Quantum cryptography is a cutting-edge technology that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to provide secure communication channels. Unlike classical cryptography, which relies on mathematical algorithms, quantum cryptography uses the unique properties of quantum particles to guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the communication. The technology has been hailed as the future of secure communication because it is virtually unbreakable, even by the most sophisticated hacking techniques.
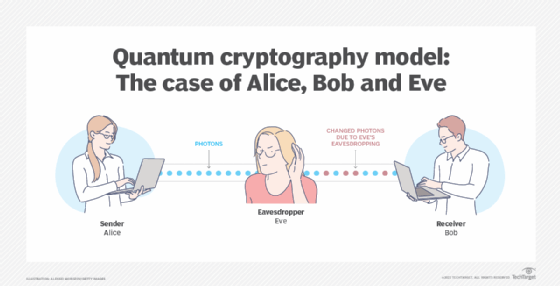
One of the main advantages of quantum cryptography is its ability to detect any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication. This is achieved through the use of quantum entanglement, a phenomenon where two quantum particles become linked in such a way that any change in one particle affects the other, regardless of the distance between them. If an eavesdropper tries to intercept the communication, the entangled particles will be disturbed, and the communication will be immediately terminated. This makes it impossible for any unauthorized party to intercept the communication without being detected, ensuring that the communication remains secure and confidential.
Quantum cryptography is used to secure the transfer of data by using the laws of quantum mechanics. It is more secure than traditional cryptography as it utilizes the laws of physics to guarantee the security of data transmission. Quantum cryptography is used to encrypt data, verify its authenticity and ensure the integrity of the data.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a method of sending secure messages using the principles of quantum mechanics. It relies on the fact that any attempt to measure the state of a quantum system will disrupt it, which makes it impossible for an eavesdropper to read the message without being detected. Quantum cryptography is also known as quantum key distribution (QKD).
This technology is based on the principle of quantum entanglement, where two particles interact with each other and can be measured in tandem. By using quantum keys, which are strings of random numbers, two parties can securely exchange messages without the possibility of interception.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
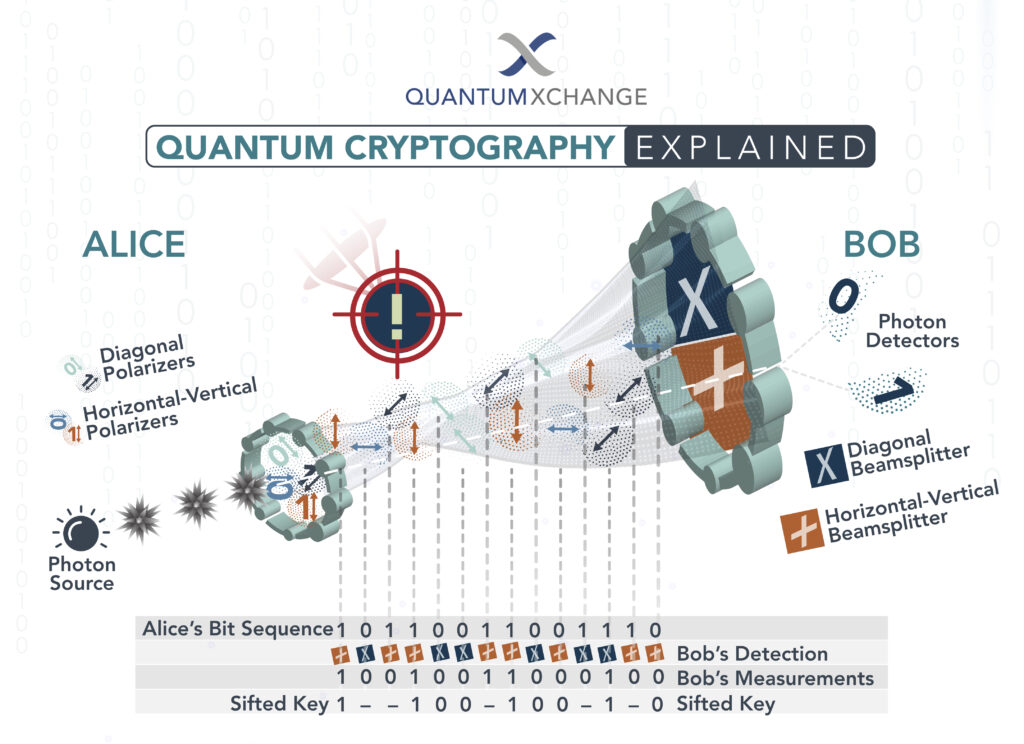
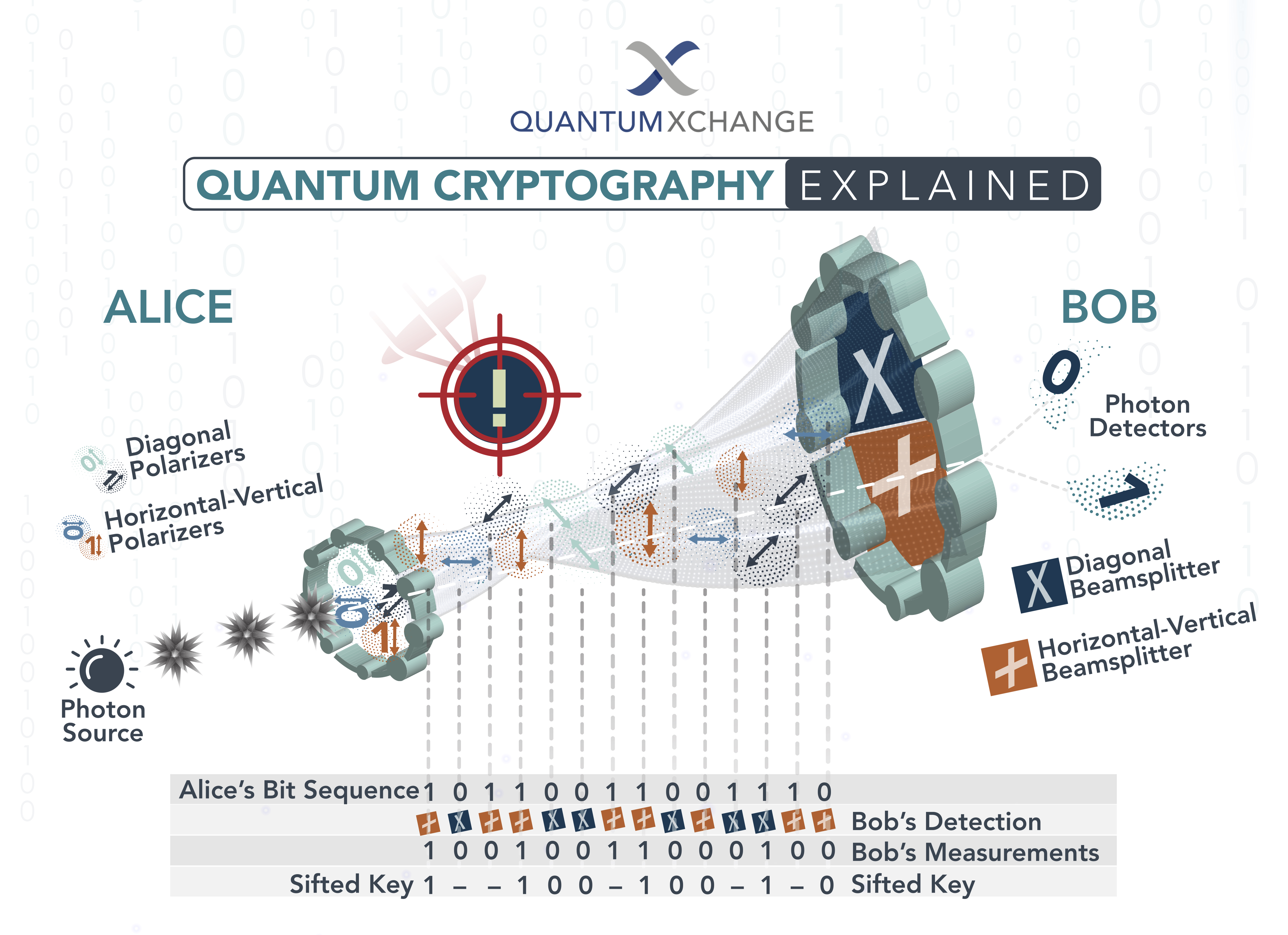
Quantum cryptography works by taking advantage of the laws of quantum mechanics. In this system, a sender (Alice) and a receiver (Bob) use a quantum key distribution (QKD) system to exchange messages. This system uses quantum entanglement to generate random numbers, which are then used to create a secure key.
Alice and Bob then use the key to encrypt their messages, which can only be decrypted by the other party. The key is then destroyed, ensuring that it can’t be used again. This process is repeated for each message that is sent, creating a unique key for each message.
What Are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
The biggest benefit of quantum cryptography is that it is virtually impossible to intercept or decode the messages that are sent using this system. This makes it ideal for highly sensitive information, such as financial transactions or military communications.
In addition, quantum cryptography is also much faster than traditional encryption methods. This is because the key is generated and destroyed in a matter of seconds, instead of minutes or hours. This makes it ideal for applications where speed is essential.
What Are the Drawbacks of Quantum Cryptography?
One of the biggest drawbacks of quantum cryptography is that it is still relatively new. This means that there is still a lot of work to be done in terms of developing the technology and making it more secure. In addition, quantum cryptography requires specialized equipment and can be expensive to implement.
Finally, quantum cryptography is not suitable for all applications. For example, it is not suitable for large-scale data transmission, as the amount of data that can be securely transmitted is limited. Additionally, quantum cryptography is not a replacement for traditional encryption methods, as it can only be used for specific applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is an emerging field of cryptography that uses the principles of quantum physics to enhance the security of cryptographic systems. It is a rapidly developing technology that promises to revolutionize the security of data transmissions, and is being adopted by a growing number of organizations.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is the use of quantum mechanics to secure the transmission of data. It is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which allow for secure communication between two parties without the risk of eavesdropping or tampering. In quantum cryptography, information is encoded in the form of photons, which are particles of light. These photons are sent from one point to another, and the secure transmission of the data is ensured by the principles of quantum mechanics.
The use of quantum cryptography is becoming increasingly popular as a means of securing sensitive data. It provides a higher level of security than traditional methods of cryptography, as it is not possible for a third party to intercept the information being transmitted. This makes it ideal for applications such as banking and government communications, where the security of the data is of paramount importance.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by encoding data into photons, which are then sent from one point to another. The recipient then uses a quantum computer to decode the information. The quantum computer is able to identify the key used to encrypt the data, and then decode it. This ensures that only the intended recipient can access the data, and that no one else can intercept it.
The quantum computer is also able to detect any attempts to tamper with the data, and if any tampering is detected, the data will not be decoded. This makes quantum cryptography highly secure, as it is virtually impossible for a third party to gain access to the data.
What are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
The main benefit of quantum cryptography is the increased security it provides. Traditional methods of cryptography can be broken by third parties, but quantum cryptography is virtually unbreakable. This makes it ideal for applications where the security of the data is of paramount importance, such as banking and government communications.
Another benefit is that quantum cryptography is much faster than traditional methods of encryption. This is because the quantum computer is able to process the data much faster than a traditional computer, which means that the transmission of data can be completed in a much shorter time frame.
What are the Drawbacks of Quantum Cryptography?
The main drawback of quantum cryptography is the cost. The quantum computers needed to implement the technology are expensive, and not all organizations can afford them. Additionally, quantum computers need to be kept in a secure environment, and this can add to the cost of the system.
Another drawback is that quantum cryptography is not yet widely used, and as such, there is still a risk of a third party being able to intercept the data. This means that organizations need to be aware of the risks involved and take measures to protect the data.
What is the Future of Quantum Cryptography?
The future of quantum cryptography looks bright, as the technology continues to develop and become more widely used. As the cost of quantum computers decreases, and the technology becomes more accessible, more organizations are likely to adopt quantum cryptography. This will help to ensure that sensitive data is kept secure, and that the transmission of data is kept private.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a powerful tool that offers unparalleled security features in the field of data communication. Its use of quantum mechanics principles ensures that any attempt to intercept or eavesdrop on data transmissions is immediately detected, thereby guaranteeing the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the information being exchanged. The potential applications of quantum cryptography are vast, ranging from secure communication between governments, military organizations, and financial institutions to protecting personal information in the healthcare and legal sectors. As technology advances and cyber threats become more sophisticated, quantum cryptography remains at the forefront of securing sensitive data in the digital age.
Overall, quantum cryptography is a game-changer in the world of data security, offering a level of protection that traditional encryption methods cannot match. It is a technology that is continually evolving, with new breakthroughs being made regularly to improve its efficiency and effectiveness. As more organizations recognize the importance of securing their data, quantum cryptography is set to become an essential tool for safeguarding sensitive information. By embracing this technology, we can ensure that our online interactions remain secure and that our personal and professional data remains protected from prying eyes.