In the modern world of science and technology, quantum mechanics has become one of the most intriguing and fascinating fields of study. This branch of physics has revolutionized our understanding of the world around us, revealing the mysterious behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic level. One of the fundamental concepts of quantum mechanics is the description of electrons in the quantum mechanical model.
Electrons are the building blocks of matter, and their behavior is critical to understanding the properties of atoms and molecules. In the quantum mechanical model, electrons are described as wave-like entities that exist in energy levels or orbitals around the nucleus of an atom. These energy levels are quantized, meaning that they can only take on specific values. The quantum mechanical model has allowed us to explain the chemical and physical properties of elements, and it continues to be an essential tool for scientists today.
What Are Electrons Described As in the Quantum Mechanical Model?
Electrons are one of the most important components of an atom. In the quantum mechanical model, electrons are described as particles with wave-like properties. This means that electrons can exist in a variety of energy states, and these states determine the behavior of electrons.
Wave-Particle Duality
In classical physics, particles are discrete objects that obey the laws of motion. However, in quantum mechanics, particles also exhibit wave-like behavior. This phenomenon is known as wave-particle duality, and it is one of the most important aspects of the quantum mechanical model.
Wave-particle duality means that electrons can be described as both particles and waves. As particles, electrons have a position and a momentum. As waves, electrons can have a wavelength and an amplitude. These two distinct descriptions of electrons are important for understanding how electrons interact with other particles and with electromagnetic radiation.
Quantum States
In the quantum mechanical model, electrons exist in a variety of energy states. The energy states of an electron determine its behavior. For example, electrons in a low-energy state are more likely to remain in that state, while electrons in a high-energy state are more likely to move to a higher energy state.
The energy states of electrons are determined by their position and momentum. Electrons can exist in a variety of energy states, and each energy state has its own unique properties. These properties determine how the electron will interact with other particles and with electromagnetic radiation.
Electrons in higher energy states are more likely to interact with other particles and with electromagnetic radiation, while electrons in lower energy states are more likely to remain in their current state. This is why it is important to understand the energy states of electrons in order to understand how they interact with other particles and with electromagnetic radiation.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section contains information about electrons in the quantum mechanical model.
What are electrons described as in the quantum mechanical model?
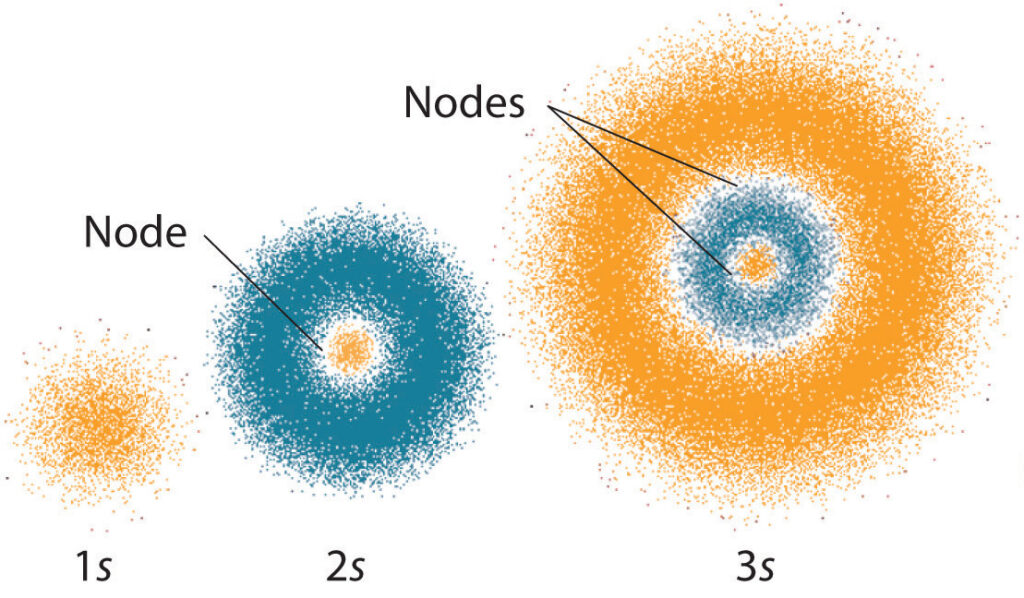
Electrons in the quantum mechanical model are described as particles of matter that exist in certain energy levels, which are determined by the quantum number. This means that electrons are not particles in the classical sense, but instead are described as probability waves. Electrons can exist in multiple energy levels and can be found in different positions within an atom at any given time. This is known as the wave-particle duality of electrons, and it is one of the key principles of quantum mechanics.
The energy levels of electrons are determined by the quantum numbers, which are related to the angular momentum of the particle. The wave-like nature of the electrons means that they cannot be observed in a classical sense, but instead must be observed through probability distributions. This means that the position of the electron can only be known with a certain degree of probability.

In conclusion, electrons are described as wave functions in the quantum mechanical model, which allows for a probabilistic understanding of their behavior. Rather than being viewed as particles following a predictable trajectory, electrons are treated as a cloud of possibilities, with their location and momentum determined by the probability of their wave function at any given moment. This model has revolutionized our understanding of the subatomic world, leading to exciting discoveries and advancements in fields ranging from chemistry to electronics.
Overall, the quantum mechanical model provides a fascinating and complex perspective on the behavior of electrons. While challenging to grasp fully, it offers a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the smallest building blocks of matter. As we continue to explore and refine this model, we can expect to uncover even more remarkable insights into the nature of the universe and the fundamental particles that make it up.