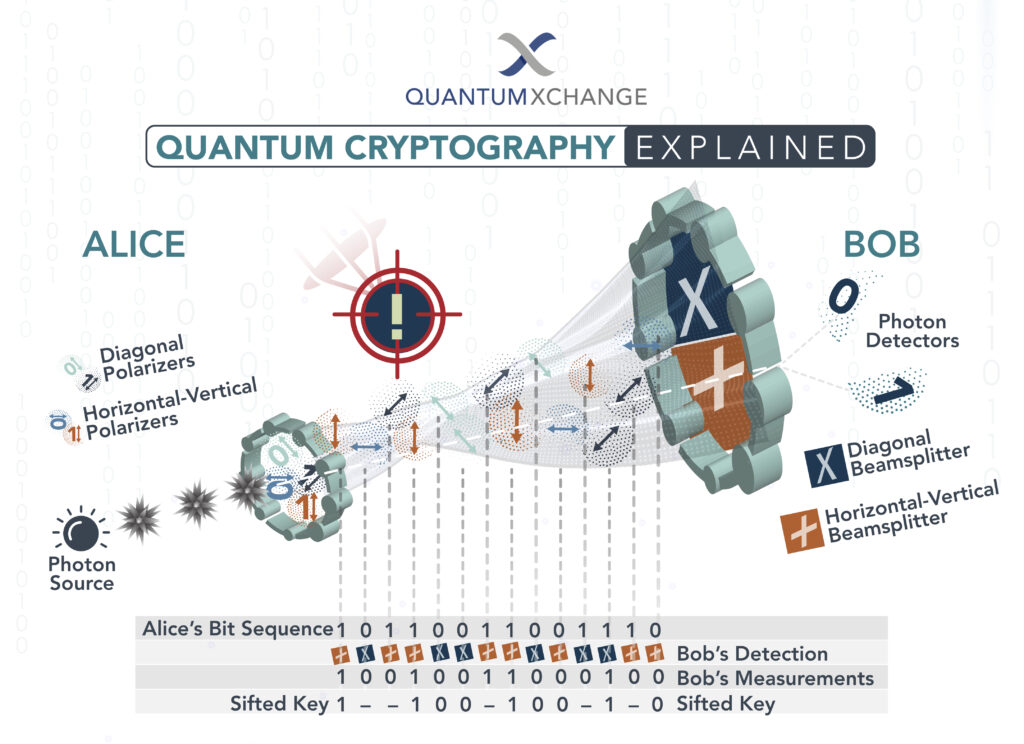
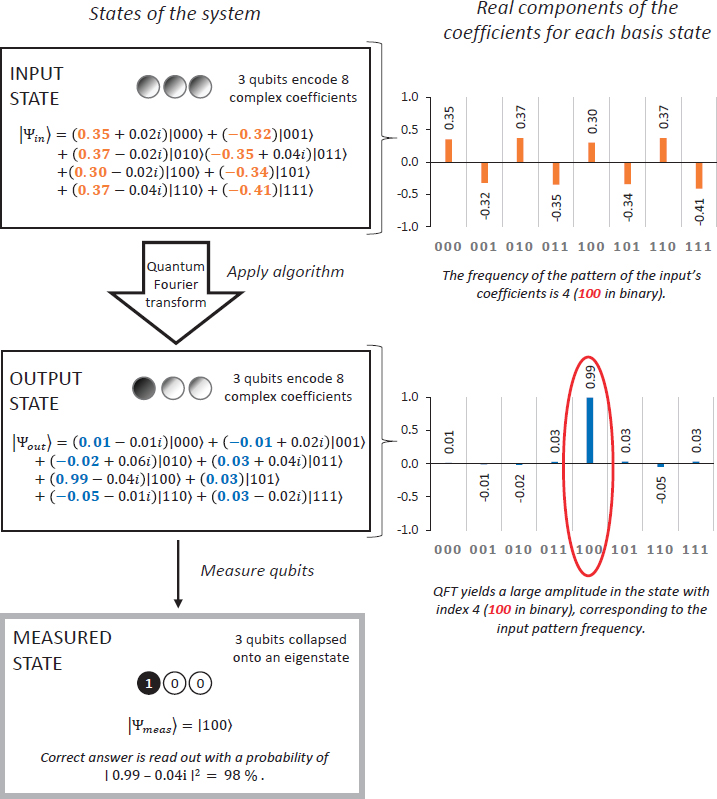
Quantum computing is a relatively new field of computing that has the potential to revolutionize how we process information. While traditional computing relies on bits, which can only be processed as either a zero or a one, quantum computing uses quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist as both a zero and a one simultaneously. This allows for exponentially faster processing speeds and the ability to solve complex problems that are currently impossible for traditional computers. However, this breakthrough in computing power also poses a threat to cryptography, the science of secure communication.
Cryptography is an essential tool for securing sensitive information such as financial data, military secrets, and personal information. It relies on mathematical algorithms to encrypt data in such a way that it can only be decrypted with a specific key. However, quantum computing has the potential to easily break many of the mathematical algorithms that are currently used for encryption. This would render much of our current cryptographic infrastructure useless and leave sensitive information vulnerable to attack. As such, the rise of quantum computing has sparked a race to develop new quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to ensure that our data remains secure in the age of quantum computing.
Quantum computing is a threat to cryptography because it is able to solve certain mathematical problems much faster than classical computers. This means that it could potentially break certain types of encryption that are currently used to secure data. Quantum computing also has the potential to create new types of encryption that are not vulnerable to attack.

What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a form of computing which uses quantum-mechanical phenomena, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform operations on data. It is based on the observation that the laws of quantum mechanics allow for the manipulation of information in ways that are fundamentally different from conventional computing. Quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems much faster than classical computers.
Why is Quantum Computing a Threat to Cryptography?
Shorter Encryption Keys
One of the primary threats posed by quantum computing is the potential for shorter encryption keys. Quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, which can store more information than the traditional binary bits used in classical computers. This means that quantum computers can generate encryption keys that are much shorter than those used by traditional computers, making them more susceptible to attack.
Another issue is that quantum computing can be used to break existing encryption algorithms. For example, the widely used RSA encryption algorithm relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. However, quantum computers can easily factor large numbers, making the RSA algorithm obsolete.
Improved Attack Methods
Quantum computing also allows for improved attack methods. For example, quantum computers can use Grover’s algorithm to search large databases more efficiently, making it easier to find passwords or other sensitive information. Additionally, quantum computers can be used to break hash functions, which are used to store passwords, as well as digital signatures, which are used to authenticate digital documents.
Finally, quantum computers can be used to break public-key cryptography, which is the most common form of encryption used today. This is due to the fact that quantum computers can easily factor large numbers, which are used as the basis of public-key cryptography.
Conclusion
Quantum computing poses a serious threat to cryptography, as it enables shorter encryption keys and improved attack methods. This means that existing encryption algorithms and protocols are no longer secure, and new measures must be taken to protect sensitive data.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum computing is an emerging technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we use computers. It has been the subject of much research over the past few decades and is now beginning to offer real-world applications. One area where quantum computing could have a significant impact is in cryptography, where it could potentially be used to break existing encryption algorithms.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a form of computing that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to manipulate information. It is based on the idea that a quantum system can exist in multiple states at the same time and can be used to process information more efficiently than traditional computers. Quantum computers use qubits, which are units of quantum information, instead of the traditional bits used by conventional computers.
How does Quantum Computing Threaten Cryptography?
The main threat posed by quantum computing to cryptography is that it could be used to break existing encryption algorithms. Traditional computers use binary code to store and process information, and existing encryption algorithms are designed to be difficult for a computer to crack. However, quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states at once, allowing them to process information much more quickly and efficiently than traditional computers. This means that they could potentially be used to break even the most secure encryption algorithms.
What Encryption Algorithms are at Risk?
The encryption algorithms most at risk from quantum computing are those that rely on the difficulty of solving certain mathematical problems. These algorithms, known as public-key encryption algorithms, are used in a number of applications, including secure communication, digital signatures, and secure storage of data. Examples of public-key encryption algorithms include RSA, Diffie-Hellman, and Elliptic Curve Cryptography.
Are there any Solutions to this Threat?
Yes, there are a number of solutions to the threat posed by quantum computing to cryptography. One such solution is to use post-quantum cryptography, which uses algorithms that are designed to be resistant to attack by quantum computers. Another solution is to use quantum-resistant algorithms, which are designed to be secure against both traditional computers and quantum computers.
What is the Current Status of Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is still in its early stages, and there are currently no commercially available quantum computers. However, researchers are making rapid progress in the field, and quantum computers are expected to become a reality in the near future. As quantum computing technology advances, the threat to cryptography will become more and more real.
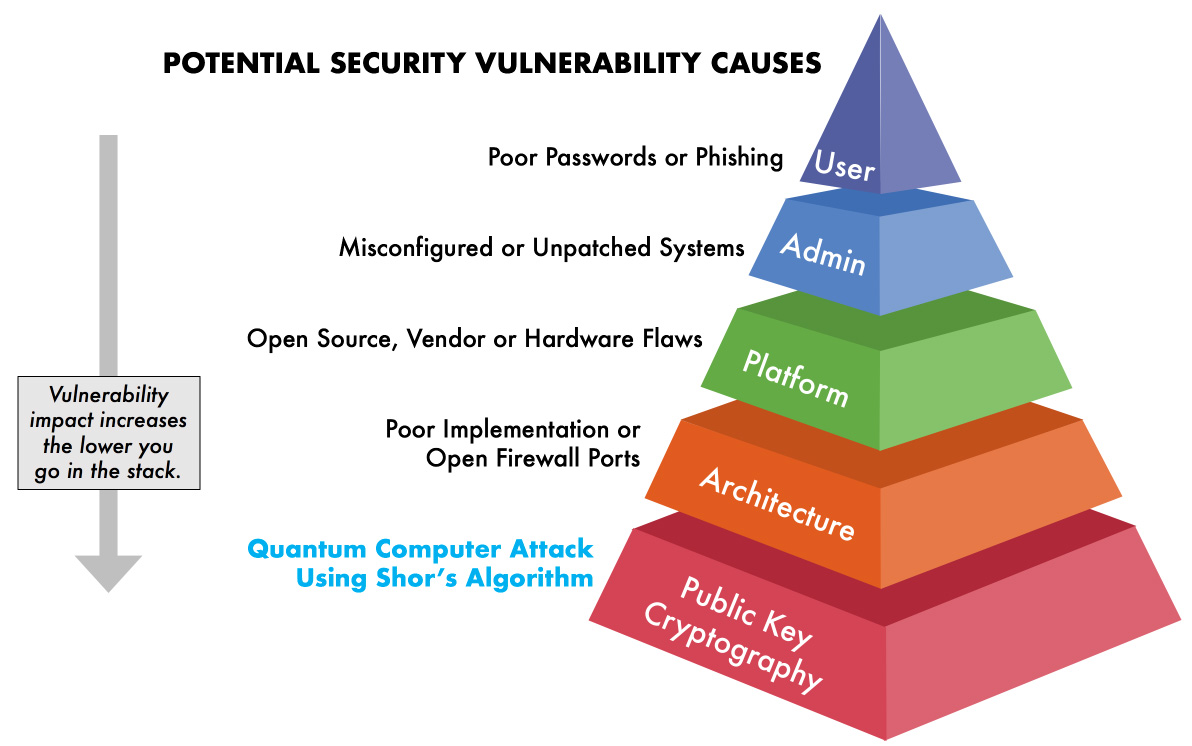
In conclusion, it is evident that quantum computing poses a significant threat to cryptography. While cryptography has been the backbone of secure communication and data protection for decades, the arrival of quantum computing technology has the potential to render it obsolete. With the ability to break traditional encryption methods in a fraction of the time it would take a classical computer, quantum computers can expose sensitive data, including financial transactions, classified government information, and personal data.
As the development of quantum computing continues, it is essential that the cryptography community keeps pace with advancements in technology. New encryption methods that are resistant to quantum attacks are already being developed and tested, but implementation on a large scale will take time. In the meantime, it is crucial that individuals and organizations take steps to safeguard their data through multi-factor authentication, regular password changes, and data backups. Ultimately, the future of secure communication and data protection hinges on the ability of cryptography to adapt and evolve in response to the ever-changing technological landscape.