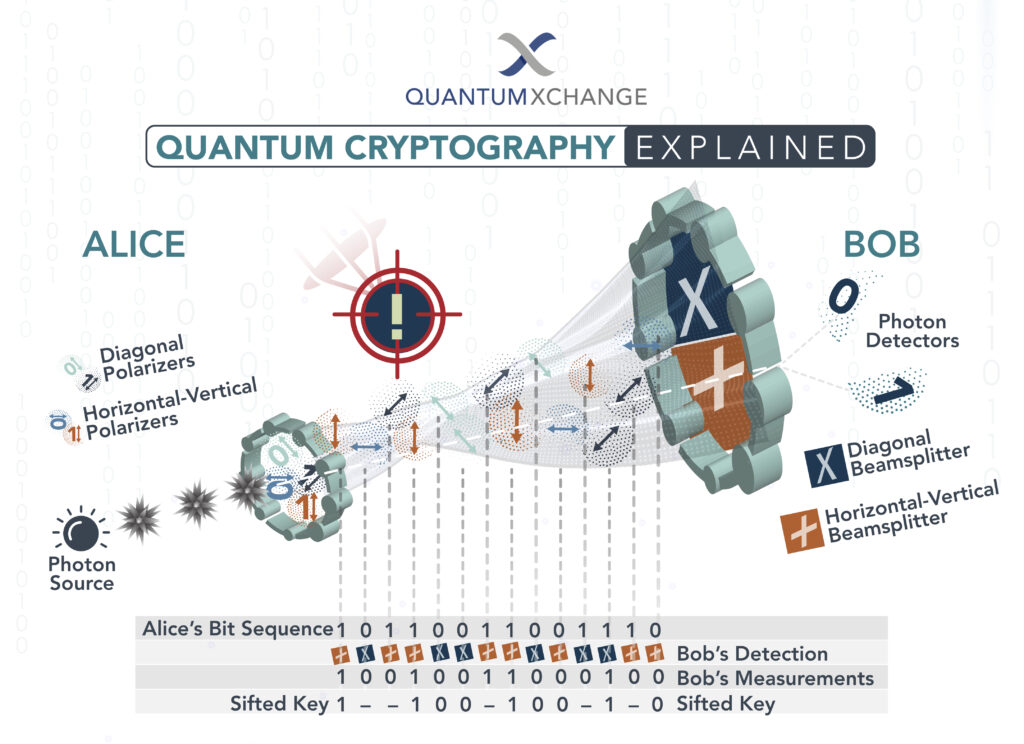
Quantum cryptography is a fascinating field that has gained a lot of attention in recent years. The idea behind it is to use the principles of quantum mechanics to create an unbreakable encryption system. This is achieved by exploiting the properties of quantum particles, such as photons, to create a secure communication channel that is immune to eavesdropping.
At a basic level, quantum cryptography works by using the polarisation of photons to create a secure key. This key can then be used to encrypt messages that are sent between two parties. The key is generated by sending a series of photons between the sender and receiver. If someone tries to intercept the photons, their interference will be detected, and the key will be immediately invalidated. This means that any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication would be immediately detected, making it impossible for the interceptor to read the message.
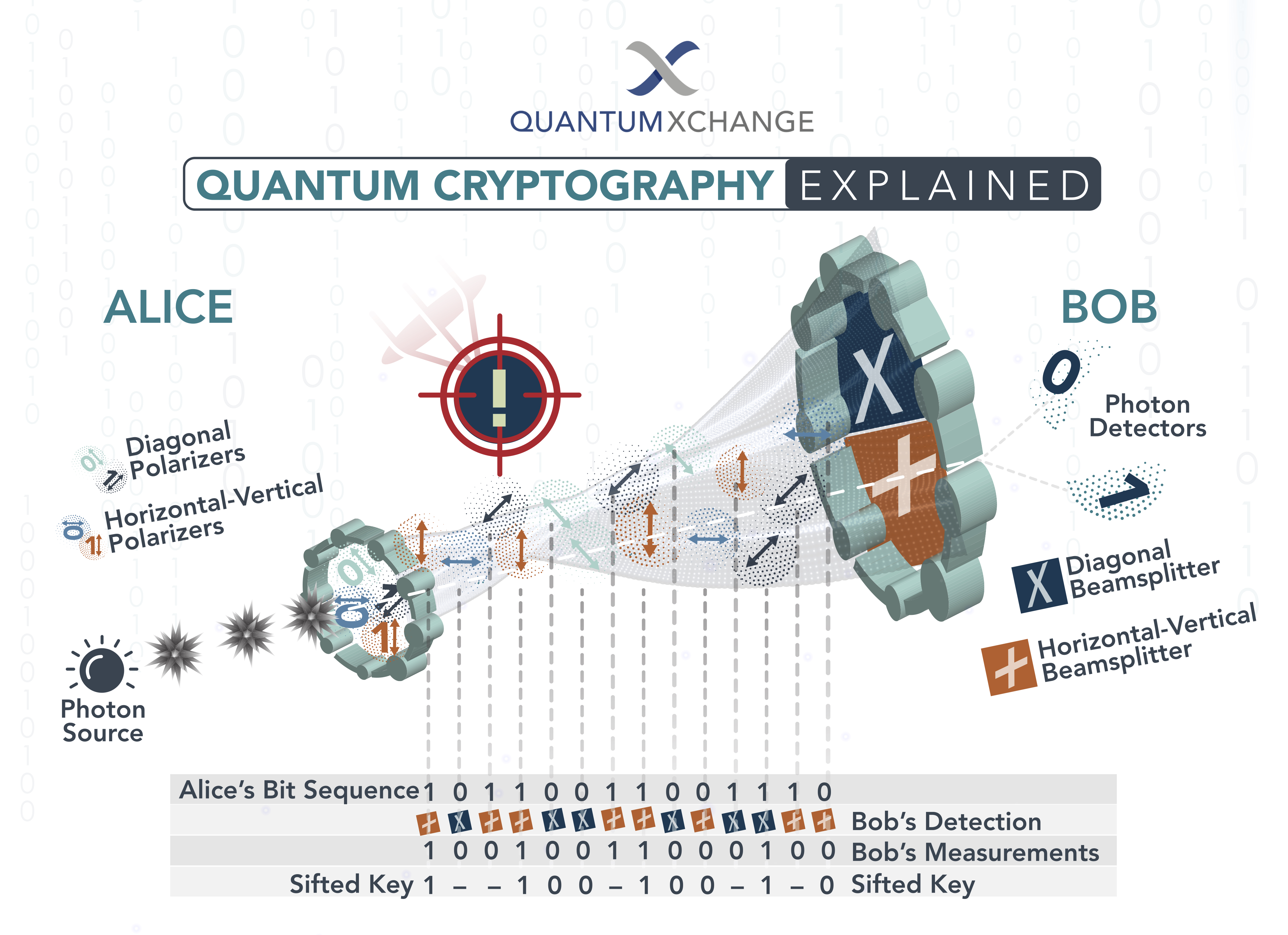
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a type of encryption that uses quantum mechanical properties to secure data. It is used to protect sensitive information from being intercepted or decrypted. Quantum cryptography utilizes quantum mechanics to create a secure communication channel between two parties. It is designed to be impossible to break, even if the encryption key is known.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by using quantum mechanical properties to encode information. This means that the data is encrypted in such a way that it is impossible to decrypt without the encryption key. The encryption key is generated using a quantum key distribution (QKD) protocol. The QKD protocol is used to generate a unique encryption key that is shared between two parties. This ensures that only the two parties have access to the data.
Quantum Key Distribution
The process of quantum key distribution (QKD) is used to generate a unique encryption key that is shared between two parties. This encryption key is generated using a combination of quantum mechanics and mathematics. In a QKD process, the two parties generate a random string of bits that are then used as the encryption key. This key is then used to encrypt the data that is being sent between the two parties.
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement is another key element of quantum cryptography. Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon in which two or more particles become linked together. This means that when one particle changes, the other particles linked to it will also change. This phenomenon is used in quantum cryptography to ensure that the encryption key is secure. In a quantum entanglement process, two particles are linked together and the two parties exchange information regarding the particles. This information is then used to create the encryption key.
Quantum Encryption
Once the quantum key distribution process is completed, the encryption key is then used to encrypt the data. This is done using a quantum encryption algorithm, which is a type of encryption algorithm that is secure and impossible to break. The data is then transmitted between the two parties, and only the two parties have access to the encrypted data.
Advantages of Quantum Cryptography
One of the major advantages of quantum cryptography is its security. It is designed to be impossible to break, even if the encryption key is known. This makes it ideal for protecting sensitive data from being intercepted or decrypted. Additionally, quantum cryptography is also more secure than traditional encryption methods, as it uses quantum mechanics to generate a unique encryption key.
Another advantage of quantum cryptography is its scalability. It can be used for large amounts of data, making it an ideal choice for businesses that need to securely transmit large amounts of data. Additionally, quantum cryptography is also more secure than traditional encryption methods, as it is not vulnerable to attacks such as man-in-the-middle attacks.
Disadvantages of Quantum Cryptography
One of the major disadvantages of quantum cryptography is its cost. It is much more expensive than traditional encryption methods, as it requires specialized hardware and software. Additionally, quantum cryptography is also more complex than traditional encryption methods, as it requires a greater understanding of quantum mechanics and mathematics.
Additionally, quantum cryptography is also vulnerable to attacks such as quantum hacking. Quantum hacking is a type of attack that uses quantum computers to break the encryption key. While quantum cryptography is still secure, it is vulnerable to this type of attack.
Finally, quantum cryptography is also not without its risks. As with any form of encryption, there is always the risk that the encryption key can be stolen or lost. Additionally, there is also the risk that the quantum encryption algorithm can be broken, resulting in the data being compromised.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Quantum Cryptography
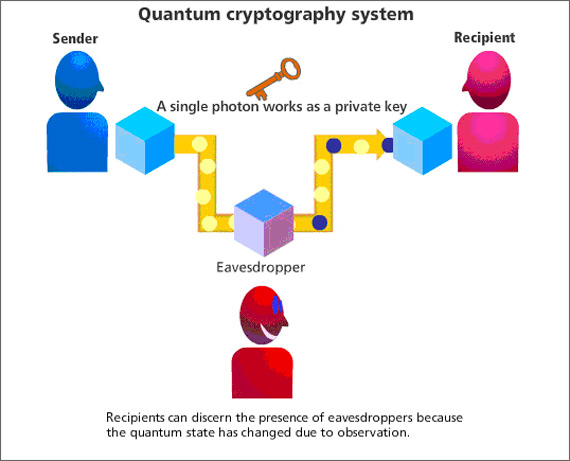
Quantum cryptography is an emerging field of research that relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to ensure data security. It is based on the idea that any attempt to eavesdrop on a quantum communication channel will leave a detectable trace, allowing for secure data transmission.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a field of research that focuses on using quantum mechanics to secure data transmission. It is based on the idea that any attempt to eavesdrop on a quantum communication channel will leave a detectable trace. This allows for secure data transmission, as any eavesdropper can be detected. The technology is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about data security.
Quantum cryptography relies on the concept of entanglement, which is when two particles are linked together in a way that any change in one particle will immediately be reflected in the other. This property of entanglement allows for data to be encrypted in a way that is virtually unbreakable. Quantum cryptography also uses the principles of quantum key distribution, which is a form of public key cryptography. This is used to securely exchange cryptographic keys between users.
How Does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography relies on a number of different principles to create a secure data transmission channel. Firstly, it uses the principle of entanglement to link two particles together, so that any change made to one particle will immediately be reflected in the other. This property of entanglement is used to encrypt data in a virtually unbreakable way.
Quantum cryptography also uses the principle of quantum key distribution, which is a form of public key cryptography. This is used to securely exchange cryptographic keys between users, allowing them to securely exchange data. In addition to this, quantum cryptography also employs the principle of quantum teleportation, which allows for the secure transmission of data over long distances.
What Are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
The primary benefit of quantum cryptography is its superior data security. By relying on the principles of quantum mechanics, quantum cryptography is able to provide virtually unbreakable encryption. This means that data can be securely transmitted without the risk of it being intercepted or compromised.
In addition to this, quantum cryptography also offers improved scalability. By using a distributed network of users, quantum cryptography can provide secure communication across a wide range of networks and devices. This makes it ideal for applications such as the Internet of Things, where secure communication across a wide range of devices is essential.
What Are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
Despite its many advantages, there are some limitations to quantum cryptography. Firstly, the technology is still in its early stages of development, so it is not yet widely available. Additionally, the equipment needed to implement quantum cryptography is expensive, and so it may not be suitable for all applications.
In addition to this, quantum cryptography is only able to provide secure communication between two points. This means that it is not suitable for applications that require secure communication between multiple users. Finally, the technology is subject to certain physical limitations, such as noise, which can interfere with the transmission of data.
Is Quantum Cryptography Secure?
Yes, quantum cryptography is extremely secure. By relying on the principles of quantum mechanics, quantum cryptography is able to provide virtually unbreakable encryption. This means that data can be securely transmitted without the risk of it being intercepted or compromised.
In addition to this, quantum cryptography also offers improved scalability. By using a distributed network of users, quantum cryptography can provide secure communication across a wide range of networks and devices. This makes it ideal for applications such as the Internet of Things, where secure communication across a wide range of devices is essential.
What is Quantum Cryptography? An Introduction
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a fascinating field that has the potential to revolutionize how we approach cybersecurity. The use of quantum mechanics to create unbreakable codes is not only groundbreaking but also essential in today’s digital age. The security of sensitive data is paramount, and quantum cryptography provides a solution that is both secure and efficient.
Although quantum cryptography is still in its early stages, it holds a promising future. As technology continues to advance, so too will quantum cryptography, providing an ever-increasing level of security for our digital world. As we move forward, it is crucial to keep a close eye on these developments and continue to explore this exciting field. Ultimately, the potential benefits of quantum cryptography are vast, and it is a field that is well worth watching.