In today’s technology-driven world, the use of cloud computing has become increasingly popular. As more and more businesses move their operations to the cloud, the need for a reliable and secure network infrastructure has become paramount. The solution to this problem is the virtual cloud network.
A virtual cloud network is a software-defined network infrastructure that is built on top of a cloud computing platform. It provides businesses with a flexible and scalable network architecture that can be easily customized to meet the unique needs of their operations. This technology allows businesses to create and manage virtual networks that can span across multiple cloud providers, data centers, and even on-premises environments. With a virtual cloud network, businesses can achieve better performance, security, and efficiency in their network operations.

What is a Virtual Cloud Network?
A virtual cloud network (VCN) is a private network that connects cloud resources, such as a web server, database, and applications, hosted in the cloud. VCNs use the same technologies and protocols as traditional networks, such as Ethernet, IP addressing, and routing. The main difference is that VCNs are hosted in the cloud and are managed by a cloud provider.
Benefits of a Virtual Cloud Network
A VCN provides many benefits to organizations, including the ability to quickly deploy and scale cloud applications, improved security, and greater control over network resources. With a VCN, organizations can quickly deploy and scale applications without the need to purchase additional hardware or software. This saves time and money, as well as reducing the risk of downtime due to hardware or software maintenance.
In addition, VCNs provide improved security compared to traditional networks. VCNs are isolated from each other, and all traffic is encrypted, providing an additional layer of security. VCNs also offer greater control over network resources, allowing organizations to control bandwidth, latency, and other network related factors.
Components of a Virtual Cloud Network
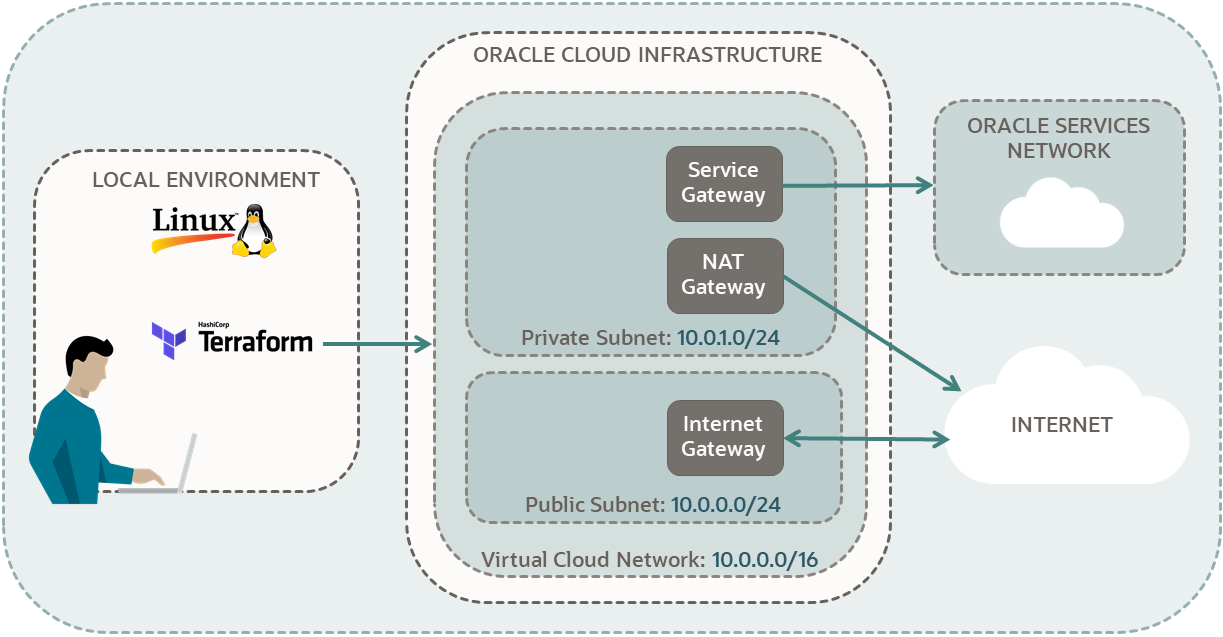
A VCN is composed of several components, including a gateway, subnets, and routing tables. The gateway is a virtual appliance that acts as a router and firewall and provides access to the cloud environment. Subnets are a way to divide the VCN into separate networks, allowing organizations to better control access to resources. Routing tables define how traffic is routed within the VCN and provide an additional layer of security.
In addition to these components, VCNs also require a virtual private cloud (VPC) to provide network security and isolation. A VPC is a virtual private network that is isolated from other networks and allows organizations to securely connect to the cloud. A VPC also provides additional security measures, such as encryption, access control, and network isolation.
Conclusion
A virtual cloud network (VCN) is a private network that connects cloud resources, such as a web server, database, and applications, hosted in the cloud. VCNs use the same technologies and protocols as traditional networks, such as Ethernet, IP addressing, and routing. The main benefit of a VCN is that it allows organizations to quickly deploy and scale applications without the need to purchase additional hardware or software. VCNs also provide improved security compared to traditional networks and offer greater control over network resources. VCNs are composed of several components, including a gateway, subnets, and routing tables, and require a virtual private cloud (VPC) for additional security and isolation.
Frequently Asked Questions
A virtual cloud network is a secure, virtualized network in the cloud that is made up of interconnected virtual machines (VMs). It allows for the deployment of applications and services in an isolated, private environment with the benefits of cloud computing.
What Is a Virtual Cloud Network?
A virtual cloud network is a secure, virtualized network in the cloud made up of interconnected virtual machines (VMs). It allows for the deployment of applications and services in an isolated, private environment with the benefits of cloud computing. The virtual network is hosted in the cloud and provides users with a virtualized environment that can be accessed from anywhere. Virtual cloud networks enable organizations to quickly and easily deploy applications and services in a secure, cost-effective manner.
What Are the Benefits of a Virtual Cloud Network?
The benefits of virtual cloud networks are numerous. They enable organizations to quickly and easily deploy applications and services in a secure, cost-effective manner. Additionally, virtual cloud networks provide users with an isolated, private environment that can be accessed from anywhere. This allows users to access their applications and services securely, without having to worry about security breaches. Furthermore, virtual cloud networks enable organizations to scale their resources quickly, as they can easily add or remove VMs as needed.
How Is a Virtual Cloud Network Configured?
A virtual cloud network is typically configured by creating a virtual private cloud (VPC) in the cloud provider’s infrastructure. The VPC is then configured to define the virtual network, including IP address ranges, DNS settings, network security rules, and other settings. Once the virtual network is configured, applications and services can then be deployed within the VPC. This is done by creating virtual machines (VMs), which are then connected to the virtual network.
What Is the Difference Between a Virtual Cloud Network and a Private Cloud?
The primary difference between a virtual cloud network and a private cloud is that a virtual cloud network is hosted in the cloud, while a private cloud is hosted on-premise. A virtual cloud network provides the same benefits of cloud computing, such as scalability, cost savings, and security, but it is hosted in the cloud. A private cloud, on the other hand, is hosted on premise and is typically managed by the organization itself. Additionally, a private cloud is often used for more specialized applications and services that require high levels of control and security.
What Are the Security Features of a Virtual Cloud Network?
A virtual cloud network provides users with a secure environment, as it is isolated from the public Internet. Additionally, virtual networks are typically configured with network security rules, such as firewalls and access control lists (ACLs), to ensure that only authorized users can access the network. Furthermore, virtual networks can also be configured with encryption to ensure that data is secure while in transit. Finally, virtual networks can also be configured with monitoring and logging tools to ensure that any suspicious activity is detected and investigated.
In conclusion, a virtual cloud network is a powerful and flexible solution for businesses looking to establish a secure and scalable network infrastructure. With its ability to connect remote locations, provide centralized management, and offer a range of security features, a virtual cloud network has become an essential tool for modern enterprises.
As we move towards an increasingly digital future, the demand for virtual cloud networks is only set to grow. Businesses of all sizes are recognizing the benefits of this technology, from increased productivity to enhanced security. By leveraging the power of virtual cloud networks, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and achieve success in the ever-evolving world of technology.